1. Preface¶
1.1. Who Should Use This Guide¶
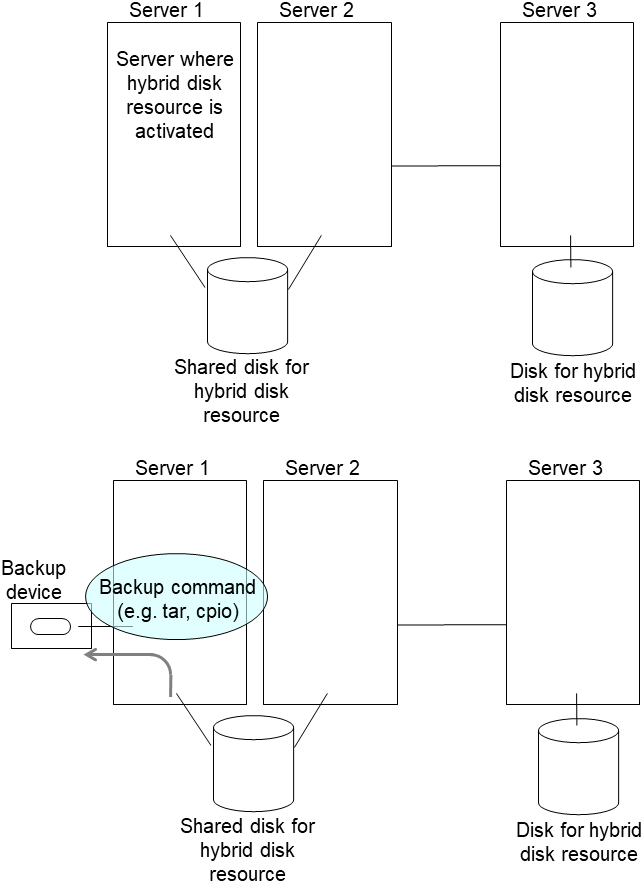
The EXPRESSCLUSTER X Maintenance Guide describes maintenance-related information, intended for administrators. See this guide for information required for operating the cluster.
1.2. How This Guide is Organized¶
2. The system maintenance information: Provides maintenance information for EXPRESSCLUSTER.
1.3. EXPRESSCLUSTER X Documentation Set¶
The EXPRESSCLUSTER manuals consist of the following six guides. The title and purpose of each guide is described below.
EXPRESSCLUSTER X Getting Started Guide
This guide is intended for all users. The guide covers topics such as product overview, system requirements, and known problems.
EXPRESSCLUSTER X Installation and Configuration Guide
This guide is intended for system engineers and administrators who want to build, operate, and maintain a cluster system. Instructions for designing, installing, and configuring a cluster system with EXPRESSCLUSTER are covered in this guide.
EXPRESSCLUSTER X Reference Guide
This guide is intended for system administrators. The guide covers topics such as how to operate EXPRESSCLUSTER, function of each module and troubleshooting. The guide is supplement to the Installation and Configuration Guide.
EXPRESSCLUSTER X Maintenance Guide
This guide is intended for administrators and for system administrators who want to build, operate, and maintain EXPRESSCLUSTER-based cluster systems. The guide describes maintenance-related topics for EXPRESSCLUSTER.
EXPRESSCLUSTER X Hardware Feature Guide
This guide is intended for administrators and for system engineers who want to build EXPRESSCLUSTER-based cluster systems. The guide describes features to work with specific hardware, serving as a supplement to the Installation and Configuration Guide.
EXPRESSCLUSTER X Legacy Feature Guide
This guide is intended for administrators and for system engineers who want to build EXPRESSCLUSTER-based cluster systems. The guide describes EXPRESSCLUSTER X 4.0 WebManager, Builder, and EXPRESSCLUSTER Ver 8.0 compatible commands.
1.4. Conventions¶
In this guide, Note, Important, See also are used as follows:
Note
Used when the information given is important, but not related to the data loss and damage to the system and machine.
Important
Used when the information given is necessary to avoid the data loss and damage to the system and machine.
See also
Used to describe the location of the information given at the reference destination.
The following conventions are used in this guide.
Convention |
Usage |
Example |
|---|---|---|
Bold
|
Indicates graphical objects, such as fields, list boxes, menu selections, buttons, labels, icons, etc.
|
In User Name, type your name.
On the File menu, click Open Database.
|
Angled bracket within the command line |
Indicates that the value specified inside of the angled bracket can be omitted. |
clpstat -s[-h host_name] |
# |
Prompt to indicate that a Linux user has logged on as root user. |
# clpcl -s -a |
Monospace (courier) |
Indicates path names, commands, system output (message, prompt, etc.), directory, file names, functions and parameters. |
|
Monospace bold (courier)
|
Indicates the value that a user actually enters from a command line.
|
Enter the following:
# clpcl -s -a
|
Monospace italic
(courier)
|
Indicates that users should replace italicized part with values that they are actually working with.
|
rpm -i expresscls-<version_number>-<release_number>.x86_64.rpm
|
1.5. Contacting NEC¶
For the latest product information, visit our website below:
2. The system maintenance information¶
This chapter provides information you need for maintenance of your EXPRESSCLUSTER system. Resources to be managed are described in detail.
This chapter covers:
2.5. System resource statistics information collection function
2.10. Configuring the settings to temporarily prevent execution of failover
2.12. How to replace a server with a new one ~For a shared disk~
2.13. How to replace a server with a new one ~For a mirror disk~
2.14. How to replace a server with a new one ~For a hybrid disk~
2.17. Changing offset or size of a partition on mirror disk resource
2.18. Changing offset or size of a partition on hybrid disk resource
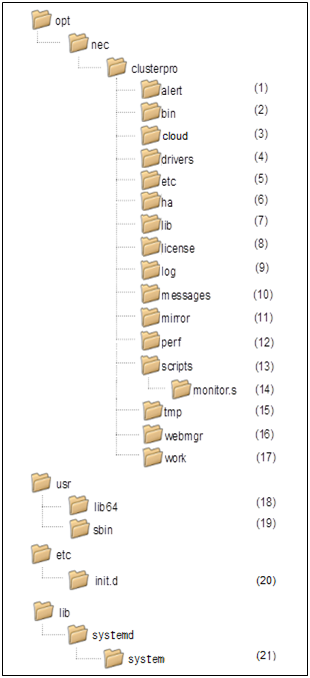
2.1. Directory structure of EXPRESSCLUSTER¶
Note
Executable files and script files that are not described in "EXPRESSCLUSTER command reference" in the "Reference Guide" can be found under the installation directory. Run these files only with EXPRESSCLUSTER. Any failure or trouble caused by executing them by applications other than EXPRESSCLUSTER is not supported.
EXPRESSCLUSTER directories are structured as described below:
- Directory for alert synchronizationThis directory stores EXPRESSCLUSTER Alert Synchronization's modules and management files.
- Directory for cluster modulesThis directory stores the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server's executable files.
- Directory for cloud environmentThis directory stores script files for cloud environment.
- Directory for cluster drivers
- Mirror driverThis directory stores the executable files of the data mirror driver.
- Kernel mode LAN heartbeat, keepalive driverThis directory stores the executable files of the kernel mode LAN heartbeat and keepalive driver.
- Directory for cluster configuration dataThis directory stores the cluster configuration files and policy file of each module.
- Directory for HA products linkageThis directory stores binaries and configuration files for the Java Resource Agent and System Resource Agent.
- Directory for cluster librariesThis directory stores the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server's library.
- Directory for licensesThis directory stores licenses for licensed products.
- Directory for module logsThis directory stores logs produced by each module.
- Directory for report messages (alert, syslog, mail)This directory stores alert, syslog and mail messages reported by each module.
- Directory for mirror disk and hybrid diskThis directory stores the executable files and policy files etc. of the modules for mirror disk and hybrid disk.
- Directory for the performance logsThis directory stores the information of performance about disk and system.
- Directory for EXEC resource script of group resourcesThis directory stores EXEC resource scripts of group resources.
- Directory for the recovery scriptThis directory stores the script executed by this function when an error is detected in the monitor resource if execution of a recovery script is in effect.
- Directory for temporary filesThis directory stores archive files created when logs are collected.
- Directory for the WebManager server and Cluster WebUI.This directory stores the WebManager's server modules and management files.
- Directory for module tasksThis is a work directory for modules.
- usr/lib64This directory stores the symbolic links to the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server's library.
- /usr/sbinThis directory stores the symbolic links to the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server's executable files.
- /etc/init.dFor init.d environment, this directory stores the EXPRESSCLUSTER Service's Start/Stop scripts.
- /lib/systemd/system (for SUSE Linux, the path will be /usr/lib/ systemd/system.)For systemd environment, the setting file of EXPRESSCLUSTER service is stored in this directory.
2.2. Log structure of EXPRESSCLUSTER¶
The log directory in the EXPRESSCLUSTER installation directory has the following structure:
EXPRESSCLUSTER service logs
The EXPRESSCLUSTER service logs include the following types and generations.
init_*.start.cur: Log collected when the current service startedinit_*.start.pre: Log collected when the service one generation older startedinit_*.stop.cur: Log collected when the current service stoppedinit_*.stop.pre: Log collected when the service one generation older stopped- * represents a character string specific to each service.evt: clusterpro_evttrn: clusterpro_trnib : clusterpro_ibapi : clusterpro_apimd: clusterpro_mdmain: clusterprowebmgr: clusterpro_webmgralert: clusterpro_alertsync
The log level and size cannot be changed.
Two generations are automatically rotated. Generations older than the second are removed, starting with the oldest data.
Internal logs for each module
The EXPRESSCLUSTER internal logs include the following types and generations for each module.
*.log.cur: Current internal log*.log.pre: Internal log one generation older*.err.cur: Current error log*.err.pre: rror log one generation older
* represents the module name. For the module list, see "Modifying the log level and size (clplogcf command)" in "EXPRESSCLUSTER command reference" in the "Reference Guide".
Two generations are automatically rotated. Generations older than the second are removed, starting with the oldest data.
Logs for error occurrence
These logs are used to collect emergency information when an error occurs during EXPRESSCLUSTER processing.
For details on collection, see "Collecting logs (clplogcc command) Collecting in formation when a failure occurs" in "EXPRESSCLUSTER command reference" in the "Reference Guide".
elog_*0.tar.gz: Current log collected when errors occurredelog_*1.tar.gz: Previous-generation error log:elog_*4.tar.gz: Four generations old error log- * represents the module name.pm: When an EXPRESSCLUSTER service starts or stopsrc: When an a group resource activation or deactivation error occurredrm: When a monitor resource error is detected
- Error occurrence information is saved for five generations (10 generations for rm only).For the fifth and older generations, information is discarded, starting from the oldest.
The log level and size cannot be changed.
2.3. How to delete EXPRESSCLUSTER logs or alerts¶
To delete EXPRESSCLUSTER logs or alerts, perform the following procedure.
Disable all cluster services on all servers in a cluster .
clpsvcctrl.sh --disable -aShut down the cluster with the Cluster WebUI or clpstdn command, and then reboot the cluster.
To delete logs, delete the files and directories in the following directory. Perform this operation on the server for which you want to delete the logs.
/opt/nec/clusterpro/log/
To delete alerts, delete the files in the following directory. Perform this operation on the server for which you want to delete the alerts.
/opt/nec/clusterpro/alert/log/
Enable all cluster services on all servers in a cluster .
clpsvcctrl.sh --enable -aRun the reboot command on all the servers in the cluster to reboot the cluster.
2.4. Mirror statistics information collection function¶
If the Collect Mirror Statistics check box is already checked on the Mirror Agent tab of Cluster Properties in the config mode of Cluster WebUI, information on the mirror performance is collected and saved to install_path/perf/disk according to the following file naming rules. In the following explanations, this file is represented as the mirror statistics information file.
nmpN.cur
nmpN.pre[X]
|
|
|---|---|
cur |
Indicates the latest information output destination. |
pre |
Indicates the previous, rotated, information output destination. |
N |
Indicates the target NMP number. |
[X] |
Indicates the generation number.
For a file that is one generation older, the generation number is omitted.
For a file that is m generations older, X is assumed to be m-1.
If the total number of generations is n, X of the oldest file is assumed to be n-2.
|
The collected information is saved to the mirror statistics information file. The time during which statistics information is output to this file (=sampling interval) is 60 seconds. .If the size of current log file reached 16MB, it is rotated to new log file. And two generation log files can be saved. Information recorded to the mirror statistics information file can be used as a reference for the tuning related to the mirror function. The collected statistics information contains the following items.
Note
Statistic value name
|
Unit
|
Description
|
Output
|
|---|---|---|---|
Write, Total
(Write amount)
|
Byte
(MB)
|
Total amount of data written to the mirror partition
The value to be output is the amount of data written by every sampling.
|
LOG,
CMD
(A)
|
Write, Avg
(Write amount, average value)
|
Byte/s
(MB/s)
|
Amount of data written to the mirror partition per unit time
|
LOG,
CMD
(A)
|
Read, Total
(Read amount)
|
Byte
(MB)
|
Total amount of data read from the mirror partition
The value to be output is the amount of data read by every sampling.
|
LOG,
CMD
(A)
|
Read, Avg
(Read amount, average value)
|
Byte/s
(MB/s)
|
Amount of data read from the mirror partition per unit time
|
LOG,
CMD
(A)
|
Local Disk Write, Total
(Local disk write amount)
|
Byte
|
Total amount of data written to the local disk (data partition)
The value to be output is the amount of data written by every sampling.
|
LOG
(B)
|
Local Disk Write, Avg
(Local disk average write amount)
|
Byte/s
|
Amount of data written to the local disk (data partition) per unit time
|
LOG
(B)
|
Local Disk Read, Total
(Local disk read amount)
|
Byte
|
Total amount of data read from the local disk (data partition)
The value to be output is the amount of data read by every sampling.
|
LOG
(B)
|
Local Disk Read, Avg
(Local disk average read amount)
|
Byte/s
|
Amount of data read from the local disk (data partition) per unit time
|
LOG
(B)
|
Send, Total
(Mirror communication amount, total value)
|
Byte
(KB)
|
Total amount of mirror communication sent up until mirror disk connect
The value to be output is the communication amount by every sampling.
