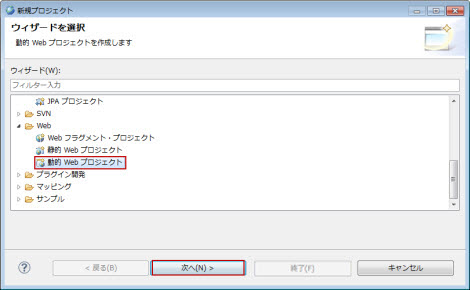
�}1.2.15.1-1

�}1.2.15.1-1
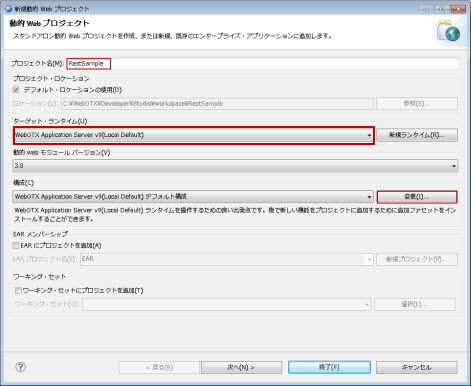
�}1.2.15.1-2
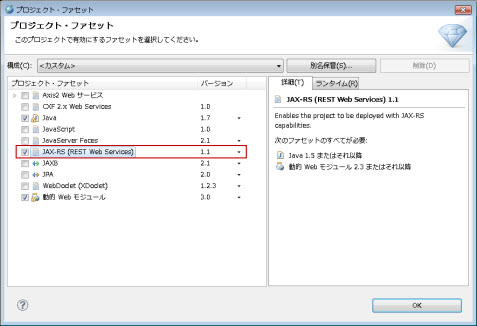
�}1.2.15.1-3
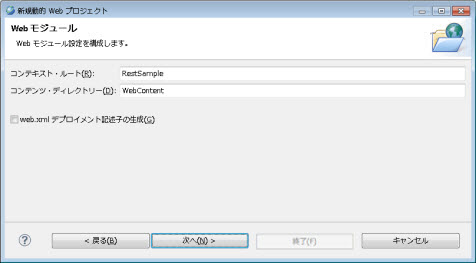
�}1.2.15.1-4
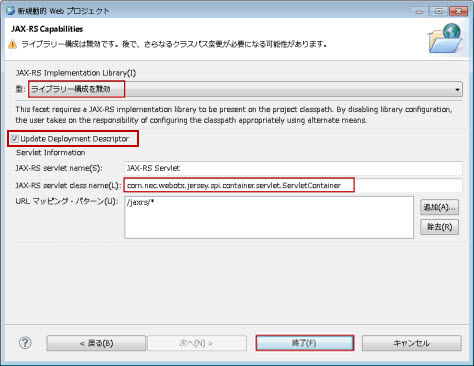
�}1.2.15.1-5
|
���� |
���� |
|---|---|
|
JAX-RS servlet name |
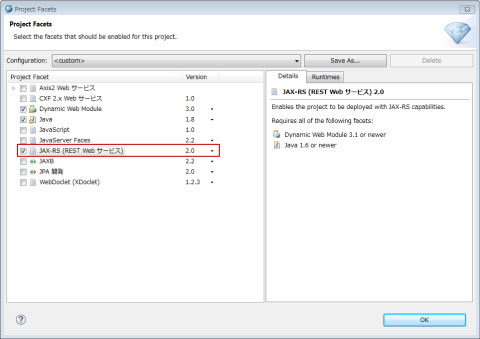
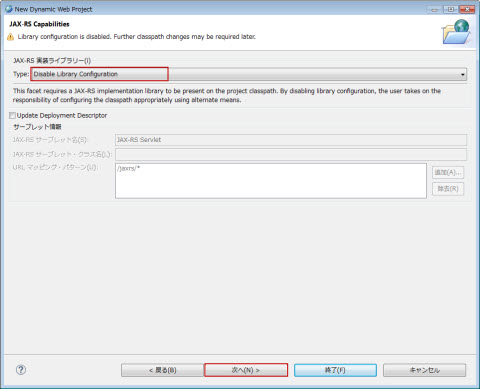
�K�{�BJAX-RS�T�[�u���b�g����ݒ肵�܂��B |
|
JAX-RS servlet class name |
�K�{�Bcom.nec.webotx.jersey.spi.container.servlet.ServletContainer��ݒ肵�܂��B |
|
URL �}�b�s���O�E�p�^�[�� |
JAX-RS�T�[�u���b�g�Ƀ}�b�s���O����URL�p�^�[����ݒ肵�܂��B�ʏ��[/jaxrs/*]��ݒ肵�܂��B |
�}1.2.15.1-6
�}1.2.15.1-7
�}1.2.15.1-8

�}1.2.15.1-9

�}1.2.15.1-10
�}1.2.15.1-11
�}1.2.15.1-12
�}1.2.15.1-13

�}1.2.15.1-14
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<display-name>RestSample</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>JAX-RS Servlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.nec.webotx.jersey2.servlet.ServletContainer</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>JAX-RS Servlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/jaxrs/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
|
���� |
���� |
|---|---|
|
servlet-name |
�K�{�BJAX-RS�T�[�u���b�g����ݒ肵�܂��B <servlet>����<servlet-name>��<servlet-mapping>����<servlet-name>�ɓ����l��ݒ肵�Ă��������B |
|
servlet-class |
�K�{�Bcom.nec.webotx.jersey2.servlet.ServletContainer��ݒ肵�܂��B |
|
load-on-startup |
JAX-RS�T�[�u���b�g�̏�����������ݒ肵�܂��B�ʏ��[1]��ݒ肵�܂��B |
|
url-pattern |
JAX-RS�T�[�u���b�g�Ƀ}�b�s���O����URL�p�^�[����ݒ肵�܂��B�ʏ��[/jaxrs/*]��ݒ肵�܂��B |

�}1.2.15.1-15
�}1.2.15.1-16
1 package com.nec.webotx.ws.rest.samples.helloworld.resources;
2
3 import javax.ws.rs.GET;
4 import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
5 import javax.ws.rs.Path;
6
7 // The Java class will be hosted at the URI path "/helloworld"
8 @Path("/helloworld")
9 public class HelloWorldResource {
10
11 // The Java method will process HTTP GET requests
12 @GET
13 // The Java method will produce content identified by the MIME Media
14 // type "text/plain"
15 @Produces("text/plain")
16 public String getClichedMessage() {
17 // Return some cliched textual content
18 return "Hello World";
19 }
20 }
@Path("ResourceTest1")
public class Resource1{
private String query1;
public Resource1(@Encoded @DefaultValue("abc") @QueryParam("queryParam1") String query) {
query1 = query;
}
@GET
@Path("/queryParam1Value")
public String getQuery1Value() {
return "query1=" + query1;
}
}
���̗�ł́A�N���C�A���g����URL http://sample.com/example/ResourceTest1/queryParam1Value?queryParam1=queryValue�ŃA�N�Z�X����ƁAqueryValue��ԋp���܂��B
| ���� | �C���W�F�N�V�����p�A�m�e�[�V���� | �I�v�V�����̃A�m�e�[�V���� | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encoded | DefaultValue | ||
| 1 | MatrixParam | �� | �� |
| 2 | QueryParam | �� | �� |
| 3 | PathParam | �� | �~ |
| 4 | CookieParam | �~ | �� |
| 5 | HeaderParam | �~ | �� |
| 6 | FormParam | �~ | �� |
| 7 | Context | �~ | �~ |
private @Encoded @DefaultValue("value1") @QueryParam("id") String id;
URL�Łg��Ёh��UTF-8��encode�����p�����[�^�̒l�g%E4%BC%9A%E7%A4%BE�h�ŃA�N�Z�X�����
(http://sample.com/example/ResourceTest3/queryParam1Value?id=%E4%BC%9A%E7%A4%BE)
���\�[�X�N���X�Ŏ擾�ł���id�̒l�́g%E4%BC%9A%E7%A4%BE�h�ƂȂ�Aencode���ꂽ���e�ɂȂ�܂��B
private String property1;
@DefaultValue("10") @QueryParam("paramProperty1")
public void setProperty1(String property1) {
this.property1 = property1;
}
���̗�ł́AURL�́gparamProperty1�hQueryParam�̒l�������I��property1�ɃC���W�F�N�V�������܂��B
@Path("resource_method")
public class ResourceMethodResource {
@GET
public String resourceMethod() {
return "this is a resource method.";
}
}
���[�g���\�[�X�N���XResourceMethodResource�̃��\�b�hresourceMethod()�̓��\�[�X���\�b�h�ł��B
�N���C�A���g����URI�uresource_method�v�ɃA�N�Z�X���鎞�AJAX-RS�G���W���͂��̃��\�b�h���Ăяo���܂��B
@Path("/resourceTest1")
public class Resource1 {
public Resource1(){
}
...
@GET
@Path("/testPathParam/{arg1}/{arg2}")
public String listPathParam(@PathParam("arg1") String arg1,@PathParam("arg2") String arg2) {
return "arg1="+arg1+" and arg2="+arg2;
}
...
�p
listPathParam���\�b�h�̓T�u���\�[�X���\�b�h�ł��B
/resourceTest1/testPathParam/{arg1}/{arg2}��URI�Ƀ��N�G�X�g����ƁAlistPathParam()�͂��̃��N�G�X�g���������܂��B
@Path("/resourceTest1")
public class Resource1 {
@Path("/testSubResourceLocator/{id}")
public Resource1_1 getResource1_1(@PathParam("id") String id){
return new Resource1_1(id);
}
...
