8. EXPRESSCLUSTER command reference¶
This chapter describes commands that are used on EXPRESSCLUSTER.
8.9. Creating a cluster and backing up configuration data (clpcfctrl command)
8.19. Controlling chassis identify lamp (clpledctrl command)
8.21. Requesting processing to cluster servers (clprexec command)
8.23. Controlling cluster activation synchronization wait processing (clpbwctrl command)
8.25. Estimating the amount of resource usage (clpprer command)
8.27. Setting an action for OS shutdown initiated by other than cluster service (clpstdncnf command)
8.28. Controlling the rest point of DB2 (clpdb2still command)
8.29. Controlling the rest point of Oracle (clporclstill command)
8.30. Controlling the rest point of PostgreSQL (clppsqlstill command)
8.31. Controlling the rest point of SQL Server (clpmssqlstill command)
8.32. Displaying the cluster statistics information (clpperfc command)
8.33. Checking the cluster configuration information (clpcfchk command)
8.1. Operating the cluster from the command line¶
EXPRESSCLUSTER provides various commands to operate a cluster by the command prompt. These commands are useful for things like constructing a cluster or when you cannot use the WebManager. You can perform greater number of operations using the command line than Cluster WebUI.
Note
8.2. EXPRESSCLUSTER commands¶
Commands for configuring a cluster
Command |
Description |
Page |
|---|---|---|
clpcfctrl.exe |
Distributes configuration data created by the Cluster WebUI to servers.
Cluster WebUI up the cluster configuration data to be used by the Cluster WebUI.
|
|
clplcnsc.exe |
Manages the product or trial version license of this product. |
|
clpcfchk.exe |
Checks the cluster configuration information. |
Commands for displaying status
Command |
Description |
Page |
|---|---|---|
clpstat.exe |
Displays the cluster status and configuration information. |
|
clphealthchk.exe |
Check the process health. |
Commands for cluster operation
Command |
Description |
Page |
|---|---|---|
clpcl.exe |
Starts, stops, suspends, or resumes the EXPRESSCLUSTER service. |
|
clpdown.exe |
Stops the EXPRESSCLUSTER service and shuts down the server. |
|
clpstdn.exe |
Stops the EXPRESSCLUSTER service across the whole cluster and shuts down all servers. |
|
clpgrp.exe |
Starts, stops, or moves groups. This command also migrates the virtual machine. |
|
clptoratio.exe |
Extends or displays the various time-out values of all servers in the cluster. |
|
clpmonctrl.exe |
Controls monitor resources. |
|
clprsc.exe |
Stops or resumes group resources |
|
clpcpufreq.exe |
Controls CPU frequency |
|
clpledctrl.exe |
Controls Chassis Identify |
|
clptrnreq.exe |
Requests the server to execute a process |
|
clprexec.exe |
Requests that an EXPRESSCLUSTER server execute a process from external monitoring. |
|
clpbmccnf.exe |
Changes the information on BMC user name and password |
|
clpbwctrl.exe |
Controls the cluster activation synchronization wait processing. |
|
clpregctrl.exe |
Displays and/or initializes reboot count on a single server |
|
clpstdncnf.exe |
Setting Operations for Shutting Down OS from Outside Clusters |
Log-related commands
Command |
Description |
Page |
|---|---|---|
clplogcc.exe |
Collects logs and OS information. |
|
clplogcf.exe |
Modifies and displays a configuration of log level and the file size of log output. |
|
clpperfc.exe |
Displays the cluster statistics data about groups and monitor resources. |
Script-related commands
Command |
Description |
Page |
|---|---|---|
clplogcmd.exe |
Writes texts in the script resource script to create a desired message to the output destination. |
Important
The installation directory contains executable-format files and script files that are not listed in this guide. Do not execute these files by programs or applications other than EXPRESSCLUSTER. Any problems caused by not using EXPRESSCLUSTER will not be supported.