TCP control information and the like are excluded.
|
LOG,
CMD
(B)
|
Send, Avg
(Mirror communication amount, average value)
|
Byte/s
(KB/s)
|
Mirror communication amount sent by up until mirror disk connect per unit time
|
LOG,
CMD
(B)
|
Compress Ratio
(Compression ratio)
|
%
|
Mirror data compression ratio
(Post-compression size) / (pre-compression size)
x 100
100 for noncompression
The value to be output is calculated based on the communication data for every sampling.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Sync Time, Max
(Mirror communication time, maximum value)
|
Second/time
|
Time needed until the first piece of mirror synchronization data is synchronized.[#f3]_ The value to be output is the longest mirror synchronization data time.
Mirror synchronization data that failed to be synchronized due to non-communication or the like (resulting in a mirror break) is excluded.
Moreover, the value to be output is obtained for communication for every sampling.
|
LOG,
CMD
(A)
|
Sync Time, Avg
(Mirror communication time, average value)
|
Second/time
|
Time needed until the first piece of mirror synchronization data is synchronized. 3 The value to be output is the average for all the communications.
Mirror synchronization data that failed to be synchronized due to non-communication or the like (resulting in a mirror break) is excluded.
Moreover, the value to be output is obtained for communication for every sampling.
|
LOG,
CMD
(A)
|
Sync Ack Time, Max
(Mirror synchronization ACK response time, maximum value)
|
Millisecond
|
Time that elapses between mirror synchronization data being sent to the other server and ACK being received from the other server. 3 The maximum value of all such times is output.
This value is used as a reference to determine Ack Timeout of the Mirror Driver tab that is set with the mirror disk resource or hybrid disk resource.
However, mirror synchronization data that results in an ACK timeout is excluded from the measurement.
The value to be output is the time after the mirror daemon (mirror agent) starts.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Sync Ack Time, Cur
(Mirror synchronization ACK response time, latest value)
|
Millisecond
|
Of the lengths of time needed for mirror synchronization data ACK reception, this value is the time that needed for the most recent ACK reception. 3
However, mirror synchronization data that results in an ACK timeout is excluded from the measurement.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Recovery Ack Time, Max
(Mirror recovery ACK response time, maximum value)
|
Millisecond
|
Time that elapses between mirror recovery data being sent to the other server and ACK being received from the other server
The maximum value of all such times is output.
This value is used as a reference to determine Ack Timeout of the Mirror Driver tab that is set with the mirror disk resource or hybrid disk resource.
However, mirror synchronization data that results in an ACK timeout is excluded from the measurement.
The value to be output is the time after the mirror daemon (mirror agent) starts.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Recovery Ack Time, Max2
(Mirror recovery ACK response time, maximum value during a certain period)
|
Millisecond
|
Maximum value of the time that elapses between mirror recovery data being sent to the other server and ACK being received from the other server.
The maximum value during one sampling period is output.
However, mirror synchronization data that results in an ACK timeout is excluded from the measurement.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Recovery Ack Time, Cur
(Mirror recovery ACK response time, latest value)
|
Millisecond
|
Time that elapses between the mirror recovery data being sent to the other server and ACK being received from the other server
The value to be output is the time needed for the most recent ACK reception.
However, mirror synchronization data that results in an ACK timeout is excluded from the measurement.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Sync Diff, Max
(Difference amount, maximum value)
|
Byte
(MB)
|
Amount of mirror synchronization data that has not yet been synchronized with the other server. The value to be output is the maximum from among all the samplings.
Mirror synchronization data that failed to be synchronized due to non-communication or the like (resulting in a mirror break) is excluded.
|
LOG,
CMD
(A)
|
Sync Diff, Cur
(Difference amount, latest value)
|
Byte
(MB)
|
Amount of mirror synchronization data that has not yet been synchronized with the other server. The value to be output is that which was used most recently for collection.
Mirror synchronization data that failed to be synchronized due to non-communication or the like (resulting in a mirror break) is excluded.
|
LOG,
CMD
(A)
|
Send Queue, Max
(Number of send queues, maximum value)
|
Quantity
|
Number of queues used when mirror synchronization data is sent. The value to be output is the maximum used after the mirror daemon (mirror agent) starts.
This value is used as a reference to determine Number of Queues in Asynchronous mode that is set with the mirror disk resource or hybrid disk resource.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Send Queue, Max2
(Number of send queues, maximum value during a certain period)
|
Quantity
|
Number of queues used when mirror synchronization data is sent. The maximum value during one sampling period is output.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Send Queue, Cur
(Number of send queues, latest value)
|
Quantity
|
Number of queues used when mirror synchronization data is sent. The value to be output is that which was used most recently for collection.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Request Queue, Max
(Number of request queues, maximum value)
|
Quantity
|
Number of I/O requests being processed that were sent to the mirror partition. The value to be output is the maximum used after the mirror daemon (mirror agent) starts.
This value is used as a reference to determine Request Queue Maximum Number of the Mirror Driver tab of cluster properties.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Request Queue, Max2
(Number of request queues, maximum value during a certain period)
|
Quantity
|
Number of I/O requests being processed that were sent to the mirror partition. The maximum value during one sampling period is output.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Request Queue, Cur
(Number of request queues, latest value)
|
Quantity
|
Number of I/O requests being processed that were sent to the mirror partition. The value to be output is that which was used most recently for collection.
|
LOG
(A)
|
MDC HB Time Max
(Mirror disconnect heartbeat time, maximum value)
|
Second
|
Time that elapses between ICMP ECHO being sent to the other server through mirror disconnect and ICMP ECHO REPLY being received from the other server.
The value to be output is the maximum used after the mirror daemon (mirror agent) starts.
|
LOG
(B)
|
MDC HB Time, Max2
(Mirror disconnect heartbeat time, maximum value during a certain period)
|
Second
|
Time that elapses between ICMP ECHO being sent to the other server through mirror disconnect and ICMP ECHO REPLY being received from the other server.
The maximum value during one sampling period is output.
|
LOG
(B)
|
MDC HB Time Cur
(Mirror disconnect heartbeat time, latest value)
|
Second
|
Time that elapses between ICMP ECHO being sent to the other server through mirror disconnect and ICMP ECHO REPLY being received from the other server.
The value to be output is that which was used most recently for collection.
|
LOG
(B)
|
Local-Write Waiting Recovery-Read Time, Total
(Mirror synchronization I/O exclusion time, total value)
|
Second
|
If writing to the same area of the disk occurs during mirror recovery, writing is held until the mirror recovery for that area is complete.
The value to be output is the cumulative value of the hold time, from when the mirror daemon (mirror agent) starts.
That hold time may be long if Recovery Data Size of the Mirror Agent tab of the cluster properties is made large. This value is used as a reference to determine this size.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Local-Write Watiting Recovery-Read Time, Total2
(Mirror synchronization I/O exclusion time, total value during a certain period)
|
Second
|
If writing to the same area of the disk occurs during mirror recovery, writing is held until the mirror recovery for that area is complete.
The value to be output is the cumulative value of the hold time during one sampling period.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Recovery-Read Waiting Local-Write Time, Total
(Mirror recovery I/O exclusion time, total value)
|
Second
|
If reading of mirror recovery data from the same area of the disk occurs during writing to the mirror partition, reading of the mirror recovery data is held until writing to that area is complete.
The value to be output is the cumulative value of the hold time, from when the mirror daemon (mirror agent) starts.
That hold time may be long if Recovery Data Size of the Mirror Agent tab of the cluster properties is made large. This value is used as a reference to determine this size.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Recovery-Read Waiting Local-Write Time, Total2 |
Second |
If reading of mirror recovery data from the same area of the disk occurs during writing to the mirror partition, reading of the mirror recovery data is held until writing to that area is complete. |
LOG |
X(Mirror recovery I/O exclusion time, total value during a certain period) |
The value to be output is the cumulative value of the hold time during one sampling period. |
||
Unmount Time, Max
(Unmount time, maximum value)
|
Second
|
Time needed for unmount to be executed when the mirror disk resource or hybrid disk resource is deactivated
This value is used as a reference to determine Timeout of the Unmount tab that is set with the mirror disk resource or hybrid disk resource.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Unmount Time, Last
(Unmount time, latest value)
|
Second
|
Time needed for unmount to be executed when the mirror disk resource or hybrid disk resource is deactivated
The value to be output is the time needed when unmount was most recently executed.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Fsck Time, Max
(fsck time, maximum value)
|
Second
|
Time needed for fsck to be executed when the mirror disk resource or hybrid disk resource is activated
This value is used as a reference to determine fsck Timeout of the Fsck tab that is set with the mirror disk resource or hybrid disk resource.
|
LOG
(A)
|
Fsck Time, Last
(fsck time, latest value)
|
Second
|
Time needed for fsck to be executed when the mirror disk resource or hybrid disk resource is activated
The value to be output is the time needed when fsck was most recently executed.
|
LOG
(A)
|
- 1
- The unit in parentheses is used for command display. During output, a value of up to two decimal places is output. The third decimal place is truncated.The conversion rules are as follows:1 KB = 1024 bytes, 1 MB = 1048576 bytesIf a value is truncated to 0, "0.00" is output. If the value is 0 without truncation, "None" is displayed for commands, or "0" for the mirror statistics information file.
- 2
- CMD : Information that is visible with commands (clpmdstat, clphdstat)LOG : Information that is output to the mirror statistics information file(A) : In case of Active, the valid value is output.(B) : In both cases of Active/Standby, the valid value is output.Further, only mirror statistics information on a local server is recorded, information on other servers is not recorded.
- 3(1,2,3)
- If the mode is "synchronous", "time taken from sending a mirror synchronous data to receiving ACK from the other server".If the mode is "asynchronous", "time taken from placing mirror synchronous data on the synchronization queue to receiving ACK from the other server".
If Collect Mirror Statistics is already checked, part of information (information with CMD in the Output column in the above table) can be collected and displayed with the clpmdstat/clphdstat command. For information on how to use this command, see "Displaying the mirror status (clpmdstat command)" in "EXPRESSCLUSTER command reference" in the "Reference Guide".
Display with commands can be used only when Gather Statistical information is already enabled in the Mirror Agent tab of Cluster Properties in Cluster WebUI.
2.5. System resource statistics information collection function¶
If the Collect Mirror Statistics check box is already checked on the Monitor tab of Cluster Properties in the Cluster WebUI config mode and if system monitor resources or process resource monitor resources are already added to the cluster, information on the system resource is collected and saved under install_path/perf/system according to the following file naming rules.
This file is in CSV-format. In the following explanations, this file is represented as the system resource statistics information file.
system.cur
system.pre
|
|
|---|---|
cur |
Indicates the latest information output destination. |
pre |
Indicates the previous, rotated, information output destination. |
The collected information is saved to the system resource statistics information file. The time during which statistics information is output to this file (=sampling interval) is 60 seconds. .If the size of current log file reached 16MB, it is rotated to new log file. And two generation log files can be saved. Information recorded to the system resource statistics information file can be used as a reference for analyzing the system performance.The collected statistics information contains the following items.
Statistic value name |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|
CPUCount |
Quantity |
Number of CPUs |
CPUUtilization |
% |
CPU utilization |
CPUTotal |
10 Millisecond |
Total CPU time |
CPUUser |
10 Millisecond |
CPU usage time in the user mode |
CPUNice |
10 Millisecond |
CPU usage time in the user mode with low priority |
CPUSystem |
10 Millisecond |
CPU usage time in the system mode |
CPUIdle |
10 Millisecond |
CPU idle time |
CPUIOWait |
10 Millisecond |
I/O wait time |
CPUIntr |
10 Millisecond |
Interrupt processing time |
CPUSoftIntr |
10 Millisecond |
Software interrupt processing time |
CPUSteal |
10 Millisecond |
Time when CPU was consumed by the OS on another virtual machine for virtual environment |
MemoryTotalSize |
Byte (KB) |
Total memory capacity |
MemoryCurrentSize |
Byte (KB) |
Memory usage |
MemoryBufSize |
Byte (KB) |
Buffer size |
MemoryCached |
Byte (KB) |
Cache memory size |
MemoryMemFree |
Byte (KB) |
Available memory capacity |
MemoryDirty |
Byte (KB) |
Memory data waiting to be written on hard disk |
MemoryActive(file) |
Byte (KB) |
Buffer or page cache memory |
MemoryInactive(file) |
Byte (KB) |
Available buffer or available page cache memory |
MemoryShmem |
Byte (KB) |
Shared memory size |
SwapTotalSize |
Byte (KB) |
Available swap size |
SwapCurrentSize |
Byte (KB) |
Currently used swap size |
SwapIn |
Times |
Number of times of swap-in |
SwapOut |
Times |
Number of times of swap-out |
ThreadLimitSize |
Quantity |
Maximum number of threads |
ThreadCurrentSize |
Quantity |
Current number of threads |
FileLimitSize |
Quantity |
Maximum number of opened files |
FileCurrentSize |
Quantity |
Current number of opened files |
FileLimitinode |
Quantity |
Number of inodes in the whole system |
FileCurrentinode |
Quantity |
Current number of inodes |
ProcessCurrentCount |
Quantity |
Current total number of processings |
The following output is an example of system resource statistics information file.
system.cur
"Date","CPUCount","CPUUtilization","CPUTotal","CPUUser","CPUNice","CPUSystem","CPUIdle","CPUIOWait","CPUIntr","CPUSoftIntr","CPUSteal","MemoryTotalSize","MemoryCurrentSize","MemoryBufSize","MemoryCached","MemoryMemFree","MemoryDirty","MemoryActive(file)","MemoryInactive(file)","MemoryShmem","SwapTotalSize","SwapCurrentSize","SwapIn","SwapOut","ThreadLimitSize","ThreadCurrentSize","FileLimitSize","FileCurrentSize","FileLimitinode","FileCurrentinode","ProcessCurrentCount" "2019/10/31 15:44:50","2","0","34607369","106953","59","23568","34383133","89785","0","3871","0","754236","231664","948","334736","186888","12","111320","167468","50688","839676","0","0","0","5725","183","71371","1696","22626","22219","121" "2019/10/31 15:45:50","2","0","34619340","106987","59","23577","34395028","89816","0","3873","0","754236","231884","948","334744","186660","12","111320","167476","50688","839676","0","0","0","5725","183","71371","1696","22867","22460","121" "2019/10/31 15:46:50","2","0","34631314","107022","59","23586","34406925","89846","0","3876","0","754236","231360","948","334764","187164","4","111348","167468","50688","839676","0","0","0","5725","183","71371","1696","22867","22460","121" :
2.6. Cluster statistics information collection function¶
If the Cluster Statistics check box is already checked on the Extension tab of Cluster Properties in the Cluster WebUI config mode, it collects the information of the results and the time spent for each of the processings such as group failover, group resource activation and monitor resource monitoring. This file is in CSV format. In the following explanations, this file is represented as the cluster statistics information file.