}
�Ή�����T�u���\�[�X�N���X�̗�����Ɏ����܂��B
public class Resource1_1 {
private String resourceID;
public Resource1_1(String id){
resourceID = id;
}
@GET
public String getDetails(){
return "This resource id is "+resourceID;
}
}
���̗�ł́A���[�g���\�[�X�N���XResource1��HTTP���N�G�X�g�ڏ������܂���B�T�u���\�[�X���P�[�^getResource1_1���Ԃ��T�u���\�[�X�N���XResource1_1�����̃��N�G�X�g���������܂��B
public class Resource1_1 {
private String resourceID;
public Resource1_1(String id){
resourceID = id;
}
@GET
public String getDetails(){
return "This resource id is "+resourceID;
}
}
�T�u���\�[�X�N���X�̃C���X�^���X�́AJAX-RS�G���W���ɂ���Đ�������܂���B�T�u���\�[�X�N���X�́A�Ή�����T�u���\�[�X���P�[�^�ŃC���X�^���X������K�v������܂��B
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
@Path("optionsmethod")
public class OptionsMethodResource {
@GET
public String getHello() {
return "hello";
}
}
�N���C�A���g����HTTP OPTIONS���N�G�X�g���\�b�h��URI�uoptionsmethod�v�̃��\�[�X�����N�G�X�g���鎞�A�T�[�o���牺�L�̓��e���ԐM����܂��B
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<application xmlns="http://wadl.dev.java.net/2009/02">
<doc xmlns:jersey="http://jersey.java.net/" jersey:generatedBy="Jersey: 1.11 12/09/2011 10:27 AM"/>
<grammars/>
<resources base="http://{server-name:port}/{context-root}/{url-pattern}/">
<resource path="optionsmethod">
<method id="getHello" name="GET">
<response>
<representation mediaType="*/*"/>
</response>
</method>
</resource>
</resources>
</application>
@GET
Produces({"application/xml", "application/json"})
public String doGetAsXmlOrJson() {
...
}
�i���W���̎w��
@GET
@Produces({"application/xml; qs=0.9", "application/json"})
public String doGetAsXmlOrJson() {
...
}
//�C���^�t�F�[�X
public interface A {
@GET
public String getValue(@QueryParam("query") String query);
}
//�C���^�t�F�[�X���������郋�[�g���\�[�X�N���X
@Path("/root/")
public class Resource implements A {
public String getValue(String query) {�c}
}
URL http://sample.com/example/resource/root?query=10 �ɑ���HTTP GET���N�G�X�g�́A���\�[�X���\�b�hgetValue()�Ƀf�B�X�p�b�`����܂��B���\�[�X���\�b�hgetValue()�̓C���^�t�F�[�X��GET�A�m�e�[�V�������p�����Ă��邽�߂ł��B
//�e�N���X
public class ParentClassA {
@GET
public String getValue(@QueryParam("query1") String query1){
return "query1 = "+query1;
}
}
//�q�N���X
@Path("/inheretance")
public class SubClass extends ParentClassA {
public String getValue(String query){
return query;
}
}
URL http://sample.com/example/resource/inheretance?query1=10 �ɃA�N�Z�X����ƁAquery�̒l��10���擾�ł��܂��B
public interface InterfaceA {
@GET
public String getValue(@PathParam("path1") String path1);
}
public interface InterfaceB {
@GET
public String getValue(@QueryParam("query") String query);
}
@Path("/inheretance/{path1}")
public class SubClass implements InterfaceB, InterfaceA{
public String getValue(String param){
return param;
}
}
URL http://sample.com/example/resource/inheretance/aaa?query=456 �ɃA�N�Z�X����ƁAparam�̒l��456���擾�ł��܂��B����́AInterfaceB����ɃC���^�t�F�[�X��������Ă���AInterfaceB�̃A�m�e�[�V�������D�旘�p����邽�߂ł��B
�ȉ��̂悤��InterfaceA���ɋL�q�����ꍇ�A
@Path("/inheretance/{path1}")
public class SubClass implements InterfaceA, InterfaceB{
public String getValue(String param){
return param;
}
}
URL http://sample.com/example/resource/inheretance/aaa?query=456 �ɃA�N�Z�X����ƁAparam�̒l��aaa���擾�ł��܂��B
| ���� | �f�[�^�^ | �A�m�e�[�V���� | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PathParam | QueryParam | MatrixParam | CookieParam | HeaderParam | FormParam | Context | |||
| 1 | �v���~�e�B�u | int | ����1 | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �~ |
| 2 | short | ����1 | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �~ | |
| 3 | long | ����1 | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �~ | |
| 4 | float | ����1 | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �~ | |
| 5 | double | ����1 | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �~ | |
| 6 | char | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | |
| 7 | byte | ����1 | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �~ | |
| 8 | boolean | ����1 | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �~ | |
| 9 | String�^�̈���������R���X�g���N�^�����^ | ����1 | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �~ | |
| 10 | String�^�̈��������肻�̌^�̃C���X�^���X��Ԃ��R���X�g���N�^�������A����static��valueOf�܂���fromString���\�b�h�����^ ��2 | ����1 | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �~ | |
| 11 | List<T>�iT����L����9�A10�̃f�[�^�^�j | ����1 | �� | �� | �~ | �� | �� | �~ | |
| 12 | Set<T>�iT����L����9�A10�̃f�[�^�^�j | ����1 | �� | �� | �~ | �� | �� | �~ | |
| 13 | Sorted Set<T>�iT����L����9�A10�̃f�[�^�^�j | ����1 | �� | �� | �~ | �� | �� | �~ | |
| 14 | PathSegment | ����1 | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | |
| 15 | �R���e�L�X�g�^ | UriInfo | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | ����1 |
| 16 | HttpHeaders | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | ����1 | |
| 17 | Request | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | ����1 | |
| 18 | SecurityContext | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | ����1 | |
| 19 | Providers | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | ����1 | |
| 20 | ServletConfig | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | ����1 | |
| 21 | ServletContext | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | ����1 | |
| 22 | HttpServletRequest | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | ����1 | |
| 23 | HttpServletResponse | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | �~ | ����1 | |
| ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X�̃R���X �g���N�^�[�̃p�����[�^�[ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃��\�[�X���\�b�h�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃T�u���\�[�X���\�b�h�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃T�u���\�[�X���P�[�^�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X�̃t�B�[���h | ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X��Bean�v���p�e�B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� |
| ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X�̃R���X �g���N�^�[�̃p�����[�^�[ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃��\�[�X���\�b�h�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃T�u���\�[�X���\�b�h�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃T�u���\�[�X���P�[�^�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X�̃t�B�[���h | ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X��Bean�v���p�e�B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� |
| ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X�̃R���X �g���N�^�[�̃p�����[�^�[ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃��\�[�X���\�b�h�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃T�u���\�[�X���\�b�h�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃T�u���\�[�X���P�[�^�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X�̃t�B�[���h | ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X��Bean�v���p�e�B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� |
| ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X�̃R���X�g���N�^�[�̃p�����[�^�[ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃��\�[�X���\�b�h�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃T�u���\�[�X���\�b�h�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃T�u���\�[�X���P�[�^�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X�̃t�B�[���h | ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X��Bean�v���p�e�B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� |
| ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X�̃R���X �g���N�^�[�̃p�����[�^�[ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃��\�[�X���\�b�h�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃T�u���\�[�X���\�b�h�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃T�u���\�[�X���P�[�^�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X�̃t�B�[���h | ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X��Bean�v���p�e�B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� |
@Path("/root")
public class Resource {
private @Context UriInfo uriInfo;
@GET
public String getValue() {
String value = this.uriInfo.getQueryParameters().getFirst("query");
return value;
}
}
URL http://sample.com/example/root?query=10 �ɃA�N�Z�X����ƁAvalue�̒l��10�ɂȂ�܂��B
@Path("/root")
public class Resource {
private @Context HttpHeaders httpHeaders;
@GET
public String getValue () {
String value = this.httpHeaders.getRequestHeader("Accept").get(0);
return value;
}
}
HTTP Accept�w�b�_��"application/xml"���w�肵�A
URL http://sample.com/example/root"�ɑ���HTTP GET���N�G�X�g�ŃA�N�Z�X����ƁA value�̒l��application/xml�ɂȂ�܂��B
@Path("/root")
public class Resource {
private @Context Providers providers;
@GET
public String getValue() {
//providers�t�B�[���h�����O�}�b�s���O�v���o�C�_���擾���܂�
return this.providers.getExceptionMapper(RuntimeException.class);
}
}
URL http://sample.com/example/root �ɃA�N�Z�X����ƁAjava.lang.RuntimeException�������ł����O�}�b�s���O�v���o�C�_�C���X�^���X���擾�ł��܂��B
@Path("/root")
public class Resource {
private @Context SecurityContext securityContext;
@GET
public String getValue () {
String value = "Authentication Scheme: "
+ this.securityContext.getAuthenticationScheme()
+ ", User Principal: " + this.securityContext.getUserPrincipal()
+ ", Is secure: " + this.securityContext.isSecure()
+ ", Is user in role: " + this.securityContext.isUserInRole("admin");
return value;
}
}
�Z�L�����e�B�����܂�web.xml�̗�����Ɏ����܂��B
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app ...>
...
<security-constraint>
<web-resource-collection>
<web-resource-name>Test Resource</web-resource-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
<http-method>GET</http-method>
</web-resource-collection>
<auth-constraint>
<role-name>admin</role-name>
</auth-constraint>
</security-constraint>
<login-config>
<auth-method>BASIC</auth-method>
<realm-name>jaxrs_server</realm-name>
</login-config>
<security-role>
<role-name>admin</role-name>
</security-role>
</web-app>
URL http://sample.com/example/root �ɃA�N�Z�X����ƁAweb.xml�̐ݒ�Ǝ��ۂ̔F�؏��Ɋ�Â��ăZ�L�����e�B��擾�ł��܂��B
WebOTX��JAX-RS�ł�BASIC�F��Digest�F���g�p�ł��܂��B
@Path("/root")
public class Resource {
private @Context HttpServletRequest httpRequest;
@GET
public String getValue() {
return this.httpRequest.getParameter("TestParam");
}
}
URL: http://sample.com/example/root?TestParam=TestValue�ŃA�N�Z�X����ƁA
getValue()���TestParam�p�����[�^�̒lTestValue���擾�ł��܂��B
@Path("/root")
public class Resource {
private @Context HttpServletResponse httpResponse;
@GET
public void getValue() throws IOException {
String entity = "Response mentioned using HttpServletResponse";
httpResponse.setHeader("abc","xyz");
httpResponse.getOutputStream().write(entity.getBytes());
httpResponse.getOutputStream().flush();
httpResponse.getOutputStream().close();
}
}
URL�Fhttp://sample.com/example/root ��HTTP GET���N�G�X�g�ŃA�N�Z�X����ƁAhttpResponse�t�B�[���h��HttpServletResponse���C���W�F�N�g����A���̌�HTTP GET���N�G�X�g����������getValue()���\�b�h���Ăяo����܂��B
@Path("/root")
public class Resource {
private @Context ServletConfig config;
@GET
public String getValue() {
return this.config.getInitParameter("TestParam");
}
}
�lj��̏������p�����[�^�iinit-param�v�f�j���܂�web.xml�̗�����Ɏ����܂��B
<web-app ...>
<servlet>
<init-param>
<param-name>TestParam</param-name>
<param-value>TestValue</param-value>
</init-param>
�c�c
</servlet>
</web-app>
URL�Fhttp://sample.com/example/root ��HTTP GET���N�G�X�g�ŃA�N�Z�X����ƁA�������p�����[�^"TestParam"�̒l"TestValue"���擾�ł��܂��B
@Path("/root")
public class Resource {
private @Context ServletContext context;
@GET
public String getValue() {
return this.context.getInitParameter("TestParam");
}
}
�R���e�L�X�g�X�R�[�v�̏������p�����[�^�icontext-param�v�f�j���܂�web.xml�����Ɏ����܂��B
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app ...>
...