For groups
group.curgroup.precur
Indicates the latest information output destination.
pre
Indicates the previous, rotated, information output destination.
File location
install_path/perf/cluster/group/
For group resources
The information for each type of group resource is output to the same file.
[Group resource type].cur[Group resource type].precur
Indicates the latest information output destination.
pre
Indicates the previous, rotated, information output destination.
File location
install_path/perf/cluster/group/
For monitor resources
The information for each type of monitor resources is output to the same file.
[Monitor resource type].cur[Monitor resource type].precur
Indicates the latest information output destination.
pre
Indicates the previous, rotated, information output destination.
File location
install_path/perf/cluster/monitor/
Note
The cluster statistics information file is included in the logs collected by the clplogcc command or Cluster WebUI.
Specify type 6 to collect the log by the clplogcc command; specify Pattern 6 to collect the log by the Cluster WebUI. For details about log collection, see. "Collecting logs (clplogcc command)" in "EXPRESSCLUSTER command reference" of "Reference Guide" or the online manual.
Listed below are the timing to output the statistics information to the cluster statistics information file:
For groups 4
When the group startup processing is completed
When the group stop processing is completed
When the group move processing is completed 5
When the failover processing is completed 5
For group resources
When the group resource startup processing is completed
When the group resource stop processing is completed
For monitor resources
When the monitor processing is completed
When the monitor status change processing is completed
The statistics information to be collected includes the following items:
Statistic value name |
Description |
|---|---|
Date |
Time when the statistics information is output.
This is output in the form below (000 indicates millisecond):
YYYY/MM/DD HH:MM:SS.000 YYYY/MM/DD HH:MM:SS.000
|
Name |
Name of group, group resource or monitor resource. |
Action |
Name of the executed processing.
The following strings are output:
For groups: Start (at start), Stop (at stop), Move (at move/failover)
For group resources: Start (at activation), Stop (at deactivation)
For monitor resources: Monitor (at monitor execution)
|
Result |
Name of the results of the executed processing.
The following strings are output:
When the processing was successful: Success (no errors detected in monitoring or activation/deactivation)
When the processing failed: Failure (errors detected in monitoring or activation/deactivation)
When a warning occurred: Warning (only for monitoring, in case of warning)
When a timeout occurred: Timeout (monitoring timeout)
When the processing was cancelled: Cancel (cancelling processings such as cluster shutdown during group startup)
|
ReturnCode |
Return value of the executed processing. |
StartTime |
Start time of the executed processing.
This is output in the form below (000 indicates millisecond):
YYYY/MM/DD HH:MM:SS.000 YYYY/MM/DD HH:MM:SS.000
|
EndTime |
End time of the executed processing.
This is output in the form below (000 indicates millisecond):
YYYY/MM/DD HH:MM:SS.000 YYYY/MM/DD HH:MM:SS.000
|
ElapsedTime(ms) |
Time taken for executing the processing (in millisecond).
This is output in millisecond.
|
Here is an example of the statistics information file to be output when a group with the following configuration is started up:
Group
Group name: failoverA
Group resource which belongs to the group (failoverA)
- exec resourceResource name: exec01, exec02, exec03
group.cur
"Date","Name","Action","Result","ReturnCode","StartTime","EndTime","ElapsedTime(ms)" "2018/12/19 09:44:16.925","failoverA","Start","Success",,"2018/12/19 09:44:09.785","2018/12/19 09:44:16.925","7140" :
exec.cur
"Date","Name","Action","Result","ReturnCode","StartTime","EndTime","ElapsedTime(ms)" "2018/12/19 09:44:14.845","exec01","Start","Success",,"2018/12/19 09:44:09.807","2018/12/19 09:44:14.845","5040" "2018/12/19 09:44:15.877","exec02","Start","Success",,"2018/12/19 09:44:14.847","2018/12/19 09:44:15.877","1030" "2018/12/19 09:44:16.920","exec03","Start","Success",,"2018/12/19 09:44:15.880","2018/12/19 09:44:16.920","1040" :
2.6.1. Notes on the size of the cluster statistics information file¶
The size of the cluster statistics information file can be set between 1 and 99 MB. The number of cluster statistics information files to be generated differs depending on their configurations. Some configurations may cause a large number of files to be generated. Therefore, consider setting the size of the cluster statistics information file according to the configuration. The maximum size of the cluster statistics information file is calculated with the following formula:
The size of the cluster statistics information file =([Group file size]) x (number of generations (2)) +([Group resource file size] x [number of types of group resources which are set]) x (number of generations (2)) +([Monitor resource file size] x [number of types of monitor resources which are set]) x (number of generations (2))Example: For the following configuration, the total maximum size of the cluster statistics information files to be saved is 232 MB with this calculation. (((1MB) x 2) + ((3MB x 5) x 2) + ((10MB x 10) x 2) = 232MB)
Group (file size: 1 MB)
Number of group resource types: 5 (file size: 3 MB)
Number of monitor resource types: 10 (file size: 10 MB)
2.7. Communication ports¶
EXPRESSCLUSTER uses several port numbers. Change the firewall settings so that EXPRESSCLUSTER can use some port numbers.
For an AWS environment, configure to able to access the following port numbers in the security group setting in addition to the firewall setting.
Refer to "Getting Started Guide" > "Notes and Restrictions" > "Communication port number" for port numbers used for EXPRESSCLUSTER.
2.8. Cluster driver device information¶
The mirror driver mainly uses 218 as the major number. Make sure that no other driver uses this major number. However, this major number can be changed to avoid using 218 due to system restrictions.
The kernel mode LAN heartbeat driver uses 10 as the major number, and mainly uses 240 as the minor number. Make sure that no other driver uses these major and minor numbers.
The keepalive driver uses 10 as the major number, and mainly uses 241 as the minor number. Make sure that no other driver uses these major and minor numbers.
2.9. What causes servers to shut down¶
When any one of the following errors occurs, EXPRESSCLUSTER shuts down, resets servers, or performs panic of servers to protect resources.
2.9.1. Final action for an error in resource activation or deactivation¶
When the final action for errors in resource activation/deactivation is specified as one of the following:
Final action |
Result |
|---|---|
The cluster service stops and the OS shuts down. |
Causes normal shutdown after the group resources stop. |
The cluster service stops and the OS reboots. |
Causes normal reboot after the group resources stop. |
Sysrq Panic |
Performs a panic upon group resource activation/deactivation error. |
Keepalive Reset |
Performs a reset upon group resource activation/deactivation error. |
Keepalive Panic |
Performs a panic upon group resource activation/deactivation error. |
BMC Reset |
Performs a reset upon group resource activation/deactivation error. |
BMC Power Off |
Performs a power off upon group resource activation/deactivation error. |
BMC power Cycle |
Performs a power cycle upon group resource activation/deactivation error. |
BMC NMI |
Causes NMI upon group resource activation/deactivation error. |
I/O Fencing(High-End Server Option) |
Causes I/O fencing upon group resource activation/deactivation error. |
2.9.2. Action for resource activation or deactivation stall generation¶
When one of the following is specified as the final action to be applied upon the occurrence of an error in resource activation/deactivation, and if resource activation/deactivation takes more time than expected:
Action performed when a stall occurs |
Result |
|---|---|
The cluster service stops and the OS shuts down. |
When a group resource activation/deactivation stall occurs, performs normal shutdown after the group resources stop. |
The cluster service stops and the OS reboots. |
When a group resource activation/deactivation stall occurs, performs normal reboot after the group resources stop. |
Sysrq Panic |
When a group resource activation/deactivation stall occurs, performs a panic. |
Keepalive Reset |
When a group resource activation/deactivation stall occurs, performs a reset. |
Keepalive Panic |
When a group resource activation/deactivation stall occurs, performs a panic. |
BMC Reset |
When a group resource activation/deactivation stall occurs, performs a reset. |
BMC Power Off |
When a group resource activation/deactivation stall occurs, performs a power off. |
BMC power Cycle |
When a group resource activation/deactivation stall occurs, performs a power cycle. |
BMC NMI |
When a group resource activation/deactivation stall occurs, performs an NMI. |
I/O fencing(High-End Server Option) |
When a group resource activation/deactivation stall occurs, performs an I/O fencing. |
The OS shuts down if the resource activation or deactivation takes an unexpectedly long time. The OS shuts down, regardless of the setting of recovery in the event of a resource activation or deactivation error.
If a resource activation stall occurs, alert occurs and the following message is output to syslog.
Module type: rc
Event ID: 32
Message: Activating %1 resource has failed.(99 : command is timeout)
Description: Failed to activate 1 resource.
If a resource deactivation stall occurs, alert occurs and the following message is output to syslog.
Module type: rc
Event ID: 42
Message: Stopping %1 resource has failed.(99 : command is timeout)
Description: Failed to stop the %1 resource.
2.9.3. Final action at detection of an error in monitor resource¶
When the final action for errors in monitor resource monitoring is specified as one of the following:
Final action |
Result |
|---|---|
Stop cluster service and shut down the OS |
Causes shutdown after the group resources stop. |
Stop cluster service and reboot the OS |
Causes reboot after the group resources stop. |
Sysrq Panic |
Causes panic when an error is detected in monitor resource. |
Keepalive Reset |
Causes reset when an error is detected in monitor resource. |
Keepalive Panic |
Causes panic when an error is detected in monitor resource. |
BMC Reset |
Causes reset when an error is detected in monitor resource. |
BMC Power Off |
Causes power off when an error is detected in monitor resource. |
BMC Power Cycle |
Causes power cycle when an error is detected in monitor resource. |
BMC NMI |
Causes NMI when an error is detected in monitor resource. |
I/O Fencing(High-End Server Option) |
Causes I/O fencing when an error is detected in monitor resource. |
2.9.4. Forced stop action¶
When forced stop is configured as "Used".
Physical machine
Final action
Result
BMC reset
Causes reset in the failing server in which a failover group existed.
BMC power off
Causes power off in the failing server in which a failover group existed.
BMC power cycle
Causes power cycle in the failing server in which a failover group existed.
BMC NMI
Causes NMI in the failing server in which a failover group existed.
Virtual machine (guest OS)
Final action
Result
VMware vSphere CLI power off
Causes power off in the failing server in which a failover group existed.
2.9.5. Emergency server shutdown, emergency server reboot¶
When an abnormal termination is detected in any of the following processes, a shutdown or reboot is generated after the group resource stops. Shutdown or reboot generation depends on the setting of Action When the Cluster Service Process Is Abnormal.
clprc
clprm
clpnm
2.9.6. Resource deactivation error in stopping the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon¶
When deactivating a resource by running clpcl -t, which stops the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon fails, EXPRESSCLUSTER causes a emergency shutdown. An action for emergency shutdown depends on the settings in [Action When the Cluster Service Process Is Abnormal].
2.9.7. Stall detection in user space¶
When a server stalls longer than the heartbeat time-out, an OS hardware reset, panic, or I/O fencing is generated. Hardware reset or panic generation depends on the setting of Operation at Timeout Detection of the user-mode monitor resource.
2.9.8. Stall detection during shutdown process¶
When a server stalls during the OS shutdown process, an OS hardware reset, panic, or I/O fencing is generated. Hardware reset or panic generation depends on the setting of Operation at Timeout Detection of the shutdown monitor.
2.9.9. Recovery from network partitioning¶
When any network partition resolution resources are not set, if all heartbeats are disrupted (network partitioning), both servers failover to each other. As a result, groups are activated on both servers. Even when network partition resolution resources are set, groups may be activated on both servers.
If interconnections are recovered from this condition, EXPRESSCLUSTER causes shutdown on both or one of the servers.
For details of network partitioning, see "When network partitioning occurs" in "Troubleshooting" in the "Reference Guide".
2.9.10. Network partition resolution¶
In a cluster system where network partition resolution resources are configured, the network partition resolution is performed when all heartbeats are interrupted (network partition). If this is determined to be caused by the network partitions, some or all of the servers are shut down or stop their services. Shutdown or service stop generation depends on the setting of Action at NP Occurrence.
For details on the network partition resolution, see "Network partition resolution resources details" in the "Reference Guide".
2.9.11. Mirror disk error ~For Replicator~¶
When an error occurs in a mirror disk, the mirror agent causes reset.
2.9.12. Hybrid disk error ~For Replicator DR~¶
When an error occurs in a hybrid disk, the mirror agent causes reset.
2.9.13. Failure in suspending or resuming the cluster¶
If suspending or resuming the cluster fails, the server is shut down.
2.10. Configuring the settings to temporarily prevent execution of failover¶
Follow the steps below to temporarily prevent failover caused by a failed server from occurring.
- Temporarily adjust time-outBy temporarily adjusting time-out, you can prevent a failover caused by a failed server from occurring.The clptoratio command is used to temporarily adjust time-out. Run the clptoratio command on one of the servers in the cluster.
(Example) To extend the heartbeat time-out to an hour, or 3600 seconds, when the heartbeat time-out is set to 90 seconds:
clptoratio -r 40 -t 1hFor more information on the clptoratio command, see "Adjusting time-out temporarily (clptoratio command)" in "EXPRESSCLUSTER command reference" in the "Reference Guide". - Releasing temporary time-out adjustmentReleases the temporary adjustment of time-out. Execute the clptoratio command for any server in the cluster.
clptoratio -iFor more information on the clptoratio command, see "Adjusting time-out temporarily (clptoratio command)" in "EXPRESSCLUSTER command reference" in the "Reference Guide".
Follow the steps below to temporarily prevent failover caused by a monitor error by temporarily stopping monitor resource monitoring.
- Suspending monitoring operation of monitor resourcesBy suspending monitoring operations, a failover caused by monitoring can be prevented.The clpmonctrl command is used to suspend monitoring. Run the clpmonctrl command on all servers in the cluster.Another way is to use the -h option on a server in the cluster and run the clpmonctrl command for all the servers.
(Example) To suspend all monitoring operations:on the server in which the command is run:
clpmonctrl -s(Example) To suspend all monitoring operations on the server with -h option specified
clpmonctrl -s -h <server name>For more information on the clpmonctrl command, see "Controlling monitor resources (clpmonctrl command)" in "EXPRESSCLUSTER command reference" in the "Reference Guide". - Restarting monitoring operation of monitor resourcesResumes monitoring. Execute the clpmonctrl command for all servers in the cluster.Another way is to use the -h option on a server in the cluster and run the clpmonctrl command for all the servers.
(Example) Resuming all monitoring operations:on the server in which the command is run:
clpmonctrl -r(Example) To resume all monitoring operations on the server with -h option specified
clpmonctrl -r -h <server name>For more information on the clpmonctrl command, see "Controlling monitor resources (clpmonctrl command)" in "EXPRESSCLUSTER command reference" in the "Reference Guide".
Follow the steps below to temporarily prevent failover caused by a monitor error by disabling recovery action for a monitor resource error.
- Disabling recovery action for a monitor resource errorWhen you disable recovery action for a monitor resource error, recovery action is not performed even if a monitor resource detects an error. To set this feature, check the Recovery action when a monitor resource error is detected checkbox in Disable cluster operation under the Extension tab of Cluster properties in config mode of Cluster WebUI and update the setting.
- Not disabling recovery action for a monitor resource errorEnable recovery action for a monitor resource error. Uncheck the Recovery action when a monitor resource error is detected checkbox in Disable cluster operation under the Extension tab of Cluster properties in config mode of Cluster WebUI and update the setting.
Follow the steps below to temporarily prevent failover caused by an activation error by disabling recovery action for a group resource activation error.
- Disabling recovery action for a group resource activation errorWhen you disable recovery action for a group resource activation error, recovery action is not performed even if a group resource detects an activation error. To set this feature, check the Recovery operation when a group resource activation error is detected checkbox in Disable cluster operation under the Extension tab of Cluster properties in config mode of Cluster WebUI and update the setting.
- Not disabling recovery action for a group resource activation errorEnable recovery action for a group resource activation error. Uncheck the Recovery operation when a group resource activation error is detected checkbox in Disable cluster operation under the Extension tab of Cluster properties in config mode of Cluster WebUI and update the setting.
2.11. How to replace a mirror disk with a new one¶
When the replacement of mirror disks is necessary due to mirror disk breakdown or some reasons after starting operation, run the following steps:
See also
For details on how to stop and start daemons, see "Suspending EXPRESSCLUSTER" in "Preparing to operate a cluster system" in the "Installation and Configuration Guide".
2.11.1. In case of replacing a mirror disk constructed with a single disk(non-RAID)¶
Stop the server of which the mirror disk is going to be replaced.
Note
Before shutting down the server, it is recommended that the steps in "Disabling the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon" in the "Installation and Configuration Guide" be executed.On the target server, execute the following command to disable the daemon.clpsvcctrl.sh --disable core mgrIf a hybrid disk failure occurs, terminate all servers connected to the disk to be replaced.
Install a new disk in the server.
Start up the server in which the new disk was installed. At this time, change the setting so that the EXPRESSCLUSTER services will not be executed. In case of not having disabled the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon in the step 1, the daemons start up on run level 1 at OS startup.
Construct the same partition as the original disk to the new disk by fdisk command.
Note
To replace shared storage with the hybrid disk, create a partition and file system with any server connected to that shared storage.
Initialize the cluster partition when using the disk used as an EXPRESSCLUSTER mirror disk or hybrid disk with data discarded.
For more information on initializing the cluster partition (CLUSTER partition), see the related items ("Shared disk settings for Hybrid disk resource (Required for Replicator DR)", "Partition settings for Hybrid disk resource (Required for the Replicator DR)", and "Partition settings for Mirror disk resource (when using Replicator)") in "Settings after configuring hardware" in "Determining a system configuration" in the "Installation and Configuration Guide".
Prevent initial mirror construction from being performed automatically.
(A) In the state in which the operation is being performed on the server on which a mirror disk is not replaced (state in which the group containing mirror disk resources is active), you want to concurrently perform disk copy (initial mirror construction), there is no particular need to make sure that initial mirror construction is not automatically performed.
(B) If the operation could be stopped until disk copy is completed (the group may be deactivated), deactivate the group containing the mirror disk resource.
Note
- With procedure (A), copy is performed by the amount equal to that of disk space used, depending on the type of file system, so the copy time may depend on the amount of disk space used.Also, because the operation and copy are performed concurrently, the load may become high and copy may take time depending on the case.
With procedure (B) whereby disk copy is performed while the operation is stopped (the group is deactivated), copy is performed by the amount equal to that of disk space used, depending on the file system, so the copy time may depend on the amount of disk space used. The operation (group activation) can be started after the completion of copy.
On the server on which a new disk has been installed, enable the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon, and restart the server.
Note
- In case that the steps in "Disabling the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon" in the Installation and Configuration Guide were executed before shutting down the server, enable the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemons at this time.On the target server, execute the following command to enable the daemon.
clpsvcctrl.sh --enable core mgr
Start the initial mirror construction (disk copy) by executing the command described below.
- (A) When performing an operation on a server on which the mirror disk has not been replacedThe initial mirror construction (disk copy) is automatically started.If you set Execute the initial mirror construction to Off, construction is not started automatically; use Mirror Disks or either of the following commands to start it manually
[For a mirror disk]
clpmdctrl --force copy_source_server_name> <mirror_disk_resource_name>[For a hybrid disk]
clphdctrl --force copy_source_server_name> <hybrid_disk_resource_name> - (B) If the operation is stopped, and the operation is to be started after the completion of disk copy(When performing copy when the group containing the mirror disk resource is deactivated)
[For a mirror disk]
clpmdctrl --force <copy_source_server_name> <mirror_disk_resource_name>[For a hybrid disk]
clphdctrl --force <copy_source_server_name> <hybrid_disk_resource_name>
- If initial mirror construction is started while the operation is stopped (deactivated) (B), you can start the operation (activate the group) after the completion of the initial mirror construction (after the completion of disk copy).If mirror recovery is interrupted, start initial mirror construction without activating the group.
2.11.2. In case of replacing a mirror disk constructed with a number of disks(RAID)¶
Stop the server of which the mirror disks are going to be replaced.
Note
- Before shutting down the server, it is recommended that the steps in "Disabling the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon" in the Installation and Configuration Guide be executed.On the target server, execute the following command to disable the daemon.
clpsvcctrl.sh --disable core mgr If a hybrid disk failure occurs, terminate all servers connected to the disk to be replaced.
Install the new disks in the server.
Start up the server.
Reconstruct the RAID before OS startup.
- Change the setting so that the EXPRESSCLUSTER services will not be executed at OS startup. In case of not having disabled the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon in the step 1, startup the daemons on run level 1 at OS startup, then startup the daemons on run level 3 after disabling the daemons.Back up data from the data partition as required.
If LUN is initialized, use the fdisk command to create cluster and data partitions on a new disk.
Note
If a hybrid disk failure occurs, terminate all servers connected to the disk to be replaced.
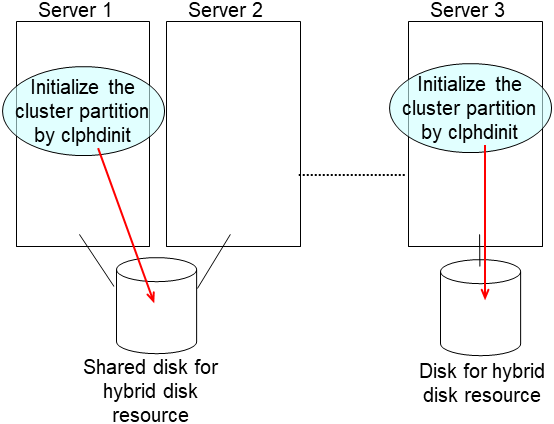
Login as the root and initialize the cluster partition using one of the following methods.
Method (1) Without using the dd command
For the mirror disk
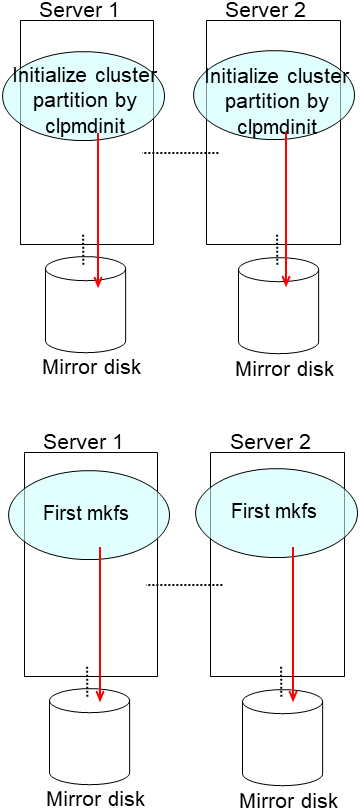
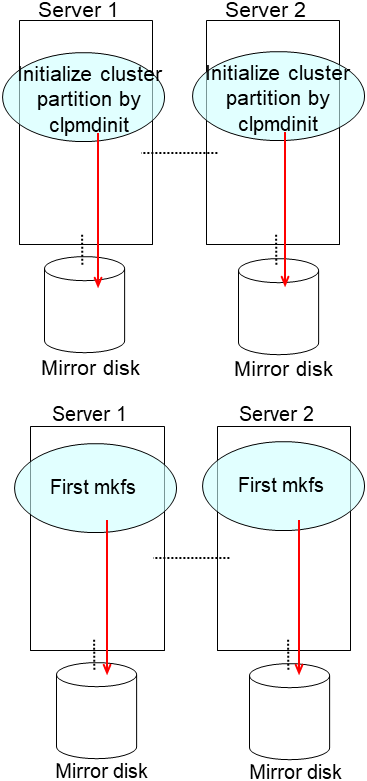
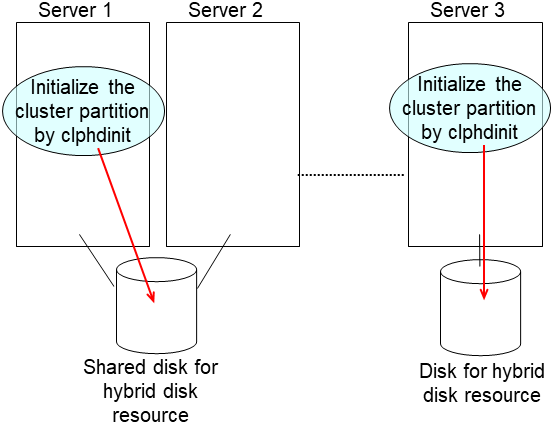
clpmdinit --create force <mirror disk resource name>For the hybrid disk
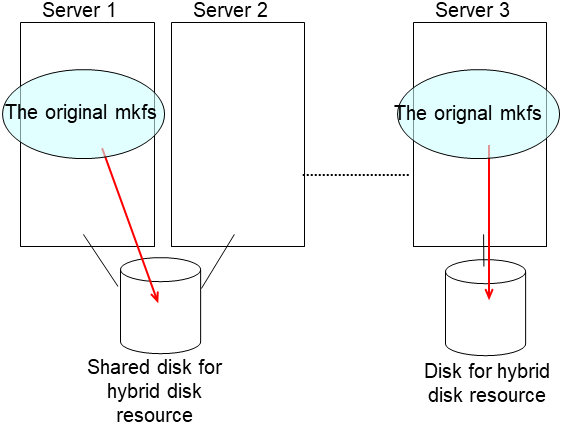
clphdinit --create force <hybrid disk resource name>Note
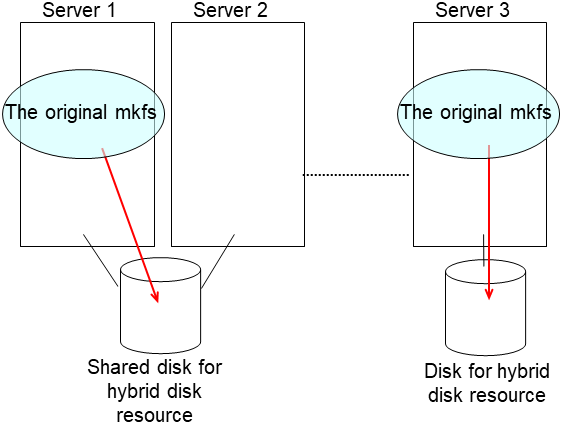
- For the mirror disk, if Execute initial mkfs is set to "on" when the mirror disk resource is set up, mkfs is executed upon execution of this command to initialize the file system.However, mkfs may take a long time to complete in the case of a large-capacity disk. (once mkfs is executed, any data saved in the data partition will be erased. Back up the data in the data partition as required, therefore, before executing this command.)Mirror data is copied from the destination server by means of the entire recovery described later.