<context-param>
<param-name>TestParam</param-name>
<param-value>TestValue</param-value>
</context-param>
</web-app>
URL�Fhttp://sample.com/example/root ��HTTP GET���N�G�X�g�ŃA�N�Z�X����ƁA�R���e�L�X�g�X�R�[�v�̏������p�����[�^"TestParam"�̒l"TestValue"���擾�ł��܂��B
| ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X�̃R���X�g���N�^�[�̃p�����[�^�[ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃��\�[�X���\�b�h�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃T�u���\�[�X���\�b�h�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�̃T�u���\�[�X���P�[�^�̃p�����[�^ | ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X�̃t�B�[���h | ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X��Bean�v���p�e�B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� |
<html> <head> <meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/xml;charset=utf-8"> <title> test RESTFulWebService @FromParam</title> </head> <body> <form action="http://localhost:8080/WebProject1/myApplication1/testFormParam" method="post" > <table> <tr> <td>FirstName:</td> <td><input type="text" name="firstname"></td> </tr> <tr> <td>Age:</td> <td><input type="text" name="age"></td> </tr> </table> <input type="submit" value="Submit" > </form> </body> </html>���\�[�X�N���X:
@Path("testFormParam")
public class FormResource {
@POST
@Consumes("application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
public String getFormString(@FormParam("firstname") String name, @FormParam("age") int age){
return "firstname="+name+";age="+age;
}
}
FirstName���̓{�b�N�X��name1����͂��Aage���̓{�b�N�X��20����͂����ꍇ�A���\�[�X�N���X��@FormParam����name1��20���擾�ł��܂��B
| �p�����[�^ | DefaultValue�g�p�̌��� | ���l�i���N�G�X�g�p�X�Ɏw��p�����[�^�̑��ݏɂ���āADefaultValue�̗��p��������܂��j |
|---|---|---|
| MatrixParam | �Ή�����Param�����N�G�X�g�p�X�ɑ��݂��Ȃ��ꍇ�ADefaultValue�l���g�p����܂��B�i���l���̇A�̏ꍇ�ADefaultValue���g�p���Ȃ��j | �@���N�G�X�g�p�X�Ɏw��p�����[�^���Ȃ��ꍇ�ADefaultValue�l�𗘗p����B�Ⴆ�A���N�G�X�g�p�X�Ɂu;null�v���邢�́u; �w��p�����[�^�ȊO�̃p�����[�^= XXX�v���w�肷��B �A���N�G�X�g�p�X�Ɏw��p�����[�^������ꍇ�ADefaultValue�l�𗘗p���Ȃ��B�w��p�����[�^�ɒl��^���Ȃ��ꍇ�A�l��null�ɂȂ�B�w��p�����[�^�ɒl��^�����ꍇ�͂��̒l�𗘗p����B�Ⴆ�A���N�G�X�g�p�X�Ɂu;�w��p�����[�^���v�����w�肵�Ȃ��ꍇ�A�l��null�ɂȂ�B |
| QueryParam | ���� | ���� |
| FormParam | ���� | ���� |
| CookieParam | ���� | ���� �����̃p�����[�^�l���w�肷��ꍇ�A�Ō�̒l�𗘗p����B |
| HeaderParam | �Ή�����Param�����N�G�X�g�ɑ��݂��Ȃ��ꍇ�ADefaultValue�l���g�p����܂��B�i���l���̇A�̏ꍇ�ADefaultValue���g�p���Ȃ��j | �@���N�G�X�g�p�X�Ɏw��p�����[�^���Ȃ��ꍇ�ADefaultValue�l�𗘗p����B���N�G�X�g�p�X�Ɉ�ԖڂɎw�肷��p�����[�^�̒l���w�肵�Ȃ��ꍇ�i�u�w��p�����[�^�v�̂悤�Ɏw�肷��j�ADefaultValue�l�𗘗p����B �A��Ԗڂ̃p�����[�^�͎w��p�����[�^�ŁA���L���Ȓl���w�肷��ꍇ�ADefaultValue�l�𗘗p���Ȃ��B |
| PathParam | DefaultValue�A�m�e�[�V���������܂��B | -- |
| Context | DefaultValue�A�m�e�[�V���������܂��B | -- |
| BeanParam | DefaultValue�A�m�e�[�V���������܂��B | -- |
public class MyBeanParam {
@PathParam("p")
private String pathParam;
@MatrixParam("m")
@Encoded
@DefaultValue("default")
private String matrixParam;
@HeaderParam("header")
private String headerParam;
private String queryParam;
public MyBeanParam(@QueryParam("q") String queryParam) {
this.queryParam = queryParam;
}
public String getPathParam() {
return pathParam;
}
...
}
���\�b�h�̃p�����[�^�Ƃ���MyBeanParam�̃C���W�F�N�V�����F
@POST
public void post(@BeanParam MyBeanParam beanParam, String entity) {
final String pathParam = beanParam.getPathParam();
...
}
��L�̗�ł́A�V���O��Bean�Ƃ��Ă�MyBeanParam�ɃC���W�F�N�V����@PathParam�A@QueryParam�A@MatrixParam��@HeaderParam�̃A�O���Q�[�^�������Ă��܂��Bpost���\�[�X���\�b�h��@BeanParam���ABean�ɒ������ꂽ�p�X�p�����[�^("p")�̐ݒ�l���擾�ł��܂��B| ���[�g���\�[�X�N���X�� �R���X�g���N�^�[�� �p�����[�^�[ |
���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�� ���\�[�X���\�b�h�� �p�����[�^ |
���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�� �T�u���\�[�X���\�b�h�� �p�����[�^ |
���[�g(�T�u)���\�[�X�N���X�� �T�u���\�[�X���P�[�^�� �p�����[�^ |
���[�g���\�[�X�N���X�� �t�B�[���h |
���[�g���\�[�X�N���X�� Bean�v���p�e�B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| �� | �� | �� | �� | �� | �� |
@Path("EntityParameter")
public class EntityParameter {
@POST
@Path("getFileBody")
public String getFileBody(File fileBody) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(fileBody),"UTF-8"));
String line=null;
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
while((line=br.readLine()) != null){
sb.append(line);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
@Path("/inputStreamRes")
public class InputStreamResource {
private Map<String, String> fileRecord = new HashMap<String, String>();
public InputStreamResource() {
fileRecord.put("id1", "�t�@�C���p�X");
}
@GET
@Path("/{fileId}")
public InputStream getInputStream(@PathParam("fileId") String fileId) {
FileInputStream inStream = null;
String filePath = fileRecord.get(fileId);
if (filePath != null) {
try {
inStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return inStream;
}
}
�p�X�p�����[�^�ufileId�v�ɂ��A�Ή�����File�t�@�C����InputStream���擾���ĕԋp���܂��B
@Path("ResponseResource")
public class ResponseResource {
@GET
@Path("helloworld")
public Response getHelloWorldByResponse() {
String entityBody = "HelloWorld";
return Response.ok(entityBody, MediaType.TEXT_HTML_TYPE).build();
}
}
2.�N���C�A���g������GET�Łu/ResponseResource/helloworld�v�����N�G�X�g����ƁA
�T�u���\�[���\�b�hgetHelloWorldByResponse()�̓��X�|���X��ԃR�[�h�u200�v�AMIME�^�C�v�utext/html�v�A�G���e�B�e�B�uHelloWorld�v�̃��X�|���X���b�Z�[�W��ԐM���܂��B
�}1.2.15.12-1
| ���� | Java�̌^ | Charset(��1) | MIME�^�C�v |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | byte[] | �~ | �C��(*/*) |
| 2 | java.lang.String | �� | �C��(*/*) |
| 3 | java.io.InputStream | �~ | �C��(*/*) |
| 4 | java.io.Reader | �� | �C��(*/*) |
| 5 | java.io.File(��2�j | �~ | �C��(*/*) |
| 6 | javax.activation.DataSource | �~ | �C��(*/*) |
| 7 | javax.xml.transform.Source(��3) | �~ | text/xml�Aapplication/xml�Aapplication/*+xml |
| 8 | javax.xml.bind.JAXBElement | �� | text/xml�Aapplication/xml�Aapplication/*+xml |
| 9 | MultivaluedMap<String,String> | �� | application/x-www-form-urlencoded |
| 10 | StreamingOutput (�����X�|���X�̂݁j | �~ | �C��(*/*) |
| 11 | java.awt.image.RenderedImage | �~ | image/*�Aapplication/octet-stream |
| 12 | org.w3c.dom.Document | �~ | pplication/xml�Atext/xml�A*/* |
| 13 | com.nec.webotx.jersey.core.provider.EntityHolder<T> | �� | T�Ɏw�肵���^�Ɠ���MIME�^�C�v�ɂȂ�܂��B |
| 14 | XmlRootElement�A�m�e�[�V���������/�܂���XmlType�A�m�e�[�V�����ŃA�m�e�[�g���ꂽJAXB�N���X | �~ | text/xml�Aapplication/xml�Aapplication/*+xml |
| 15 | com.nec.webotx.jersey.api.representation.Form | �� | �C��(*/*) |
| 16 | javax.mail.internet.MimeMultipart | �� | multipart/* |
| 17 | JSON�t�H�[�}�b�g�̃f�[�^�`�� | �� | application/javascript�Aapplication/xml�Atext/xml |
| 18 | java.util.List<T>(��4) | �� | text/xml�Aapplication/xml�Aapplication/*+xml |
| 19 | void�i���X�|���X�̂݁j | �| | �C��(*/*) |
| 20 | javax.ws.rs.core.Response�i�����X�|���X�̂݁j | �� | �C��(*/*) |
| 21 | javax.ws.rs.core.GenericEntity<T>(��5) | �� | T�Ɏw�肵���^�Ɠ���MIME�^�C�v�ɂȂ�܂��B |
�J�X�^��MessageBodyReader�G���e�B�e�B�v���o�C�_
�J�X�^��MessageBodyReader�G���e�B�e�B�v���o�C�_���쐬����ɂ́AMessageBodyReader�C���^�t�F�[�X���������A�A�m�e�[�V����@Provider��t�^���܂��B| ���\�b�h | ���� |
|---|---|