If a hybrid disk failure occurs, terminate all servers connected to the disk to be replaced.
Method (2) Using the dd command
For the mirror disk
dd if=/dev/zero of=<cluster partition device name (Example: /dev/sdb1)>clpmdinit --create quick <mirror disk resource name>For the hybrid disk
dd if=/dev/zero of=<cluster partition device name (Example: /dev/sdb1)>clphdinit --create quick <hybrid disk resource name>
Note
When the dd command is executed, data in the partition specified by of= is initialized. Confirm whether the partition device name is correct, and then execute the dd command.
- When the dd command is executed, the following message may appear. This does not, however, indicate an error.dd: writing to <CLUSTER partition device name>: No space left on device
Mirror data is copied from the destination server by means of the entire recovery described later. Back up the data in the data partition as required, therefore, before executing this command.
If a hybrid disk failure occurs, terminate all servers connected to the disk to be replaced.
Prevent initial mirror construction from being performed automatically.
(A) In the state in which the operation is being performed on the server on which a mirror disk is not replaced (state in which the group containing mirror disk resources is active), you want to concurrently perform disk copy (initial mirror construction), there is no particular need to make sure that initial mirror construction is not automatically performed.
(B) If the operation could be stopped until disk copy is completed (the group may be deactivated), deactivate the group containing the mirror disk resource.
Note
- With procedure (A), copy is performed by the amount equal to that of disk space used, depending on the type of file system, so the copy time may depend on the amount of disk space used.Also, because the operation and copy are performed concurrently, the load may become high and copy may take time depending on the case.
With procedure (B) whereby disk copy is performed while the operation is stopped (the group is deactivated), copy is performed by the amount equal to that of disk space used, depending on the file system, so the copy time may depend on the amount of disk space used. The start of the operation (group activation) can be performed after the completion of copy.
On a server on which a disk has been replaced, enable the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon, and then restart the server.
Note
- In the case that the steps in "Disabling the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon" in the "Installation and Configuration Guide" were executed before shutting down the server, enable the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemons at this time.On the target server, execute the following command to enable the daemon.
clpsvcctrl.sh --enable core mgr
Use the following command to start the initial mirror construction (disk copy).
(A) When performing an operation on a server on which the mirror disk has not been replaced
The initial mirror construction (disk copy) is automatically started.If you set Execute the initial mirror construction to Off, construction is not started automatically; use Mirror Disks or either of the following commands to start it manually[For a mirror disk]
clpmdctrl --force <copy_source_server_name> <mirror_disk_resource_name>[For a hybrid disk]
clphdctrl --force <copy_source_server_name> <hybrid_disk_resource_name>- (B) If the operation is stopped, and is to be started after disk copy has been completed(When performing copy in the state in which the group containing the mirror disk resource is deactivated)
[For a mirror disk]
clpmdctrl --force <copy_source_server_name> <mirror_disk_resource_name>[For a hybrid disk]
clphdctrl --force <copy_source_server_name> <hybrid_disk_resource_name>
- If initial mirror construction is started while the operation is stopped (deactivated) (B), you can start the operation (activate the group) after the completion of the initial mirror construction (after the completion of disk copy).If mirror recovery is interrupted, start the initial mirror construction without activating the group.
2.11.3. In case of replacing mirror disks of both servers¶
Note
The data of mirror disks are lost after replacing the mirror disks of both servers. Restore the data from backup data or other media as necessary after replacing the disks.
Stop the both servers.
Note
- Before shutting down both servers, it is recommended that the steps in "Disabling the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon" in the Installation and Configuration Guide are executed.On the target server, execute the following command to disable the daemon.
clpsvcctrl.sh --disable core mgr
Install the new disks in both servers.
Startup both servers. At this time, change the setting so that the EXPRESSCLUSTER services will not be executed. In case of not having disabled the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon in the step 1, the daemons start up on run level 1 at OS startup.
Construct the same partition as the original disk to the new disks of both servers by fdisk command.
Note
To replace shared storage with the hybrid disk, create a partition and a file system with any server connected to that shared storage.
Initialize the cluster partition when using the disk used as an EXPRESSCLUSTER mirror disk or hybid disk with data discarded. If required, initialize the file system of the data partition.
For more information on initializing the cluster partition (CLUSTER partition) and on creating a file system and whether to create one or not, see the related items ("Shared disk settings for Hybrid disk resource (Required for Replicator DR)", "Partition settings for Hybrid disk resource (Required for the Replicator DR)", and "Partition settings for Mirror disk resource (when using Replicator)") in "Settings after configuring hardware" in "Determining a system configuration" in the Installation and Configuration Guide.
Restart both servers.
Note
- In the case that the steps in "Disabling the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon" in the "Installation and Configuration Guide" were executed before shutting down the server, enable the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemons at this time.On the target server, execute the following command to enable the daemon.
clpsvcctrl.sh --enable core mgr
- The initial mirror construction (entire mirror recovery) starts automatically by restarting.If you set Execute the initial mirror construction to Off, the normal state is assumed directly without automatically starting. Thus, in this case, use the Mirror Disks of Cluster WebUI, clpmdctrl, or the clphdctrl command to manually start full mirror recovery.
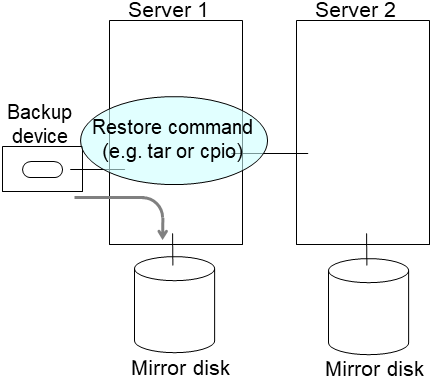
After the completion of full mirror recovery, recover the data from a backup or the like after the completion of full mirror recovery.
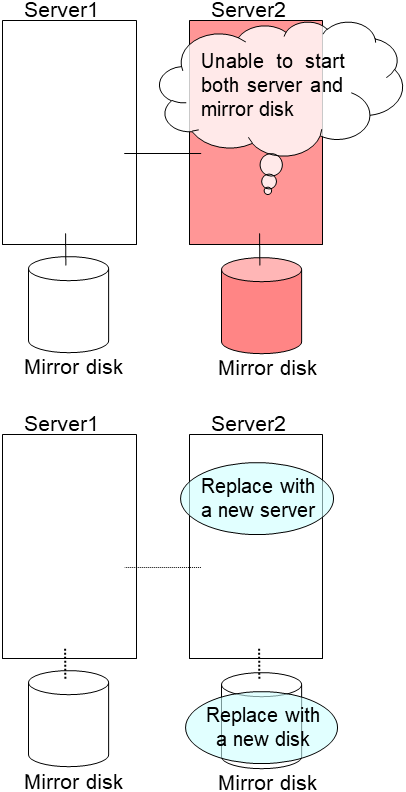
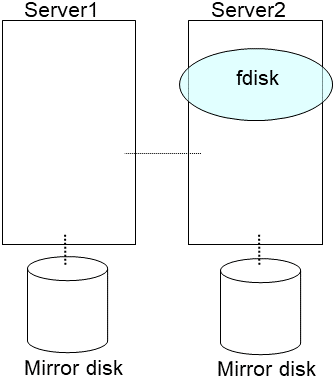
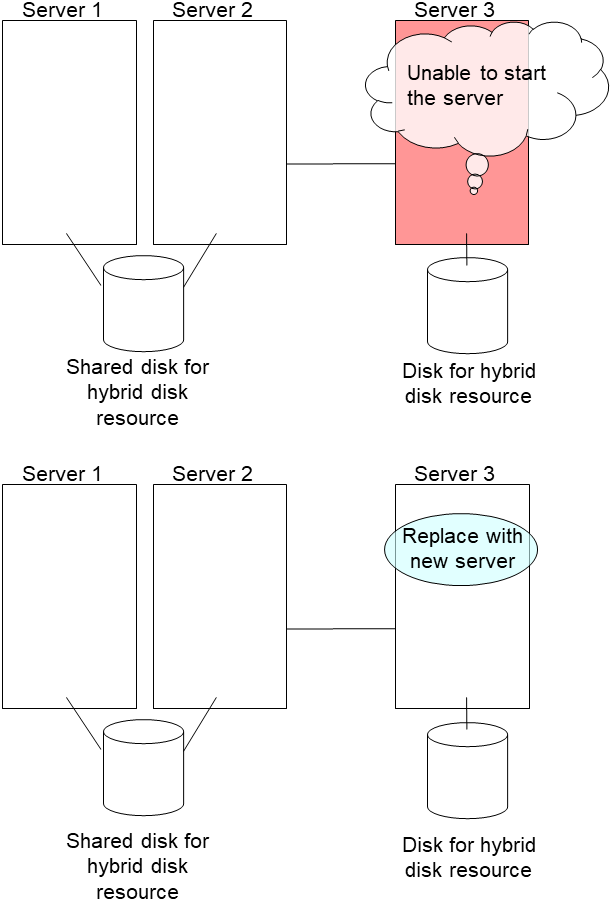
2.13. How to replace a server with a new one ~For a mirror disk~¶
2.13.1. Replacing a server and its mirror disk¶
Connect to the Cluster WebUI with a management IP address. If you do not have any management IP address, connect to it by using the IP address of a server that is not to be replaced.
Replace the failed server machine and the disk. Set the same IP address and host name in the new server as the old server.
- Create partitions in the new disk by executing the fdisk command.Install the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server on the new server. For details, see "Installing EXPRESSCLUSTER" in the Installation and Configuration Guide. The server on which you installed the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server should be restarted after the installation.
When using the disk that was used as a mirror disk before, initialize the cluster partition.
Upload the cluster configuration data in the config mode of Cluster WebUI you connected to. When uploading the data completes, restart the replaced server.
If you use a fixed term license, run the following command:
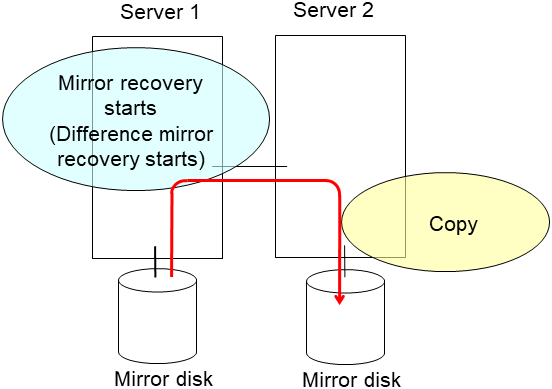
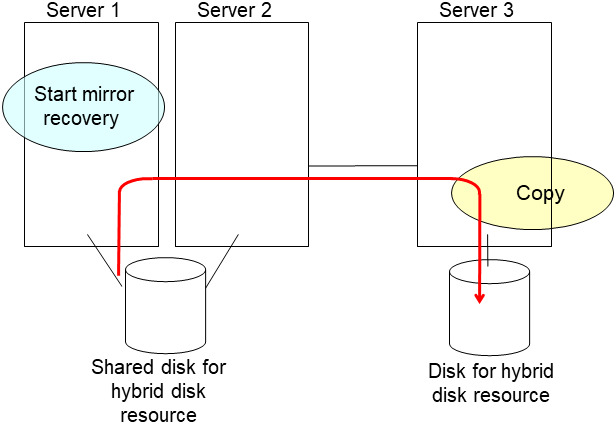
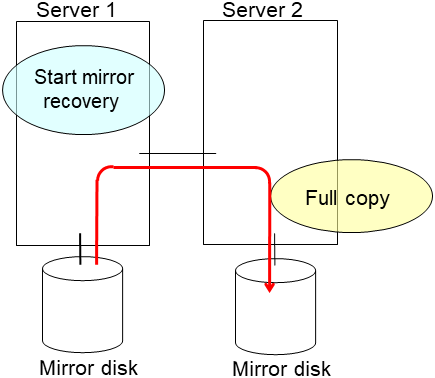
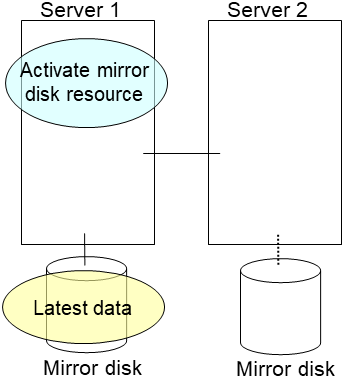
clplcnsc --reregister <a folder path for saved license files>- After the server is restarted, the cluster partitions in the new disk will be initialized and a file system will be created in the data partition.The mirror recovery is executed if the initial mirror construction is set. If not, you have to manually recover mirroring.For information on recovery of disk mirroring, refer to "Recovering mirror with a command" and "Recovering mirror using the Cluster WebUI" of "Troubleshooting" in "Reference Guide"In mirror recovery, the data is fully copied.Confirm that mirroring is successfully recovered by using the WebManager or by running the following command. For details, see "Mirror-related commands" in "EXPRESSCLUSTER command reference" in the "Reference Guide".
clpmdstat --mirror <mirror_disk_resource_name (Example: md1)>
2.13.2. Using the mirror disk of the failed server¶
Connect to the Cluster WebUI with a management IP address. If you do not have any management IP address, connect to it by using the IP address of a server that is not to be replaced.
Replace the failed server machine but continue using the mirror disk of the failed server. Set the same IP address and host name in the new server as before.
Install the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server on the new server. For details, see "Installing EXPRESSCLUSTER" in the "Installation and Configuration Guide". Restart the server on which the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server was installed.
Upload the cluster configuration data in the config mode of Cluster WebUI you connected to. When uploading the data completes, restart the replaced server.
If you use a fixed term license, run the following command:
clplcnsc --reregister <a folder path for saved license files>- If there is no difference in mirror disks, you can immediately start the operation after restarting the server. On the other hand, if there is any difference in mirror disks, you have to recover the mirroring data after restarting the server.The disk mirroring is automatically recovered when auto-mirror recovery is enabled. If not, you have to manually recover disk mirroring. For information on recovery of disk mirroring, refer to "Recovering mirror with a command" and "Recovering mirror using the Cluster WebUI" of "Troubleshooting" in "Reference Guide".Confirm that mirroring is successfully recovered by using the Cluster WebUI or by running the following command. For details, see "Mirror-related commands" in "EXPRESSCLUSTER command reference" in the "Reference Guide".
clpmdstat --mirror <mirror_disk_resource_name (Example: md1)>
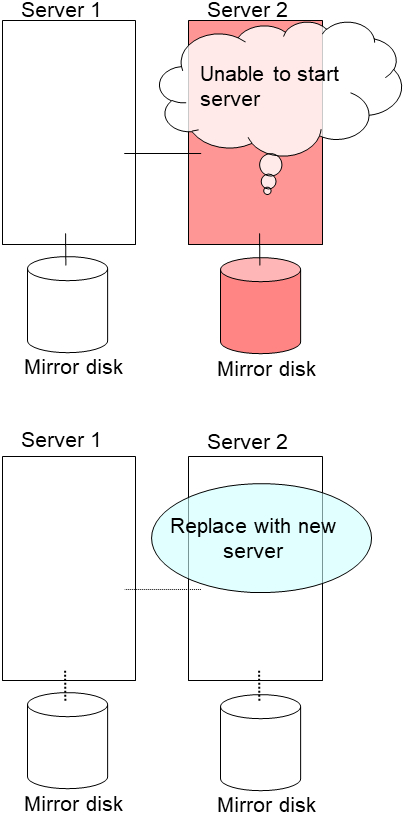
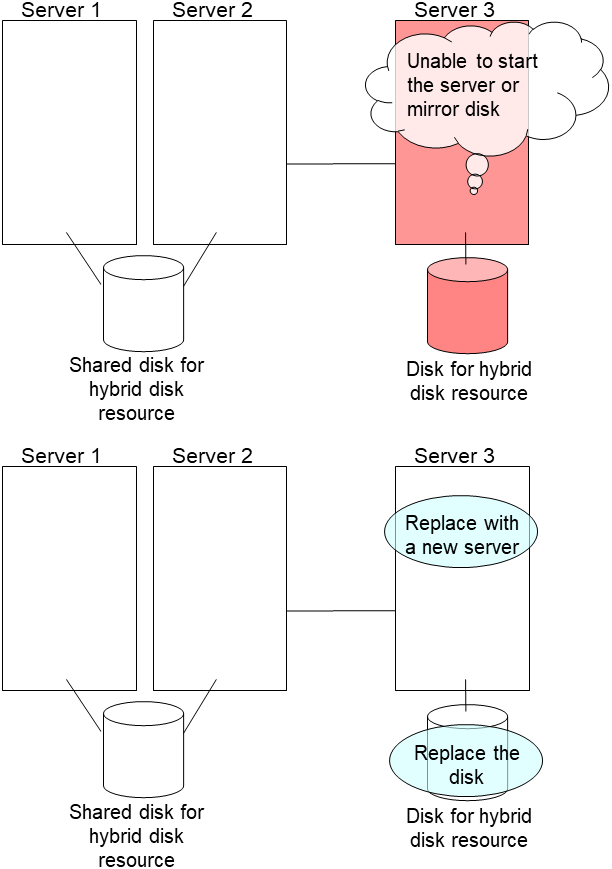
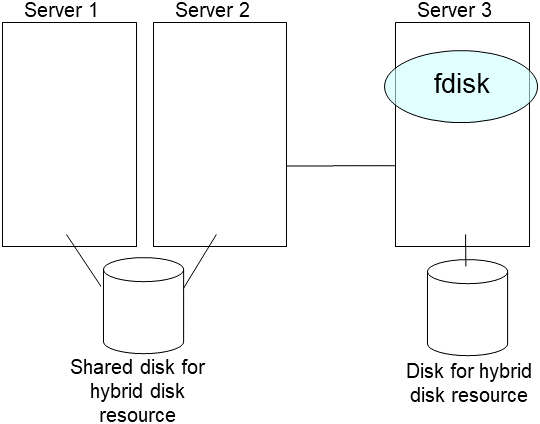
2.14. How to replace a server with a new one ~For a hybrid disk~¶
2.14.3. Using the disk of the failed server¶
Connect to the Cluster WebUI with a management IP address. If you do not have any management IP address, connect to it by using the IP address of a server that is not to be replaced.
Replace the failed server machine but continue using the disk of the failed server. Set the same IP address and host name in the new server as before.
Install the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server on the new server. For details, see "Installing EXPRESSCLUSTER" in the Installation and Configuration Guide. Restart the server on which the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server was installed.
Upload the cluster configuration data in the config mode of Cluster WebUI you connected to. When uploading the data completes, restart the replaced server.
If you use a fixed term license, run the following command:
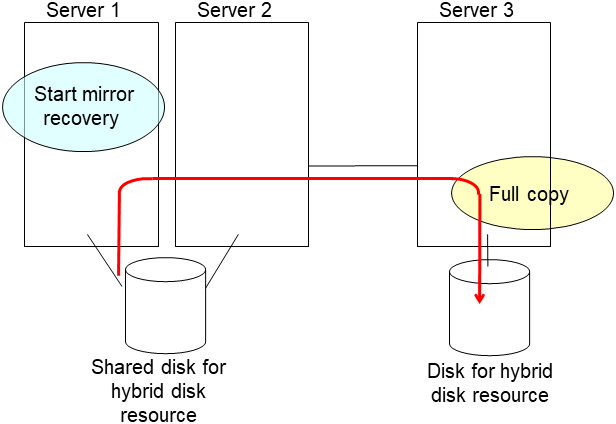
clplcnsc --reregister <a folder path for saved license files>- If there is no difference in mirror disks, you can immediately start the operation after restarting the server. On the other hand, if there is any difference in mirror disks, you have to recover the mirroring data after restarting the server.The disk mirroring is automatically recovered when auto-mirror recovery is enabled. If not, you have to manually recover disk mirroring. For information on recovery of disk mirroring, refer to "Recovering mirror with a command" and "Recovering mirror using the Cluster WebUI" of "Troubleshooting" in "Reference Guide".Confirm that mirroring is successfully recovered by using the Cluster WebUI or by running the following command. For details, see "Hybrid-disk-related commands" in "EXPRESSCLUSTER command reference" in the "Reference Guide".
clpmdstat --mirror <hybrid_disk_resource_name (Example: hd1)>
2.15. Wait time for synchronized cluster startup¶
Even all servers in a cluster are powered on simultaneously, it does not always mean that EXPRESSCLUSTER will start up simultaneously on all servers. EXPRESSCLUSTER may not start up simultaneously after rebooting the cluster following shutdown. Because of this, with EXPRESSCLUSTER, if one server is started, it waits for other servers in the cluster to start.
By default, 5 minutes is set to the startup synchronization time. To change the default value, click Cluster Properties in the Cluster WebUI, click Timeout tab, and select Synchronize Wait Time.
For more information, see "Cluster properties Timeout tab" in "Parameter details" in the "Reference Guide".
2.16. Changing disk resources file system¶
Connect to the Cluster WebUI with a management IP address. If you do not have any management IP address, connect to it by using the actual IP address of any server.
To change the disk resource file system, follow the steps below:
In the operation mode of Cluster WebUI, click Stop Cluster.
- Run the following command.For example, when the disk resources partition device is /dev/sdb5:
# clproset -w -d /dev/sdb5This makes disk partition of disk resources readable/writable regardless of the EXPRESSCLUSTER behavior.Note
Do not use this command for any other purposes.If you use this command when the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon is active, the file system may be corrupted. Create the file system in the partition device.
- Run the following command to set the disk resources partition to ReadOnly.For example, when the disk resources partition device is /dev/sdb5:
# clproset -o -d /dev/sdb5 Change the configuration data of disk resource file system in the config mode of Cluster WebUI.
Upload the cluster configuration data in the config mode of Cluster WebUI.
In the operation mode of Cluster WebUI, click Start Cluster.
The settings reflecting the changes become effective.
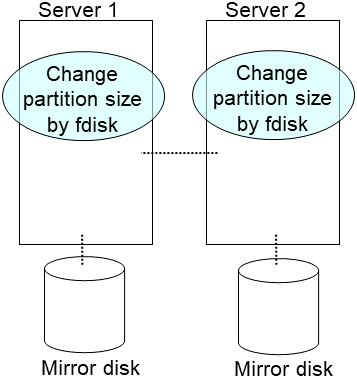
2.17. Changing offset or size of a partition on mirror disk resource¶
Follow the procedure below when changing the offset (location) or size of the data partition or cluster partition configured on a mirror disk resource after the operation of a cluster is started.
Note
Be sure to follow the steps below to change them. Mirror disk resources may not function properly if you change the partition specified as a data partition or cluster partition only by fdisk.
2.17.1. Data partition configured with LVM¶
If LVM is used for partitioning, you can extend data partition without re-creating resources or stopping your business (depending on the file system used).
File system of data partition |
Resource re-creation |
Business down |
Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
xfs, No file system |
Not required |
Not required |
2.17.1.1. Data partition extension for xfs or no file system used |
ext2, ext3, ext4 |
Not required |
Required |
2.17.1.2. Data partition extension for ext2, ext3 or ext4 file system |
Other than above |
Required |
Required |
Note
This method is intended for only extension. To shrink partitions, refer to "2.17.2. Data partition configured with other than LVM".
Note
If you follow the instruction below to extend data partition, LVM must be used for the data partition and unused PE (physical extents) of the volume group are sufficient.
2.17.1.1. Data partition extension for xfs or no file system used¶
Confirm the mirror disk resource name you want to resize by [clpstat] command or Cluster WebUI.
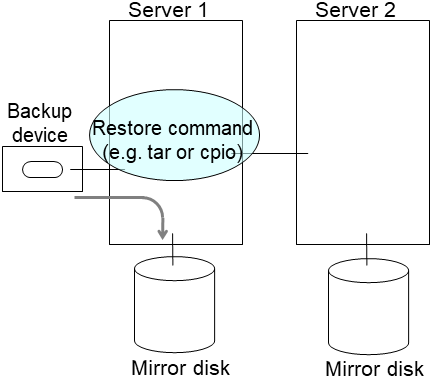
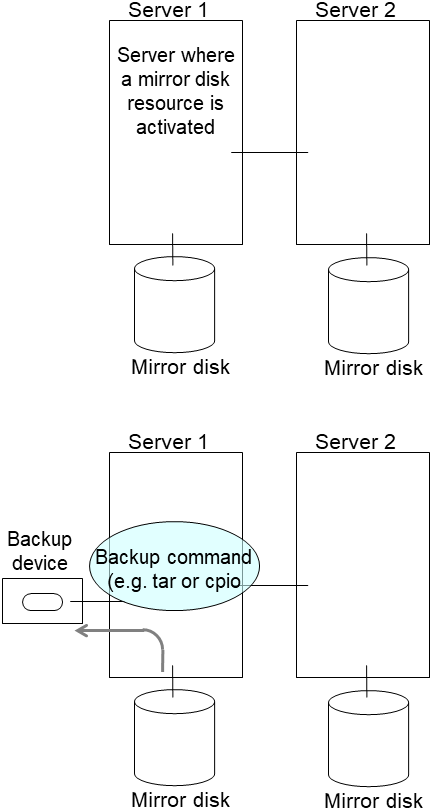
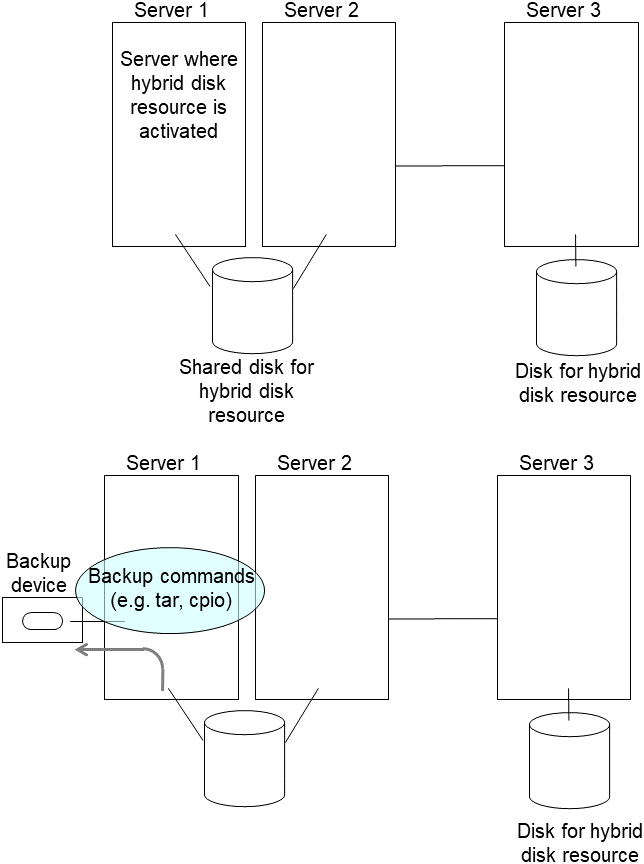
For unexpected events, back up partition data in a server where an active group has mirror disk resources you want to resize (use a backup device such as tape device). Note that backup commands to access partition device directly is not supported. Ignore this step if you can discard the data on mirror disk resources.