| boolean isReadable(java.lang.Class<?>, java.lang.reflect.Type , java.lang.annotation.Annotation[] , MediaType) | MessageBodyReader�̎����N���X�͓����Java�^�C�v�̃C���X�^���X���쐬�ł��邩�ǂ����f���܂��B true�F�쐬�ł��܂��B false�F�쐬�ł��܂���B |
| T readFrom(java.lang.Class<T>,java.lang.reflect.Type, java.lang.annotation.Annotation[],MediaType, MultivaluedMap<java.lang.String,java.lang.String>,java.io.InputStream) | InputStream��T���w�肷��Java�^�C�v�̃C���X�^���X���쐬���āA�ԋp���܂��BisReadable()��true�̏ꍇ�̂݁A���̃��\�b�h���R�[�����܂��B |
@Provider
public class NamePasswordBeanReader implements MessageBodyReader<NamePasswordBean> {
@Override
public boolean isReadable(Class<?> arg0, Type arg1, Annotation[] arg2,MediaType arg3) {
return arg0 == NamePasswordBean.class;
}
@Override
public NamePasswordBean readFrom(Class<NamePasswordBean> arg0, Type arg1,Annotation[] arg2, MediaType arg3, MultivaluedMap<String, String> arg4, InputStream arg5) throws IOException, WebApplicationException {
//NamePasswordBean�C���X�^���X���쐬�B
�c�c
}
}
�v���o�C�_�����N�G�X�g��������MIME�^�C�v�̃G���e�B�e�B�̂ݏ�������ɂ́A�N���X���x����@Consumes�A�m�e�[�V�������K�v�ɂȂ�܂��B@Consumes�A�m�e�[�V�����̒l�̓v���o�C�_���T�|�[�g����MIME�^�C�v�ł��B@Consumes�A�m�e�[�V������ݒ肵�Ȃ��ꍇ�A�C��(*/*)��MIME�^�C�v�ɂȂ�܂��B(1)MessageBodyReader�G���e�B�e�B�v���o�C�_�̃}�b�`���[��
| �N���X��/�C���^�t�F�[�X | ���� |
|---|---|
| public interface MessageBodyWriter<T> | - |
| ���\�b�h | - |
| boolean isWriteable(java.lang.Class<?>,java.lang.reflect.Type, java.lang.annotation.Annotation[], MediaType) | MessageBodyWriter�̎����N���X�������Java�^�C�v�̃C���X�^���X��HTTP���X�|���X�ɕϊ��ł��邩�ǂ����f���܂��B true�F�ϊ��ł��܂��Bfalse�F�ϊ��ł��܂���B |
| long getSize(T,java.lang.Class<?>,java.lang.reflect.Type, java.lang.annotation.Annotation[], MediaType) | writeTo()���\�b�h���R�[������O�AT�̃C���X�^���X��HTTP���X�|���X�G���e�B�e�B�ɃV���A���C�Y����o�C�g�̒������ԋp����܂��B �u-1�v:�S�Ẵo�C�g�̒��� |
| void writeTo(T,java.lang.Class<?>, java.lang.reflect.Type,java.lang.annotation.Annotation[], MediaType,MultivaluedMap<java.lang.String,java.lang.Object>, java.io.OutputStream) | �G���e�B�e�B�ɃV���A���C�Y���܂��BisWriteable()��true�̏ꍇ�̂݁A���̃��\�b�h���R�[�����܂��B |
@Provider
public class NamePasswordBeanWriter implements MessageBodyWriter<NamePasswordBean> {
@Override
public long getSize(NamePasswordBean arg0, Class<?> arg1, Type arg2,Annotation[] arg3, MediaType arg4) {
return -1;
}
@Override
public boolean isWriteable(Class<?> classType, Type arg1, Annotation[] arg2,MediaType arg3) {
return classType == NamePasswordBean.class;
}
@Override
public void writeTo(NamePasswordBean arg0, Class<?> arg1, Type arg2,Annotation[] arg3, MediaType arg4,MultivaluedMap<String, Object> arg5, OutputStream arg6) throws IOException, WebApplicationException {
// NamePasswordBean�̃C���X�^���X���V���A���C�Y���郍�W�b�N
�c�c�c�c
}
}
���̃v���o�C�_�͓���̃^�C�v�̃��X�|���X�{�f�B��Ԃ����A�N���X���x����@Produces�A�m�e�[�V�������K�v�ɂȂ�܂��B���X�|���X��ԐM���鎞�A@Produces�A�m�e�[�V�����̒l�̓��X�|���X�̃R���e���g�^�C�v(content-type)�Ƃ��܂��B@Produces�A�m�e�[�V������ݒ肵�Ȃ��ꍇ�A�uAll media type(*/*)�v�̓��X�|���X�̃R���e���g�^�C�v(content-type)�Ƃ��܂��B
(1)MessageBodyWriter�G���e�B�e�B�v���o�C�_�̃}�b�`���[��
JAXB�A�m�e�[�V����
���[�U������Java�N���X�ɂ��̃A�m�e�[�V������t�^���܂��B���\�[�X���\�b�h�̕ԋp�l���邢�̓G���e�B�e�B�p�����[�^�́A���̃��[�U������Java�N���X�𗘗p����ꍇ�A�G���e�B�e�B�v���o�C�_�𗘗p���āAXML�f�[�^�`���̃��N�G�X�g�{�f�B���炻�̃��[�U������Java�N���X�̃C���X�^���X�ɕϊ����܂��B���邢�́A���̃��[�U������Java�N���X�̃C���X�^���X����XML�f�[�^�`���̃��X�|���X�{�f�B�ɕϊ����܂��B
@XmlRootElement
public class Planet {
public int id;
public String name;
public double radius;
}
Planet�N���X�ɂ�JAXB�ɒ�`����A�m�e�[�V�������g�p�ł��܂��B
@Path("planet")
public class Resource {
@GET
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_XML)
public Planet getPlanet() {
Planet p = new Planet();
p.id = 1;
p.name = "Earth";
p.radius = 1.0;
return p;
}
}
Resource�N���X�Ƀ��\�[�X���\�b�hgetPlanet()���`����@Produces�A�m�e�[�V�������g�p���āuapplication/xml�v��ݒ肵�܂��B
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<planet>
<id>1</id>
<name>Earth</name>
<radius>1.0</radius>
</planet>
�uJAXB�A�m�e�[�V�����v�����𗘗p���A���[�U������Java�N���X��JAXB�ɒ�`����A�m�e�[�V������t�^�����ꍇ�A���\�[�X���\�b�h��@Produces�A�m�e�[�V�������g�p����MIME�^�C�v���utext/xml�Aapplication/xml �Aapplication/*+xml�v�ɐݒ肷��K�v������܂��BJAXBElement�N���X
JAXB�A�m�e�[�V�������g�p����Java�̌^��XML��Ή�����ɂ́Ajavax.xml.bind.JAXBElement<T>�N���X���g�p���܂��B
public class Planet {
public int id;
public String name;
public double radius;
}
(2)���\�[�X�N���X���`���܂��B
@Path("planet")
public class Resource {
@GET
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_XML)
public JAXBElement<Planet> getPlanet() {
Planet p = new Planet();
p.id = 1;
p.name = "Earth";
p.radius = 1.0;
return new JAXBElement<Planet>(new QName(�gmyplanet�h), Planet.class, p);
}
}
javax.xml.bind.JAXBElement�𗘗p����ꍇ�A���\�[�X���\�b�hgetPlanet()�̕ԋp�l��JAXBElement<Planet>�ɕύX���Ă��������B�J�X�^��Planet�N���X�̃C���X�^���X���쐬���AJAXBElement�̃R���X�g���N�^�̃p�����[�^�Ƃ��ė��p���܂��B
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<myplanet>
<id>1</id>
<name>Earth</name>
<radius>1.0</radius>
<myplanet>
���\�[�X�N���X��JAXBElement�������g�p����ꍇ�A@Produces�A�m�e�[�V�������g�p����MIME�^�C�v���utext/xml�Aapplication/xml �Aapplication/*+xml�v�ɐݒ肷��K�v������܂��B
Caution
�C�ӂ̃����o�ϐ����V���A���C�Y�ł��Ȃ��ꍇ�A�G���[�ƂȂ莟�̗�O���������܂��B�uJsonMappingException: No serializer found for class {�T�u���\�[�X���P�[�^�̏��} and no properties discovered to create BeanSerializer�v�B���̕ϐ�������̂ł���A�A�m�e�[�V�����u@JsonIgnoreProperties(value = {"hibernateLazyInitializer", "�ϐ���"})�v���g�p���Ă��������B
POJO
RESTful Web�T�[�r�X���쐬����ۂɁA���L�̐ݒ肪�K�v�ł��B
<init-param>
<param-name>
com.nec.webotx.jersey.api.json.POJOMappingFeature
</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
�uPOJO�x�[�X�v��JSON�\�����g�p����ꍇ�AJSONWithPadding�N���X���g�p�ł��܂��B| �N���X�� | ���� |
|---|---|
| com.nec.webotx.jersey.api.json. JSONWithPadding implements com.nec.webotx.org.codehaus.jackson.map.JsonSerializableWithType | An entity supporting JSON with Padding (JSONP) |
| �R���X�g���N�^ | - |
| public JSONWithPadding(Object jsonSource) | Pad JSON using the default function name "callback".jsonSource: the JSON to pad. |
| public JSONWithPadding(Object jsonSource, String callbackName) | Pad JSON using a declared callback function name.jsonSource: the JSON to pad.callbackName: the callback function name. |
| public void serialize(JsonGenerator jgen, SerializerProvider provider) throws IOException, JsonProcessingException | JsonSerializableWithType�C���^�t�F�[�X�ɒ�`���郁�\�b�h |
| public void serializeWithType(JsonGenerator jgen, SerializerProvider provider, TypeSerializer typeSer) throws IOException, JsonProcessingException | JsonSerializableWithType�C���^�t�F�[�X�ɒ�`���郁�\�b�h |
public class NonJAXBBean {
public String name = "non-JAXB-bean";
public String description = "I am not a JAXB bean, just an unannotated POJO";
public int[] array = {1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21};
}
(2) ���\�[�X�N���X�uNonJAXBBeanResource�v���`���܂�
import com.nec.webotx.jersey.api.json.JSONWithPadding;
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
@Path("/nonJAXBResource")
public class NonJAXBBeanResource {
@GET
@Produces({"application/javascript", MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON})
public JSONWithPadding getSimpleBeanJSONP() {
return new JSONWithPadding(new NonJAXBBean());
}
}