Confirm the followings:
Mirror disk resource status is normal.
On both servers, unused PE (physical extents) of the volume group that data partition belongs to are sufficient.
Configure mirror disk not to be recovered automatically. Refer to either of the followings:
Change mirror agent settings to disable automatic mirror disk recovery.
Stop mirror disk monitor resources temporarily.
To change mirror agent settings, refer to "Reference Guide" > "Parameter details" > "Cluster properties" > "Mirror Agent tab".
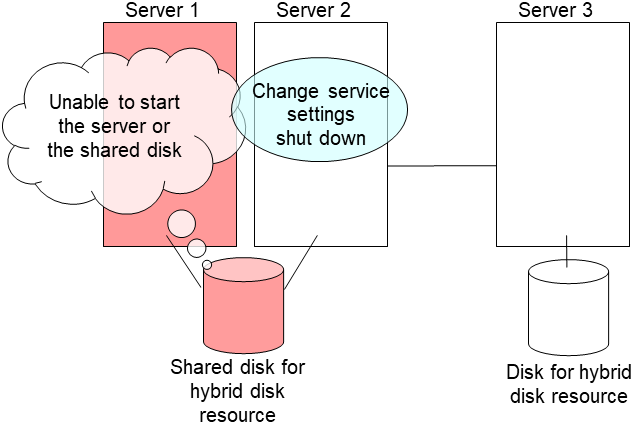
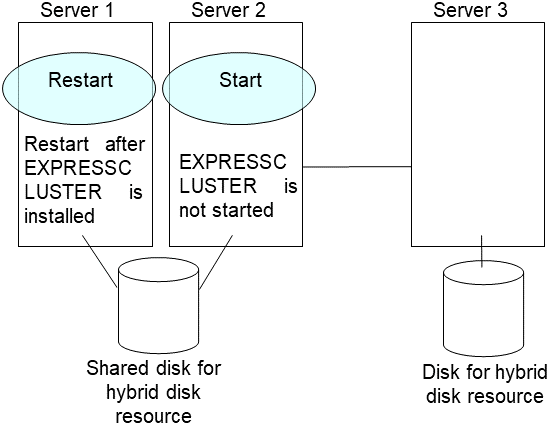
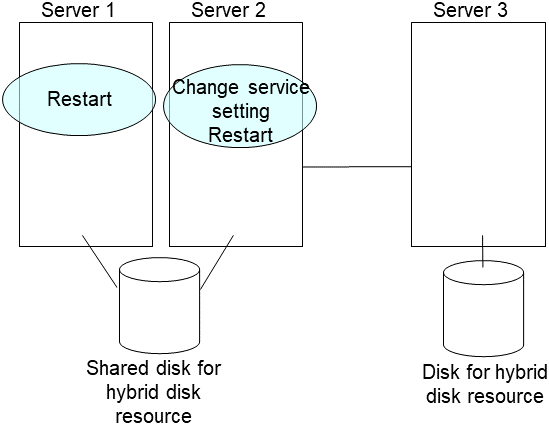
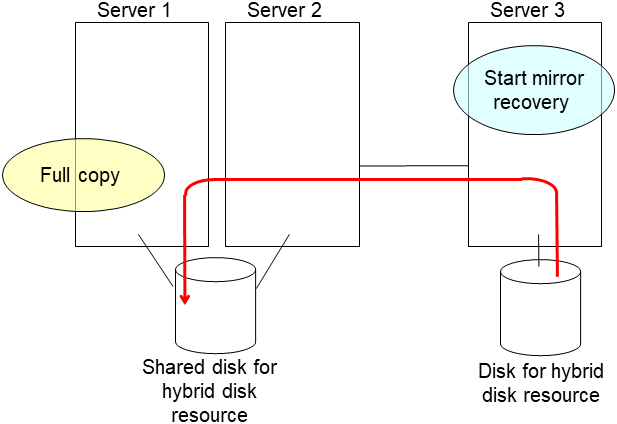
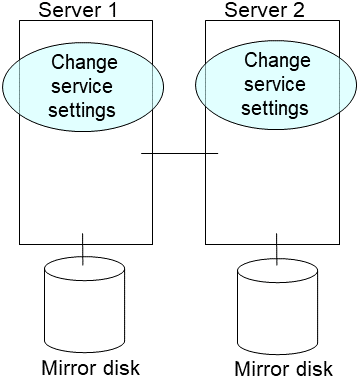
5. Run the [clpmdctrl] command on the server an inactive mirror disk resource belongs to. The following example is to extend to 500 gibibytes for a md01 data partition.
# clpmdctrl --resize 500G md01
Run the [clpmdctrl] command on the other server. The following example is to extend to 500 gibibytes for a md01 data partition.
# clpmdctrl --resize 500G md01If you configure xfs file system on the data partition, run the [xfs_growfs] command on the server where mirror disk resources are active to extend file system area.
# xfs_growfs /mnt/nmp1Change /mnt/nmp1 as necessary depending on the mirror disk resources mount point.)If you have not configured any file system on the data partition, ignore this step.
Restore the automatic mirror disk recovery settings changed in step 4 if required.
Important
# clpmdctrl --resize -force 500G md01
Note
# clpmdctrl --resize 1022M md01 is specified, the data partition size becomes 1024M and the file system extension limit becomes 1022M.Note
2.17.1.2. Data partition extension for ext2, ext3 or ext4 file system¶
Confirm the mirror disk resource name you want to resize by [clpstat] command or Cluster WebUI.
For unexpected events, back up partition data in a server where an active group has mirror disk resources you want to resize (use a backup device such as tape device). Note that backup commands to access partition device directly is not supported. Ignore this step if you can discard the data on mirror disk resources.
Confirm the followings:
Mirror disk resource status is normal.
On both servers, unused PE (physical extents) of the volume group that data partition belongs to are sufficient.
Configure mirror disk not to be recovered automatically. Refer to either of the followings:
Change mirror agent settings to disable automatic mirror disk recovery.
Stop mirror disk monitor resources temporarily.
To change mirror agent settings, refer to "Reference Guide" > "Parameter details" > "Cluster properties" > "Mirror Agent tab".
Stop a failover group that includes target mirror disk resources.
Run the [clpmdctrl] command to disable access-limit to mirror disk resources with no-mount.
# clpmdctrl --active -nomount md01Run the [clpmdctrl] command on the other server (access-limit is effective). The following example is to extend to 500 gibibytes for a md01 data partition.
# clpmdctrl --resize 500G md01Run the [clpmdctrl] command on the server (access-limit is disabled). The following example is to extend to 500 gibibytes for a md01 data partition.
# clpmdctrl --resize 500G md01Run [e2fsck] to check and repair the file system.
# e2fsck -f /dev/NMP1(Change NMP1 according to your mirror partition device name.)Run the [resize2fs] command on the server (access-limit is disabled) to expand the file system area.
# resize2fs -p /dev/NMP1(Change NMP1 according to your mirror partition device name.)Run the [clpmdctrl] command to enable access-limit again.
# clpmdctrl --deactive md01Resume the failover group which was stopped in step 5.
Restore the automatic mirror disk recovery settings changed in step 4 if required.
Important
# clpmdctrl --resize -force 500G md01
Note
# clpmdctrl --resize 1022M md01 is specified, the data partition size becomes 1024M and the file system extension limit becomes 1022M.2.17.1.3. Data partition extension for other file systems¶
The basic procedure is the same as "2.17.2. Data partition configured with other than LVM".
Note: Use the [lvextend] command instead of [fdisk] to resize partition size.
2.17.2. Data partition configured with other than LVM¶
2.17.2.1. When not changing a device name of a partition on mirror disk resource¶
Check the name of a mirror disk resource whose size you want to change by the clpstat command or by the Cluster WebUI.
- On the server where a group with a mirror disk resource whose size you want to change is activated, back up the data in a partition to a device such as tape. Note that backup commands that access a partition device directly are not supported.This step is not required if there is no problem to discard the data on a mirror disk resource.
Set the EXPRESSCLUSTER service not to start.
clpsvcctrl.sh --disable core- Shut down a cluster, and then restart the OS.To shut down a cluster, run the clpstdn command on either of a server, or execute a cluster shutdown on the Cluster WebUI.
On both servers, run the fdisk command to change the offset or size of a partition.
Run the following command on both servers.
# clpmdinit --create force <Mirror_disk_resource_name>Note
When you set Execute initial mkfs to off in the mirror disk resource setting, mkfs will not be executed automatically. Please execute mkfs manually to the data partition of mirror disk resource.
Set the EXPRESSCLUSTER service to start.
clpsvcctrl.sh --enable coreRun the reboot command to restart both servers. The servers are started as a cluster.
After a cluster is started, the same process as the initial mirror construction at cluster creation is performed. Run the following command or use the Cluster WebUI to check if the initial mirror construction is completed.
# clpmdstat --mirror <Mirror_disk_resource_name>When the initial mirror construction is completed and a failover group starts, a mirror disk resource becomes active.
- On the server where a group with a mirror partition whose size you changed is activated, restore the data you backed up. Note that backup commands that access a partition device directly are not supported.This step is not required if there is no problem to discard the data on a mirror disk resource.
2.17.2.2. When changing a device name of a partition on mirror disk resource¶
Check the name of a mirror disk resource whose size you want to change by the clpstat command or by the Cluster WebUI.
- On the server where a group with a mirror disk resource whose size you want to change is activated, back up the data in a partition to a device such as tape. Note that backup commands that access a partition device directly are not supported.This step is not required if destroying the data on a mirror disk resource does not cause any problem.
Set the EXPRESSCLUSTER service not to start.
clpsvcctrl.sh --disable core- Shut down a cluster, and then restart the OS.To shut down a cluster, run the clpstdn command on either of a server, or execute a cluster shutdown on the WebManager.
On both servers, run the fdisk command to change the offset or size of a partition.
Change and upload the cluster configuration data. Change a mirror disk resource as described in "Modifying the cluster configuration data by using the Cluster WebUI" in "Modifying the cluster configuration data" in the "Installation and Configuration Guide".
Run the following command on the both servers.
# clpmdinit --create force <Mirror_disk_rseource_name>Note
When you set Execute initial mkfs to off in the mirror disk resource setting, mkfs will not be executed automatically. Please execute mkfs manually to the data partition of mirror disk resource.
Set the EXPRESSCLUSTER service to start.
clpsvcctrl.sh --enable coreRun the reboot command to restart both servers. The servers are started as a cluster.
After a cluster is started, the same process as the initial mirror construction at cluster creation is performed. Run the following command or use the Cluster WebUI to check if the initial mirror construction is completed.
# clpmdstat --mirror <Mirror_disk_resource_name>When the initial mirror construction is completed and a failover group starts, a mirror disk resource becomes active.
- On the server where a group with a mirror partition whose size you changed is activated, restore the data you backed up. Note that backup commands that access a partition device directly are not supported.This step is not required if there is no problem to discard the data on a mirror disk resource.
2.18. Changing offset or size of a partition on hybrid disk resource¶
Follow the procedure below when changing the offset (location) or size of the data partition or cluster partition configured on a hybrid disk resource after the operation of a cluster is started.
Note
Be sure to follow the steps below to change them. Hybrid disk resources may not function properly if you change the partition specified as a data partition or cluster partition only by fdisk.
2.18.1. When not changing a device name of a partition on hybrid disk resource¶
Check the name of a hybrid disk resource whose size you want to change by the clpstat command or by the Cluster WebUI.
- On the server where a group with the hybrid disk resource whose size you want to change is activated, back up the data in a partition to a device such as tape. Note that backup commands that access a partition device directly are not supported.This step is not required if there is no problem to discard the data on the hybrid disk resource.
Set the EXPRESSCLUSTER service not to start.
clpsvcctrl.sh --disable core- Shut down a cluster, and then restart the OS.To shut down a cluster, run the clpstdn command on either of a server, or execute a cluster shutdown on the Cluster WebUI.
Run the fdisk command on a server to change the offset or size of a partition. When servers are connected to the shared disk, run the fdisk from either of the servers for the change.
- Run the following command on a server. When servers are connected to the shared disk, run the command on the server where the command in previous step was executed.
# clpmdinit --create force <Mirror_disk_resource_name> - Run the following command on a server.When servers are connected to the shared disk, run the command on the server where the command in previous step was executed.
# mkfs -t <Type of Filesystem> <Data Partition> Set the EXPRESSCLUSTER service to start.
clpsvcctrl.sh --enable coreRun the reboot command to restart all servers. The servers are started as a cluster.
After the cluster is started, the same process as the initial mirror construction at cluster creation is performed. Run the following command or use the Cluster WebUI to check if the initial mirror construction is completed.
# clphdstat --mirror <hybrid_disk_resource_name>When the initial mirror construction is completed and a failover group starts, a hybrid disk resource becomes active.
- On the server where a group with the partition whose size you changed is activated, restore the data you backed up. Note that backup commands that access a partition device directly are not supported.This step is not required if there is no problem to discard the data on a hybrid disk resource.
2.18.2. When changing a device name of a partition on hybrid resource¶
Check the name of a hybrid disk resource whose size you want to change by the clpstat command or by the Cluster WebUI.