���\�[�X�N���XNonJAXBBeanResource�̃��\�[�X���\�b�hgetSimpleBeanJSONP()��JSONWithPadding�C���X�^���X��ԋp���܂��B
{"name":"non-JAXB-bean","description":"I am not a JAXB bean, just an unannotated POJO","array":[1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21]}
��L�̃��\�[�X�N���XNonJAXBBeanResource�̃��\�[�X���\�b�hgetSimpleBeanJSONP()�ɂ�@Produces���w�肵�܂��B�w�肷��MIME�^�C�v��JSON�Ɋ֘A����MIME�^�C�v�itext/json�Aapplication/json�j�łȂ���Ȃ�܂���BJAXB
JAXB���g�p���ăf�[�^�`�����擾����ꍇ�A���[�U������Java�N���X��JAXB���`����A�m�e�[�V�������K�v�ɂȂ�܂��B���\�[�X�N���X�ɂ��̃N���X�̃C���X�^���X��ԋp���܂��B�܂��A@Produces�A�m�e�[�V������JSON�Ɋ֘A����MIME�^�C�v(application/json)���w�肵�܂��B
@XmlRootElement
public class MyJaxbBean {
public String name;
public int age;
public MyJaxbBean() {} // JAXB needs this default constructor
public MyJaxbBean(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
(2)���\�[�X���\�b�h�ɂ��̃N���X�̃C���X�^���X���ԋp����܂��B@Produces�Ɂuapplication/json�v��ݒ肵�܂��B
@GET @Produces("application/json")
public MyJaxbBean getMyBean() {
return new MyJaxbBean("Agamemnon", 32);
}
(3)�N���C�A���g�����炻�̃��\�[�X�����N�G�X�g���鎞�A���L��JSON�f�[�^�`���Ń��X�|���X��ԐM���܂��B
{"name":"Agamemnon", "age":"32"}
���\�[�X����ԐM����JSON�f�[�^�`����ύX���邽�߂ɁAContextResolver<T>�C���^�t�F�[�X�̎������K�v�ł��B
@Provider
public class JAXBContextResolver implements ContextResolver<JAXBContext> {
private JAXBContext context;
private Class[] types = {MyJaxbBean.class};
public JAXBContextResolver() throws Exception {
this.context =
new JSONJAXBContext(
JSONConfiguration.natural().build(), types);
}
public JAXBContext getContext(Class<?> objectType) {
for (Class type : types) {
if (type == objectType) {
return context;
}
}
return null;
}
}
���[�U������Java�N���X�ł���MyJaxbBean����͂��鎞�A��L��JSONJAXBContext�C���X�^���X���g�p���܂��B
@XmlRootElement
public class Address {
public String street;
public String town;
public Address(){}
public Address(String street, String town) {
this.street = street;
this.town = town;
}
}
Contact�N���X�ڍׁF
@XmlRootElement
public class Contact {
public int id;
public String name;
public List<Address> addresses;
public Contact() {};
public Contact(int id, String name, List<Address> addresses) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.addresses =
(addresses != null) ? new LinkedList<Address>(addresses) : null;
}
}
���\�[�X�N���X�ڍׁF
@Path("/JAXBJSONResource")
public class JAXBJSONResource {
@GET
@Produces("application/json")
public Contact getContact() {
Address[] addresses = new Address[]{new Address("Long Street 1", "Short Village")};
Contact contact = new Contact(2, "BOb", Arrays.asList(addresses));
return contact;
}
}
�R���e�L�X�g�v���o�C�_�ڍׁF
@Provider
public class JAXBContextResolver implements ContextResolver<JAXBContext> {
private JAXBContext context;
private Class[] types = {Contact.class};
public JAXBContextResolver() throws Exception {
this.context = new JSONJAXBContext(JSONConfiguration.mapped().build() // ��(1)
types);
}
public JAXBContext getContext(Class<?> type) {
for(Class supportType: types) {
if (type == supportType) {
return context;
}
}
return null;
}
}
��(1):�uJSONConfiguration.mapped().build()�v�́ANotaion�ɂ��p�����[�^���قȂ�܂��B
Mapped Notation
Mapped notation���g�p�������ꍇ�AJSONConfiguration�N���X��mapped()���\�b�h���g�p����K�v������܂��B �ڍׂ͏�L�̗��JAXBContextResolver�́�(1)�ŁuJSONConfiguration.mapped().build()�v���g�p���ĉ������B
{ "id":"2" ,"name":"Bob","addresses":{"street":"Long Street 1","town":"Short Village"}}
���L��Mapped notation ��JSONConfiguration�Ɋ֘A����ݒ�I�v�V������������܂��B
{"id":"2","name":"BOb","addresses":[{"street":"Long Street 1" ,"town":"Short Village"}]}
{"id":2 ,"name":"BOb","addresses":{"street":"Long Street 1","town":"Short Village"}}
�܂��AnonStrings(String... nonStrings)���\�b�h�ɕ����̕����g�p�ł��܂��B��F�uJSONConfiguration.mapped().nonStrings("field1",�hfield2�h).build()�v�B�܂��AnonStrings(String... nonStrings)���\�b�h�͌J��Ԃ��g�p�ł��܂��B��F�uJSONConfiguration.mapped().nonStrings("field1").nonStrings("field2").build()�v�B
...
@XmlAttribute
public int id;
...
JSON�f�[�^�`���͉��L�̒ʂ�\������܂��B
{"@id":"2" ...
��L�̏ꍇ�ŏo�͓��e�Ɂu@�v�L����t���Ȃ����߂ɂ́AJSONConfiguration �̐ݒ�I�v�V����attributeAsElement(String... attributeAsElements)���g�p���܂��B
JAXBContextResolver��(1)�ŁuJSONConfiguration.mapped().attributeAsElement("id").build()�v�ɕύX����K�v������܂��B�t�ɏo�͓��e�ɑ�����\�L����u@�v�L����t�^����ꍇ�AattributeAsElement(String... attributeAsElements)���g�p���Ȃ��ł��������B
{"contact":{"id":"2","name":"BOb","addresses":{"street":"Long Street 1" ,"town":"Short Village"}}}
(5)xml2JsonNs(Map<String, String> jsonXml2JsonNs)
�c
@XmlElement(namespace="http://www.nec.cn.jersey")
public List<Address> addresses;
�c
�ϐ��uaddresses�v�͖��O��ԁuhttp://www.nec.cn.jersey�v���g�p���Ă��܂��B�N���C�A���g���ŕϐ��uaddresses�v�̒l�𐳂����擾���邽�߂ɂ́AJSON��XML���O��Ԃ�t�^���܂��BJSONConfiguration �̐ݒ�I�v�V����xml2JsonNs(Map<String, String> jsonXml2JsonNs)���g�p���܂��B
Map<String, String> ns2json = new HashMap<String, String>();
ns2json.put("http://www.nec.cn.jersey", "addressesNS");
this.context = new JSONJAXBContext(
JSONConfiguration.mapped().xml2JsonNs(ns2json).build(), types);
JSON�f�[�^�`�������L�Ɏ����܂��B
{"id":"2","name":"BOb","addressesNS.addresses":{"street":"Long Street 1" ,"town":"Short Village"}}
��L�̃f�[�^�`���ł́A�f�t�H���g�Łu.�v�Ŗ��O��ԃZ�p���[�^�[�Ƃ��Ďg�p���Ă��܂��B���̃Z�p���[�^�[�ɕύX����ꍇ�́A�unsSeparator(Character separator)�v���g�p���ĉ������B
JSONConfiguration.mapped().xml2JsonNs(ns2json).nsSeparator(':').build()
JSON�f�[�^�`�������L�Ɏ����܂��B
{"id":"2","name":"BOb","addressesNS:addresses":{"street":"Long Street 1","town":"Short Village"}}
Natural Notation
�uNatural Notation�v���g�p����ꍇ�A�uMappedNotation�v�̂悤�ɐݒ�I�v�V������z�u����K�v�͂���܂���B������JAXB beans�̕ϐ��̌^�ɂ���ď������܂��B
{"id":2,"name":"BOb","addresses":[{"street":"Long Street 1","town":"Short Village"}]}
(1)rootUnwrapping(boolean rootUnwrapping)
{"contact":{"id":2,"name":"BOb","addresses":[{"street":"Long Street 1","town":"Short Village"}]}}
(2)usePrefixesAtNaturalAttributes()�c�c @XmlAttribute public int id; �c�cJSON�f�[�^�`���͉��L�Ɏ����܂��B
{"id":2,"name":"BOb","addresses":[{"street":"Long Street 1","town":"Short Village"}]}
[id]�͋L���u@�v��t�^���܂���B�L���u@�v�ŕt�^�������ꍇ�AusePrefixesAtNaturalAttributes()���\�b�h�𗘗p���܂��BJAXBContextResolver��(1)�ŁuJSONConfiguration.natural().usePrefixesAtNaturalAttributes().build()�v�ɕύX���܂��B
{"@id":2 ,"name":"BOb","addresses":[{"street":"Long Street 1","town":"Short Village"}]}
| Java�̌^ | Mapped Notation | Natural Notation | ���l |
|---|---|---|---|
| �v���~�e�B�u�ƃ��b�p�N���X�iint,short,long,float,double,byte,boolean���܂ށj | int "2",float "-1.0",Double "1.0",booleanValue:"false" | int 2,float -1.0,Double 1.0,booleanValue:false | Mapped Notation�͈��p���ŏ������܂��G Natural Notation�͈��p���Ȃ��ŏ������܂� |
| ArrayList | {"street":"Long Street 1","town":"Short Village"} | [{"street":"Long Street 1","town":"Short Village"}] | Natural Notation�́h[ ]�h�̌`���̔z��ŏ������܂� |
| ArrayObject[]{101,true,'&'}); | [{"@type":"xs:int","$":"101"},{"@type":"xs:boolean","$":"true"},{"@type":"xs:unsignedShort","$":"38"}] | [{"type":"xs:int","$":"101"},{"type":"xs:boolean","$":"true"},{"type":"xs:unsignedShort","$":"38"}] | Natural Notation�𗘗p���Ă�Natural�t�H�[�}�b�g�ɂȂ�Ȃ� |
| �J�X�^���I�u�W�F�N�g | {"contact":{"id":"3","doubleValue":"1.0"}} | {"contact":{"id":3,"doubleValue":1.0}} | Natural Notation�̓I�u�W�F�N�g���Ifield�ɓK�p |
| Mapmap.put("name", "id").map.put("id", 1); | {"map":{"entry":[{"key":{"@type":"xs:string","$":"id"},"value":{"@type":"xs:int","$":"1"}},{"key":{"@type":"xs:string","$":"name"},"value":{"@type":"xs:string","$":"id"}}]}} | {"map":{"entry":{"key":{"type":"xs:string","$":"id"},"value":{"type":"xs:int","$":"1"}},"entry":{"key":{"type":"xs:string","$":"name"},"value":{"type":"xs:string","$":"id"}}}} | Natural Notation�𗘗p���Ă�Natural�t�H�[�}�b�g�ɂȂ�܂��� |
Jettison mapped Notation
JAXB beans�ɕ�����XML���O��Ԃ�����ꍇ�A�uJettison mapped Notation�v���g�p�ł��܂��B
{"contact":{"id":2,"name":"BOb","addresses":{"street":"Long Street 1","town":"Short Village"}}}
��L�̃f�[�^�`���ŁuJettison mapped Notation�v���g�p����ꍇ�A�unumber�v�Ɓuboolean�v�́ustring�v�ɕϊ����܂���B�܂��AList�^��1�̗v�f�������݂��鎞�AJSON�f�[�^�`���ɔz��Ƃ��ĕ\�����܂���B�����̗v�f�����鎞�A�uJettison mapped Notation�v�͎����Ŕz��Ƃ��ĕ\�����܂��B
�c�c
@XmlElement(namespace="http://www.nec.cn.jersey")
public int id;
�c�c
�N���C�A���g���ŕϐ��uid�v�̒l�ɃA�N�Z�X����ɂ́AJSON��XML���O��Ԃ̒�`���K�v�ł��BJSONConfiguration �̐ݒ�I�v�V����xml2JsonNs(Map<String, String> jsonXml2JsonNs)���g�p�ł��܂��B
��L��JAXBContextResolver�̃R���X�g���N�^�ɉ��L�̂悤�Ɏ������܂��B
Map<String, String> ns2json = new HashMap<String, String>();
ns2json.put("http://www.nec.cn.jersey", "idNS");
this.context = new JSONJAXBContext(
JSONConfiguration.mappedJettison().xml2JsonNs(ns2json).build(), types);
JSON�f�[�^�`���͉��L�Ɏ����܂��B
{"contact":{"idNS.id":2,"name":"BOb","addresses":{"street":"Long Street 1" ,"town":"Short Village"}}
Badgerfish Notation
�uBadgerfish Notation�v���g�p���邽�߁A�uJSONConfiguration.badgerFish().build()�v���g�p����K�v������܂��B
{"contact":{"id":2,"name":"BOb","addresses":{"street":"Long Street 1","town":"Short Village"}}}
public class Contact {
public int id;
public String name;
public Contact(int id, String name) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
}
}
(2)���\�[�X���`���܂�
@Path("/JSONObject")
public class MyJSONObjectResource {
@GET
@Produces("application/json")
public JSONObject getContact() {
Contact contact = new Contact(2, "BOb");
JSONObject jsonOb = new JSONObject();
try {
jsonOb.put("id", contact.id).put("name", contact.name);
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return jsonOb;
}
}
�N���C�A���g�����炻�̃��\�[�X�ɃA�N�Z�X�������ɕԋp�����JSON�f�[�^�`�������L�Ɏ����܂��B
{"id":2,"name":"BOb"}
| �N���X��/�C���^�t�F�[�X | ���� |
|---|---|
| public interface ContextResolver<T> | �C���^�t�F�[�X |
| ���\�b�h | - |
| T getContext(java.lang.Class<?> type) | Get a context of type T that is applicable to the supplied type. |
@Provider
public class JAXBContextResolver implements ContextResolver<JAXBContext> {
private JAXBContext context;
private Class[] types = {MyJaxbBean.class};
public JAXBContextResolver() throws Exception {
this.context =
new JSONJAXBContext(
JSONConfiguration.natural().build(), types);
}
public JAXBContext getContext(Class<?> objectType) {
for (Class type : types) {
if (type == objectType) {
return context;
}
}
return null;
}
}
��L�̗�ɁA���[�U������Java�N���X�ł���MyJaxbBean��JAXBContext�v���o�C�_���`���܂��BgetContext(Class<?> objectType)���\�b�h�ł̓N���X�f���ăJ�X�^��JAXBContext�ԋp���܂��B
@Provider
@Produces(�gapplication/json�h)
public class JAXBContextResolver implements ContextResolver<JAXBContext> {
�c�c
}
�u@Produces�v��t�^���Ȃ����A�S��MIME�^�C�v���T�|�[�g���邱�Ƃ��Ӗ����܂��B
import javax.ws.rs.client.Client;
import javax.ws.rs.client.ClientBuilder;
import javax.ws.rs.client.Entity;
import javax.ws.rs.client.WebTarget;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
public class UserClient {
private static String serverUri = "http://localhost:80/WSDemo/rest";
private static void addUser() {
User user = new User("219","�R��","25");
Client client = ClientBuilder.newClient();
WebTarget target = client.target(serverUri + "/users");
Response response = target.request().buildPost(Entity.entity(user, MediaType.APPLICATION_XML)).invoke();
response.close();
}
ClientConfig�𗘗p���ēƎ��̃t�B���^�[��C���^�[�Z�v�^�Ȃ�Provider���N���C�A���g�I�u�W�F�N�g�ɓo�^�ł��܂��B
�ȉ��́A���[�U�[�Ǝ��̃t�B���^�[��o�^���܂��BClientConfig clientConfig = new ClientConfig(); clientConfig.register(MyClientResponseFilter.class); clientConfig.register(new AnotherClientFilter()); Client client = ClientBuilder.newClient(clientConfig);�N���C�A���g�̃C���X�^���X���쐬���ꂽ��́AWeb���\�[�X�����ł��܂��Btarget(uri)���\�b�h����WebTarget�̃I�u�W�F�N�g���ԋp����܂��BWebTarget�𗘗p���ăT�[�o�[�̃T�u���\�[�X�����ł��܂��B �T�[�o�[��Web���\�[�X�̓N�G���p�����^�[�������ꍇ�́AqueryParam()��WebTarget����肵�܂��B
WebTarget webTarget = client.target("http://example.com/rest");
WebTarget resourceWebTarget = webTarget.path("resource"); // URI "http://example.com/rest/resource"
WebTarget helloworldWebTarget = resourceWebTarget.path("helloworld"); //"http://example.com/rest/resource/helloworld".
WebTarget helloworldWebTargetWithQueryParam = helloworldWebTarget.queryParam("greeting", "Hi World!");
����HTTP���N�G�X�g���쐬���܂��B���N�G�X�g�̃��f�B�A�̃^�C�v���w�肵����A�w�b�_��ݒ肵���肵�����ꍇ�́A�ȉ��̂悤�ɍs���܂��B
Invocation.Builder invocationBuilder = helloworldWebTargetWithQueryParam.request(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN_TYPE);
invocationBuilder.header("some-header", "true");
Invocation.Builder �̃��\�b�h�𗘗p���āAHTTP���X�|���X�I�u�W�F�N�g���擾�ł��܂��BResponse response = invocationBuilder.get();post�̏ꍇ
Response response = invocationBuilder.post(Entity.entity("A string entity to be POSTed", MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN));
���̌�́A���X�|���X�̌��ʂ��m�F����ɂ�System.out.println(response.getStatus()); System.out.println(response.readEntity(String.class));
�t�B���^�[��Http�w�b�_�Ȃǃ��N�G�X�g�ƃ��X�|���X�̃p�����[�^��ύX�������ꍇ�Ɏg�p���܂��B�T�[�o�[���̃t�B���^�[�ƃN���C�A���g���̃t�B���^�[�A2��ނɕ�����Ă��܂��B
�}1.2.15.14-1
�}1.2.15.14-2
Memo
�t�B���^�[�� JAX-RS 2.0 �K�͂ɒ�`�����@�\�ł��邽�߁A�t�B���^�[�쐬�őI�������v���W�F�N�g�� JAX-RS 2.0 �t�@�Z�b�g�����K�v������܂��B
�}1.2.15.14-3
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.ws.rs.container.ContainerRequestContext;
import javax.ws.rs.container.ContainerResponseContext;
import javax.ws.rs.container.ContainerResponseFilter;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
public class PoweredByResponseFilter implements ContainerResponseFilter {
@Override
public void filter(ContainerRequestContext requestContext, ContainerResponseContext responseContext)
throws IOException {
responseContext.getHeaders().add("X-Powered-By", "Jersey :-)");
}
}
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.ws.rs.container.ContainerRequestContext;
import javax.ws.rs.container.ContainerRequestFilter;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
import javax.ws.rs.core.SecurityContext;
public class AuthorizationRequestFilter implements ContainerRequestFilter {
@Override
public void filter(ContainerRequestContext requestContext)
throws IOException {
final SecurityContext securityContext =
requestContext.getSecurityContext();
if (securityContext == null ||
!securityContext.isUserInRole("privileged")) {
requestContext.abortWith(Response
.status(Response.Status.UNAUTHORIZED)
.entity("User cannot access the resource.")
.build());
}
}
}
public class CheckRequestFilter implements ClientRequestFilter {
@Override
public void filter(ClientRequestContext requestContext)
throws IOException {
if (requestContext.getHeaders(
).get("Client-Name") == null) {
requestContext.abortWith(
Response.status(Response.Status.BAD_REQUEST)
.entity("Client-Name header must be defined.")