- On the server where a group with the hybrid disk resource whose size you want to change is activated, back up the data in a partition to a device such as tape. Note that backup commands that access a partition device directly are not supported.This step is not required if destroying the data on the hybrid disk resource does not cause any problem.
Set the EXPRESSCLUSTER service not to start.
clpsvcctrl.sh --disable core- Shut down a cluster, and then restart the OS.To shut down a cluster, run the clpstdn command on either of a server, or execute a cluster shutdown on the Cluster WebUI.
On a server, run the fdisk command to change the offset or size of a partition. When servers are connected to the shared disk, run the fdisk command from either of servers to change.
Change and upload the cluster configuration data. Change a hybrid disk resource as described in "Modifying the cluster configuration data by using the Cluster WebUI" in "Modifying the cluster configuration data" in the "Installation and Configuration Guide".
Run the following command on the server. When servers are connected to the shared disk, execute the command on the server where the command was executed in step 5.
# clphdinit --create force <Hybrid_disk_reseource_name>- Run the following command on the server.When servers are connected to the shared disk, run the command on the server where the command in previous step was executed.
# mkfs -t <Type of Filesystem> <Data Partition> Set the EXPRESSCLUSTER service to start.
clpsvcctrl.sh --enable coreRun the reboot command to restart all servers. The servers are started as a cluster.
After the cluster is started, the same process as the initial mirror construction at cluster creation is performed. Run the following command or use the Cluster WebUI to check if the initial mirror construction is completed.
# clphdstat --mirror <Hybrid_disk_resource_name>When the initial mirror construction is completed and a failover group starts, a hybrid disk resource becomes active.
- On the server where a group with the partition whose size you changed is activated, restore the data you backed up. Note that backup commands that access a partition device directly are not supported.This step is not required if there is no problem to discard the data on the hybrid disk resource.
2.19. Changing the server configuration (add/delete)¶
2.19.1. Adding a server (mirror disk or hybrid disk is not used)¶
To add a server, follow the steps below:
Important
When adding a server in changing the cluster configuration, do not make any other changes such as adding a group resource.
Make sure that the cluster is working normally.
Install the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server on a new server. For details, see "Setting up the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server Installing the EXPRESSCLUSTER RPM" in "Installing EXPRESSCLUSTER" in the "Installation and Configuration Guide". Restart the server on which the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server was installed.
Access the other server in the cluster with a Web browser and click Add server in the Cluster WebUI config mode.
By using the config mode of Cluster WebUI, configure the following settings of theAdd server.
Information on the Source IP Address of the server to add on the Details tab of Properties of the virtual IP resource (when using the virtual IP resource).
Information on the ENI ID of the server to add on the Details tab of Properties of the AWS elastic IP resources (when using an AWS Elastic IP resource).
Information on the ENI ID of the server to add on the Details tab of Properties of the AWS virtual IP resources (when using an AWS virtual IP resource).
Information on the IP Address of the server to add on the Details tab of Properties of the Azure DNS resources (when using an Azure DNS resource).
Click Apply the Configuration File in the config mode of Cluster WebUI to apply the cluster configuration information on the cluster.
Note: Apply the configuration when the confirmation message is displayed.
Perform Start server service of the server added from the Cluster WebUI config mode.
Click Refresh data in the operation mode of Cluster WebUI to verify the cluster is properly working.
2.19.2. Adding a server (Mirror disk or hybrid disk is used)¶
To add a server, follow the steps below:
Important
When adding a server in changing the cluster configuration, do not make any other changes such as adding a group resource.
- The additional server license must be registered.To register licenses, refer to "Installation and Configuration Guide" > "Registering the license".
Make sure that the cluster is working normally.
Install the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server on a new server. For details, see "Setting up the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server Installing the EXPRESSCLUSTER RPM" in "Installing EXPRESSCLUSTER" in the "Installation and Configuration Guide". Restart the server on which the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server was installed.
In the operation mode of Cluster WebUI, click Stop cluster.
Perform Stop Mirror Agent in the Cluster WebUI operation mode.
Access to other server in the cluster via the Web browser and click the server to add in the config mode of Cluster WebUI.
By using the config mode of Cluster WebUI, configure the following settings of theAdd server.
Information on the Source IP Address of the server to add on the Details tab of Properties of the virtual IP resource (when using the virtual IP resource).
Information on the ENI ID of the server to add on the Details tab of Properties of the AWS elastic IP resources (when using an AWS Elastic IP resource).
Information on the ENI ID of the server to add on the Details tab of Properties of the AWS virtual IP resources (when using an AWS virtual IP resource).
Information on the IP Address of the server to add on the Details tab of Properties of the Azure DNS resources (when using an Azure DNS resource).
When using a hybrid disk resource in the added server, click Properties of Servers in the Conf mode of Cluster WebUI. From the Server Group tab, add the server to the servers that can run the Group. Do this for required servers only.
Click Apply the Configuration File in the config mode of Cluster WebUI to apply the cluster configuration information on the cluster. Select OK when the service restart dialog appears.
Perform Start Mirror Agent in the Cluster WebUI operation mode.
In the operation mode of Cluster WebUI, click Start cluster.
Click Refresh data in the operation mode of Cluster WebUI to verify the cluster is properly working.
2.19.3. Deleting a server (Mirror disk or hybrid disk is not used)¶
To delete a server, follow the steps below:
Important
When adding a server in changing the cluster configuration, do not make any other changes such as adding a group resource.
Refer to the following information for licenses registered in the server you want to delete.
No action required for CPU licenses.
No action required for fixed term licenses. Unused licenses are automatically collected and provided to other servers.
Make sure that the cluster is working normally. If any group is active on the server you are going to delete, move the group to another server.
When the server to be deleted is registered in a server group, click Properties of Server of the config mode of Cluster WebUI. Delete the server from Servers that can run the Group in the Server Group tab.
Click Remove Server of the server to delete in the config mode of Cluster WebUI.
Click Apply the Configuration File in the config mode of Cluster WebUI to apply the cluster configuration information on the cluster**.
Note: Apply the configuration when the confirmation message is displayed.
Click Refresh data in the operation mode of Cluster WebUI to verify the cluster is properly working.
- Deleted servers will not belong to clusters. To uninstall EXPRESSCLUSTER servers, refer to "Installation and Configuration Guide" > "Uninstalling and reinstalling EXPRESSCLUSTER" > "Uninstallation" > " Uninstalling the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server".Note: In the uninstallation reference, assume server rebooting as OS rebooting in the deleted server.
2.19.4. Deleting a server (Mirror disk or hybrid disk is used)¶
To delete a server, follow the steps below:
Important
When adding a server in changing the cluster configuration, do not make any other changes such as adding a group resource.
Refer to the following information for licenses registered in the server you want to delete.
No action required for CPU licenses.
- VM node licenses and other node licenses are discarded when EXPRESSCLUSTER is uninstalled.Back up the serial numbers and keys of licenses if required.
No action required for fixed term licenses. Unused licenses are automatically collected and provided to other servers.
Make sure that the cluster is working normally. If any group is active on the server you are going to delete, move the group to another server.
In the operation mode of Cluster WebUI, click Stop cluster.
Perform Stop Mirror Agent in the Cluster WebUI operation mode.
Click Remove resource of mirror disk resources or hybrid disk resources in the Cluster WebUI config mode.
When the server to be deleted is registered in a server group, click Properties of Server of the config mode of Cluster WebUI. Delete the server from Servers that can run the Group in the Server Group tab.
Click Remove Server of the server to delete in the config mode of Cluster WebUI.
Click Apply the Configuration File in the config mode of Cluster WebUI to apply the cluster configuration information on the cluster**.
In the operation mode of Cluster WebUI, click Start Mirror Agent (if Mirror Agent is stopped) and then Start Cluster. Perform Start Mirror Agent and Start cluster in the Cluster WebUI operation mode.
Click Refresh data in the operation mode of Cluster WebUI to verify the cluster is properly working.
- Deleted servers will not belong to clusters. To uninstall EXPRESSCLUSTER servers, refer to "Installation and Configuration Guide" > "Uninstalling and reinstalling EXPRESSCLUSTER" > "Uninstallation" > "Uninstalling the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server".Note: In the uninstallation reference, assume server rebooting as OS rebooting in the deleted server.
2.20. Changing the server IP address¶
To change the server IP address after you have started the cluster system operation, follow the instructions below.
2.20.1. Changing the interconnect IP address / mirror disk connect IP address¶
Use the clpstat command or the Cluster WebUI to verify all servers in the cluster are working normally.
- Back up the cluster configuration data. Use the clpcfctrl command to back up the data.If you have the configuration data that contains the data at the cluster creation, use that configuration data.
In the config mode of Cluster WebUI, change the server IP address based on the back up cluster configuration data, and then save it.
Disable the startup settings of the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon in all servers in the cluster. For more information, see "Suspending EXPRESSCLUSTER Disabling the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon" in "Preparing to operate a cluster system" in the Installation and Configuration Guide.
By the clpstdn command or in the operation mode of Cluster WebUI, to shut down the cluster, and then restart all servers.
Change the IP address. If a server reboot is required after changing the IP address, run the reboot command or use other means on the server where the IP address has changed.
Verify the changed IP address is valid by running the ping command or using other means.
Distribute the cluster configuration data to all the servers. Use the clpcfctrl command to deliver the data.
Enable the startup settings of the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon in all servers in the cluster.
Run the reboot command or use other means on all servers in the cluster to reboot them.
Use the clpstat command or the Cluster WebUI to verify all servers in the cluster are working normally.
2.20.2. Changing only the subnet mask of the interconnect IP address¶
Use the clpstat command or the Cluster WebUI to verify all servers in the cluster are working normally.
- Back up the cluster configuration data. Use the clpcfctrl command to back up the data.If you have the configuration data that contains the data at the cluster creation, use that configuration data.
In the config mode of Cluster WebUI, change the server IP address based on the back up cluster configuration data, and then save it.
Disable startup settings of the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon in all servers in the cluster.
By the clpstdn command or in the operation mode of Cluster WebUI, to shut down the cluster, and then restart all servers.
Change the subnet mask of the IP address. If server reboot is required after changing the subnet mask of IP address, run the reboot command or use other means on the server where the subnet mask of the IP address has been changed.
Verify the changed IP address is valid by running the ping command or using other means.
Distribute the cluster configuration data to all servers. Use the clpcfctrl command to deliver the data.
Enable the startup settings of the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon in all servers in the cluster.
Run the reboot command or use other means on all the servers in the cluster.
Use the clpstat command or the Cluster WebUI to verify all the servers in the cluster are working normally.
2.21. Changing the host name¶
Follow the steps below if you want to change the host name of a server after you have started the cluster system operation.
2.21.1. Changing the host name¶
Use the clpstat command or the Cluster WebUI to verify all the servers in the cluster are working normally.
- Back up the cluster configuration data. Use the clpcfctrl command to back up the data.If you have the configuration data that contains the data at the cluster creation, use that configuration data
In the config mode of Cluster WebUI, change the host name of your target server based on the back up cluster configuration data, and then save it.
Disable the startup settings of the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon in all servers in the cluster. For more information, see "Suspending EXPRESSCLUSTER Disabling the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon" in "Preparing to operate a cluster system" in the "Installation and Configuration Guide".
By the clpstdn command or in the operation mode of Cluster WebUI, to shut down the cluster, and then restart all servers.
Change the host name. If the server needs to be rebooted after changing the host name, run the reboot command or use other means on the server.
Verify the changed host name is valid by running the ping command or using other means.
Distribute the cluster configuration data to all the servers. Use the clpcfctrl command to deliver the data.
Note
Check cluster configuration information before the distribution if required.
Enable the startup settings of the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon in all servers in the cluster.
Run the reboot command or use other means on all the servers in the cluster to reboot them.
Use the clpstat command or the Cluster WebUI to verify all the servers in the cluster are in the normal status.
See also
2.22. How to add a resource without stopping the group¶
You can add, to a group that is already running, a resource that supports dynamic resource addition without stopping the group.
Group resources that currently support dynamic resource addition are as follows:
Group resource name |
Abbreviation |
Supported version |
|---|---|---|
Exec resource |
exec |
4.0.0-1~ |
Disk resource |
disk |
4.0.0-1~ |
Floating IP resource |
fip |
4.0.0-1~ |
Virtual IP resource |
vip |
4.0.0-1~ |
Volume manager resource |
volmgr |
4.0.0-1~ |
See also
Perform the following procedure to dynamically add a resource after starting the operation.
2.22.1. How to dynamically add a resource¶
Confirm that all servers in the cluster are operating normally by running the [clpstat] command or using the Cluster WebUI.
Confirm that all resources in the group to which a resource is added are started normally by running the [clpstat] command or using the Cluster WebUI.
Use the config mode of Cluster WebUI to add a resource to the group and save it.
Run the [clpcl --suspend] command or use the operation mode of Cluster WebUI to suspend the cluster.
Distribute the cluster configuration data to all the servers. Run the [clpcfctrl] command to deliver the data. Run the following command to dynamically add a resource.
Do either of the following depending on the type of configuration data saved in the config mode of Cluster WebUI.
To deliver the configuration information saved on a file system on Linux by using Cluster WebUI, execute the command below.
clpcfctrl --dpush -l -x <path of configuration data file>If the Cluster WebUI is used on Window to save a configuration information file, execute the command below.
clpcfctrl --dpush -w -x <path of configuration data file>
Run the [clpcl --resume] command or use the operation mode of Cluster WebUI to resume the cluster.
Confirm that the resource has been added by running the [clpstat] command or using the Cluster WebUI.
See also
For information on troubleshooting [clpcfctrl] problems, see "Changing, backing up, and checking cluster configuration data (clpcfctrl command)" in "EXPRESSCLUSTER command reference" in the "Reference Guide".