.build());
}
}
}
public class ClientResponseLoggingFilter implements ClientResponseFilter {
@Override
public void filter(final ClientRequestContext reqCtx,
final ClientResponseContext resCtx) throws IOException {
System.out.println("status: " + resCtx.getStatus());
System.out.println("media-type: " + resCtx.getMediaType().getType());
}
�C���^�[�Z�v�^�[�́A���o�̓X�g���[����ʂ��ăG���e�B�e�B�[�̓ǂݏ����������s�����Ɏg���܂��B�T�[�o�[���ƃN���C�A���g���͋���API�𗘗p���܂��B
�C���^�[�Z�v�^�[��
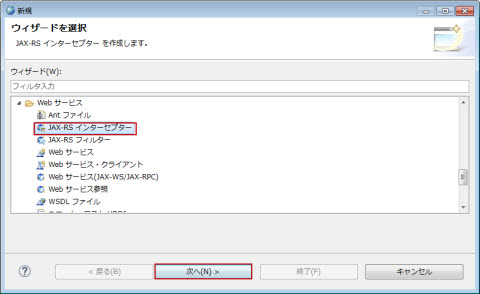
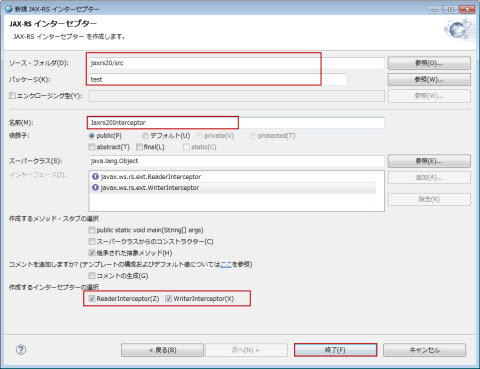
�}1.2.15.15-1
�}1.2.15.15-2
Memo
�C���^�[�Z�v�^�[�� JAX-RS 2.0 �K�͂ɒ�`�����@�\�ł��邽�߁A�C���^�[�Z�v�^�[�쐬�őI�������v���W�F�N�g�� JAX-RS 2.0 �t�@�Z�b�g�����K�v������܂��B
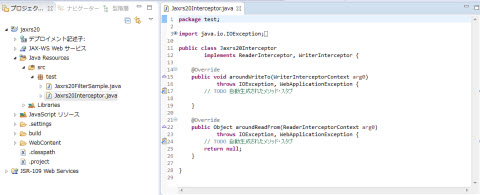
�}1.2.15.15-3
public class GZIPReaderInterceptor implements ReaderInterceptor {
@Override
public Object aroundReadFrom(ReaderInterceptorContext context)
throws IOException, WebApplicationException {
final InputStream originalInputStream = context.getInputStream();
context.setInputStream(new GZIPInputStream(originalInputStream));
return context.proceed();
}
}
public class GZIPWriterInterceptor implements WriterInterceptor {
@Override
public void aroundWriteTo(WriterInterceptorContext context)
throws IOException, WebApplicationException {
final OutputStream outputStream = context.getOutputStream();
context.setOutputStream(new GZIPOutputStream(outputStream));
context.proceed();
}
}
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Path("/")
public class SomeResource {
@Transactional
@GET
public void updateResource() {
// ...
}.
}
Spring�@�\�𗘗p����ꍇ�́ASpring��jar��WAR�t�@�C������WEB-INF/lib�Ɋ܂߂���ŁA
<?xml version="1.0" encoding"UTF-8"?>
<nec-web-app>
<context-root>sse-item-store-webapp</context-root>
<class-loader delegate="false" extra-class-path="C:/WebOTX/modules/jaxrs20.jar;C:/WebOTX/lib/jaxrs20/jersey-spring3.jar">
<property name="overrideablejavaxpackages" value="javax.ws.rs,javax.annotation,javax.validation" />
</class-loader>
......
</nec-web-app>
@Path("/resource")
public class AsyncResource {
@GET
public void asyncGet(@Suspended final AsyncResponse asyncResponse) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String result = veryExpensiveOperation();
asyncResponse.resume(result);
}
private String veryExpensiveOperation() {
// ... very expensive operation
}
}).start();
}
}
�������ɂ����āA��̃��N�G�X�g�̊Ԃɑ҂����Ԃ�����A�N���C�A���g���Ń��X�|���X�҂����s�������Ȃ��ꍇ�ɁA���^�C���A�E�g�𗘗p�ł��܂��B�f�t�H���g�̏ꍇ�A���^�C���A�E�g�͔����X�|���X�Ώۂɒ�`�E�ݒ肳��Ă��܂���̂ŁA�����I�ɒ�`����K�v������܂��B
@GET
public void asyncGetWithTimeout(@Suspended final AsyncResponse asyncResponse) {
asyncResponse.setTimeoutHandler(new TimeoutHandler() {
@Override
public void handleTimeout(AsyncResponse asyncResponse) {
asyncResponse.resume(Response.status(Response.Status.SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE)
.entity("Operation time out.").build());
}
});
asyncResponse.setTimeout(20, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String result = veryExpensiveOperation();
asyncResponse.resume(result);
}
private String veryExpensiveOperation() {
// ... very expensive operation that typically finishes within 20 seconds
}
}).start();
}
final AsyncInvoker asyncInvoker = target().path("http://example.com/resource/")
.request().async();
final Future<Response> responseFuture = asyncInvoker.get();
System.out.println("Request is being processed asynchronously.");
final Response response = responseFuture.get();
// get() waits for the response to be ready
System.out.println("Response received.");
SslConfigurator sslConfig = SslConfigurator.newInstance()
.trustStoreFile("./truststore_client")
.trustStorePassword("secret-password-for-truststore")
.keyStoreFile("./keystore_client")
.keyPassword("secret-password-for-keystore");
SSLContext sslContext = sslConfig.createSSLContext();
Client client = ClientBuilder.newBuilder().sslContext(sslContext).build();
Response response = client.target("https://example.com/resource").request().get();
�N���C�A���g��HTTP�F�ɂ́AHttpAuthenticationFeature�̃C���X�^���X�𗘗p�ł��܂����AHttpAuthenticationFeature�͓�̔F���\�b�h(basic��digest)����ĉ��L�̃��[�h�Ŏ��s���Ă��������B
HttpAuthenticationFeature feature = HttpAuthenticationFeature.basic("user", "superSecretPassword");
���L��BASIC NON-PREEMPTIVE�F���[�h�̗�ł��B
HttpAuthenticationFeature feature = HttpAuthenticationFeature.basicBuilder()
.nonPreemptive().credentials("user", "superSecretPassword").build();
ClientBuilder.newClient(new ClientConfig()
.register(JsonProcessingFeature.class)
.property(JsonGenerator.PRETTY_PRINTING, true));
���L��JSON-P�𗘗p����JAX-RS�̃A�v���P�[�V�������쐬�����ł��B
public class MyApplication extends ResourceConfig {
public MyApplication() {
packages("com.nec.webotx.jersey.examples.jsonp.resource");
register(LoggingFilter.class);
property(JsonGenerator.PRETTY_PRINTING, true);
}
}
web.xml�̗�ł��B
<web-app version="2.5" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>com.nec.webotx.jersey.examples.jsonp.MyApplication</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.nec.webotx.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>javax.ws.rs.Application</param-name>
<param-value>com.nec.webotx.jersey.examples.jsonp.MyApplication</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>javax.json.stream.JsonGenerator.prettyPrinting</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>com.nec.webotx.jersey.examples.jsonp.MyApplication</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
JSON-P(JSR 353)�̓|�[�^�u����APIs�����JSON����́A�����A�`���A�N�G�����܂��BAPIs�ɂ��ẮA��̎�ނ�API����܂��B
| Class or Interface | �L�q |
|---|---|
| Json | Json�̓ǂݏ����A�����y�уt�@�N�g���[�̃I�u�W�F�N�g |
| JsonGenerator | �X�g���[����JSON�f�[�^���������� |
| JsonReader | �X�g���[������JSON�f�[�^��ǂݏo�� |
| JsonObjectBuilder JsonArrayBuilder |
�I�u�W�F�N�g�Ɣz��̃��W���[���� |
| JsonWriter | �X�g���[���փ���������I�u�W�F�N�g�̃��W���[������������ |
| JsonValue JsonObject JsonArray JsonString JsonNumber |
JSON�f�[�^�̒l�̃^�C�v |
URL url = new URL("http://sample.com/example/?q=java&type=post");
try (InputStream is = url.openStream();
JsonReader rdr = Json.createReader(is)) {
JsonObject obj = rdr.readObject();
JsonArray results = obj.getJsonArray("data");
for (JsonObject result : results.getValuesAs(JsonObject.class)) {
System.out.print(result.getJsonObject("from").getString("name"));
System.out.print(": ");
System.out.println(result.getString("message", ""));
System.out.println("-----------");
}
���ʂ̃t�H�[�}�b�g�͉��L�̒ʂ�ł��B
{
"data" : [
{ "from" : { "name" : "xxx", ... }, "message" : "yyy", ... },
{ "from" : { "name" : "ppp", ... }, "message" : "qqq", ... },
...
],
...
}
| Class or Interface | �L�q |
|---|---|
| Json | Json�̓ǂݏ����A�����y�уt�@�N�g���[�̃I�u�W�F�N�g |
| JsonParser | �C�x���g�Ƀx�[�X���ĉ�͂��A�X�g���[������JSON�f�[�^��ǂݏo�� |
| JsonGenerator | �X�g���[����JSON�f�[�^���������� |
URL url = new URL("https://graph.facebook.com/search?q=java&type=post");
try (InputStream is = url.openStream();
JsonParser parser = Json.createParser(is)) {
while (parser.hasNext()) {
Event e = parser.next();
if (e == Event.KEY_NAME) {
switch (parser.getString()) {
case "name":
parser.next();
System.out.print(parser.getString());
System.out.print(": ");
break;
case "message":
parser.next();
System.out.println(parser.getString());
System.out.println("---------");
break;
}
}
}
}
�o�͌��ʂ�Object Model API�̎g�p����Q�Ƃ��Ă��������B
...
import com.nec.webotx.jersey.media.sse.EventOutput;
import com.nec.webotx.jersey.media.sse.OutboundEvent;
import com.nec.webotx.jersey.media.sse.SseFeature;
...
@Path("events")
public static class SseResource {
@GET
@Produces(SseFeature.SERVER_SENT_EVENTS)
public EventOutput getServerSentEvents() {
final EventOutput eventOutput = new EventOutput();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// ... code that waits 1 second
final OutboundEvent.Builder eventBuilder
= new OutboundEvent.Builder();
eventBuilder.name("message-to-client");
eventBuilder.data(String.class,
"Hello world " + i + "!");
final OutboundEvent event = eventBuilder.build();
eventOutput.write(event);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error when writing the event.", e);
} finally {
try {
eventOutput.close();
} catch (IOException ioClose) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error when closing the event output.", ioClose);
}
}
}
}).start();
return eventOutput;
}
}
�E�N���C�A���g���̎�����
Client client = ClientBuilder.newBuilder()
.register(SseFeature.class).build();
WebTarget target = client.target("http://localhost:9998/events");
EventInput eventInput = target.request().get(EventInput.class);
while (!eventInput.isClosed()) {
final InboundEvent inboundEvent = eventInput.read();
if (inboundEvent == null) {
// connection has been closed
break;
}
System.out.println(inboundEvent.getName() + "; "
+ inboundEvent.readData(String.class));
}
public class NotFoundException extends WebApplicationException {
/**
* Create a HTTP 404 (Not Found) exception.
*
* @param message the String that is the entity of the 404 response.
*/
public NotFoundException(String message) {
this(message, null);
}
/**
* Create a HTTP 404 (Not Found) exception.
*
* @param message the String that is the entity of the 404 response.exception A URI-parameter-based exception for errors with QueryParam.Contain a response with a 404 (Client error) status code.
* ParamException.HeaderParamException A parameter exception for errors with HeaderParam.Contain a response with a 400 (Client error) status code.
* ParamException.CookieParamException A parameter exception for errors with CookieParam.Contain a response with a 400 (Client error) status code.
* ParamException.FormParamException A parameter exception for errors with FormParam.Contain a response with a 400 (Client error) status code.
* @param notFoundUri the URI that cannot be found.
*/
public NotFoundException(String message, URI notFoundUri) {
super(Responses.notFound().
entity(message).type("text/plain").build());
this.notFoundUri = notFoundUri;
}
}
javax.ws.rs.WebApplicationException�̃T�u�N���X�͈ȉ��̂Ƃ���ł��B| �ُ�N���X | ���� |
|---|---|
| ConflictException | Create a HTTP 409 (Conflict) exception. |
| NotFoundException | Create a HTTP 404 (Not Found) exception. |
| ParamException | An abstract extension of WebApplicationException for the class of parameter-based exceptions. |
| ParamException.PathParamException | A URI-parameter-based exception for errors with PathParam.Contain a response with a 404 (Client error) status code. |
| ParamException.MatrixParamException | A URI-parameter-based exception for errors with MatrixParam.Contain a response with a 404 (Client error) status code. |
| ParamException.QueryParamException | A URI-parameter-based exception for errors with QueryParam.Contain a response with a 404 (Client error) status code. |
| ParamException.HeaderParamException | A parameter exception for errors with HeaderParam.Contain a response with a 400 (Client error) status code. |
| ParamException.CookieParamException | A parameter exception for errors with CookieParam.Contain a response with a 400 (Client error) status code. |
| ParamException.FormParamException | A parameter exception for errors with FormParam.Contain a response with a 400 (Client error) status code. |
@Provider
public class EntityNotFoundMapper implements
ExceptionMapper<EntityNotFoundException> {
public Response toResponse(EntityNotFoundException ex) {
return Response.status(404).
entity(ex.getMessage()).
type("text/plain").
build();
}
}
������O�N���X�̌^�ƃ}�b�`�����O�N���XMapper���g�p���܂����A��̗�O�N���X�ɑ��ĕ����̗�O�N���XMapper���}�b�`�����ꍇ�A�ȉ��̑I�����[���ɂ���O�N���XMapper���g�p���܂��B
| �f�B���N�g�� | ���l | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| / | �| | ||
| �� �� |
META-INF/ | �| | |
| �� | MANIFEST.MF | �| | |
| �� | WEB-INF/ | �| | |
| �� | web.xml | �쐬����web.xml�ł��B | |
| �� | classes/ | �R���p�C������Java�N���X���i�[���܂��B | |
| �� | lib/ | �R���p�C������Java�N���X���܂�JAR�t�@�C�����i�[���܂��B | |
| �N���X�� | ���� |
|---|---|
| public class Application | Defines the components of a JAX-RS application and supplies additional metadata. A JAX-RS application or implementation supplies a concrete subclass of this abstract class |
| �t�B�[���h | - |
| private static final Set<Object> emptyObjectSet | emptyObjectSet = Collections.emptySet() |
| private static final Set<Class<?>> emptyClassSet | emptyClassSet = Collections.emptySet() |
| ���\�b�h | - |
| public Set<Class<?>> getClasses() | Get a set of root resource and provider classes. The default lifecycle for resource class instances is per-request. The default lifecycle for providers is singleton |
| public Set<Object> getSingletons() | Get a set of root resource and provider instances. Fields and properties of returned instances are injected with their declared dependencies Context by the runtime prior to use. |
package com.nec.jersey.application;
@ApplicationPath(�gresources�h)
public class MyApplication extends Application {
public Set<Class<?>> getClasses() {
Set<Class<?>> s = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
s.add(HelloWorldResource.class);
return s;
}
}
���̏ꍇ��@ApplicationPath�Ɏw�肷��l��web.xml�́uurl-pattern�v�̒l�Ɠ����ł��B
package com.nec.jersey.application;
public class MyApplication extends PackagesResourceConfig {
public MyApplication() {
super("com.nec.jersey.resource;com.nec.jersey.providers");
}
}
�܂��AMyApplication�̃R���X�g���N�^�Ɂusuper("com.nec.jersey");�v���g�p�ł��܂��B
�p�b�P�[�W�ucom.nec.jersey�v�̃T�u�p�b�P�[�W�ucom.nec.jersey.resource�v�Ɓucom.nec.jersey.providers�v�Ƀ��[�g���\�[�X�N���X�ƃv���o�C�_�N���X���X�L�����ł��܂��B
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>Jersey Web Application</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
com.nec.webotx.jersey.spi.container.servlet.ServletContainer
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>
com.nec.webotx.jersey.config.property.packages
</param-name>
<param-value>com.nec.jersey.resource;com.nec.jersey.providers</param-value>
</init-param>
...
</servlet>
...
</web-app>
��L�́uparam-name�v�́ucom.nec.webotx.jersey.config.property.packages�v��ݒ肷��K�v������܂��B�uparam-value�v�ɂ̓��[�g���\�[�X�N���X�ƃv���o�C�_�N���X�̃p�b�P�[�W����ݒ肵�܂��B| �v�f | ���� | �d�l�͐� |
|---|---|---|
| application | the root element of a WADL description | 2.2 Application |
| doc | application�velement can have one or more child doc elements that can be used to document that element. this element has two attributes: (1):xml:lang (2):title | 2.3 Documentation |
| grammars | The grammars element acts as a container for definitions of the format of data exchanged during execution of the protocol described by the WADL document | 2.4 Grammars |
| resources | The resources element acts as a container for the resources provided by the application. | 2.5 Resources |
| resource | A resource element describes a set of resources, each identified by a URI that follows a common pattern. | 2.6 Resource |
| resource_type | A resource_type element describes a set of methods that, together, define the behavior of a type of resource. | 2.7 Resource Type |
| method | A method element describes the input to and output from an HTTP protocol method that may be applied to a resource. | 2.8 Method |
| request | A request element describes the input to be included when applying an HTTP method to a resource. | 2.9 Request |
| response | A response element describes the output that results from performing an HTTP method on a resource. | 2.10 Response |
| representation | A representation element describes a representation of a resource's state. | 2.11 Representation |
| param | A param element describes a parameterized component of its parent element. | 2.12 Parameter |
@Path("wadlResource")
public class WADLResource {
@GET
public String executeGetRequest() {
//do something
return "success";
}
@POST
public String executePostRequest() {
//do something
return "success";
}
}
web.xml�t�@�C���̊֘A����ݒ���ȉ��Ɏ����܂��B
<web-app �c�c>
�c�c
<servlet>
<servlet-name>wadlTest</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
com.nec.webotx.jersey.spi.container.servlet.ServletContainer
</servlet-class>
�c�c
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>wadlTest</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/jersey/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
�c�c
</web-app>
�N���C�A���g����URL:�uhttp://{server-name}:{port}/{context-root}/jersey/application.wadl�v�ɃA�N�Z�X����ƁA���L��WADL�t�@�C�����擾�ł��܂��B
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<application xmlns="http://wadl.dev.java.net/2009/02">
<doc xmlns:jersey=http://jersey.java.net/ �c�c />
<grammars/>
<resources base="http://{server-name}:{port}/{context-root}/{url-pattern}/">
<resource path="wadlResource">
<method id="executeGetRequest" name="GET">
<response>
<representation mediaType="*/*"/>
</response>
</method>
<method id="executePostRequest" name="POST">
<response>
<representation mediaType="*/*"/>
</response>
</method>
</resource>
</resources>
</application>
WebOTX AS V9.4�ł́AJAX-RS 1.1��������JAX-RS 2.0�𗘗p�ł��܂��B �f�t�H���g�̊��ł�JAX-RS 1.1���L���ɂȂ��Ă��܂��B JAX-RS 2.0�ɐ�ւ���ꍇ�́A��ւ��Ώۂ̃h���C�����~���A�Ǘ��h���C���Ƀ��O�C��������A �ȉ��̃R�}���h�����s���ĉ������B
otxadmin > login --user <�Ǘ��h���C���̃��[�U��> ---password <�Ǘ��h���C���̃p�X���[�h> --port <�Ǘ��h���C���̃|�[�g�ԍ�>
otxadmin > install-optional-component --domain <�h���C����> --apgroup <�A�v���P�[�V�����O���[�v��> --pgroup <�v���Z�X�O���[�v��> jaxrs20
JAX-RS 2.0����1.1��ւ���ꍇ�͈ȉ��̃R�}���h�Ő�ւ��ĉ������B
otxadmin > login --user <�Ǘ��h���C���̃��[�U��> ---password <�Ǘ��h���C���̃p�X���[�h> --port <�Ǘ��h���C���̃|�[�g�ԍ�>
otxadmin > uninstall-optional-component --domain <�h���C����> --apgroup <�A�v���P�[�V�����O���[�v��> --pgroup <�v���Z�X�O���[�v��> jaxrs20
JAX-RS�̐�ւ��ɂ��Ă̂��ڂ���������[ �h���C���\�z�E��{�ݒ�K�C�h > 3. �h���C�� > 3.2. �h���C���̍쐬�E�폜 > 3.2.1. �h���C���̍쐬 > 3.2.1.7. �I�v�V���i���R���|�[�l���g�̗L���� ] ���Q�Ƃ��ĉ������B