Mirror-related commands (when the Replicator/Replicator DR is used)
Command |
Description |
Page |
|---|---|---|
clpmdstat.exe |
Displays a mirroring status and configuration information. |
|
clpmdctrl.exe |
Activates/deactivates a mirror disk resource, or recovers mirror. |
|
clphdstat.exe |
Displays a hybrid disk status and configuration information. |
|
clphdctrl.exe |
Activates/deactivates a hybrid disk resource, or recovers mirror. |
|
clpvolsz.exe |
Checks and adjusts the size of partitions to be mirrored. |
|
clpvolctrl.exe |
Accesses a volume not registered as a resource. |
|
clphdsnapshot.exe |
Controls the access restriction or alike when snap shot backups of data partition in the hybrid disk resource are collected |
Warning-related commands (when the Alert Service is used)
Command |
Description |
Page |
|---|---|---|
clplamp.exe |
Lights off the network warning light. |
System monitor-related commands (when the System Resource Agent is used)
Command |
Description |
Page |
|---|---|---|
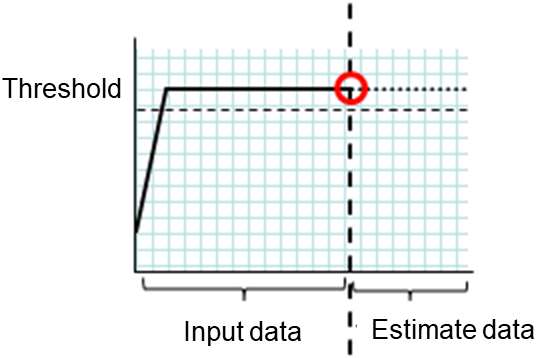
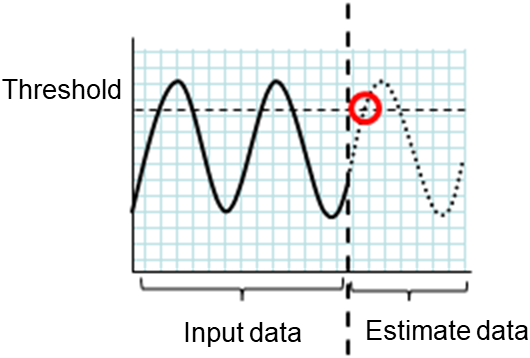
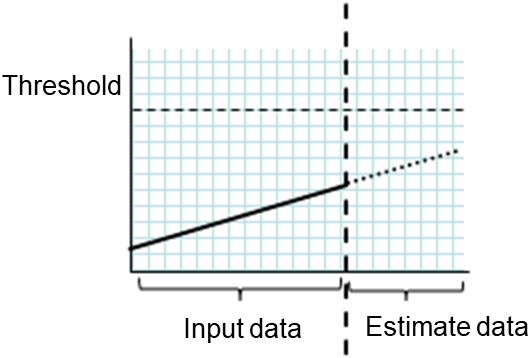
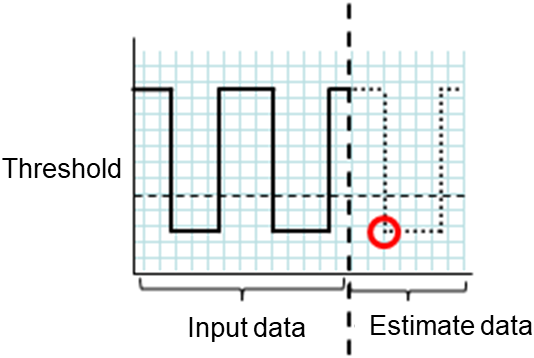
clpprer.exe |
Estimates the future value from the tendency of the given resource use amount data. |
DB rest point-related commands
Command |
Description |
Page |
|---|---|---|
clpdb2still |
Controls the securing/release of a rest point of DB2. |
|
clporclstill |
Controls the securing/release of a rest point of Oracle. |
|
clppsqlstill |
Controls the securing/release of a rest point of PostgreSQL. |
|
clpmssqlstill |
Controls the securing/release of a rest point of SQL Server. |
8.3. Displaying the cluster status (clpstat command)¶
The clpstat command displays cluster status and configuration information.
-
Command line - clpstat -s [--long] [-h <hostname>]clpstat -g [-h <hostname>]clpstat -m [-h <hostname>]clpstat -n [-h <hostname>]clpstat -p [-h <hostname>]clpstat -i [--detail] [-h <hostname>]clpstat --cl [--detail] [-h <hostname>]clpstat --sv [<srvname>] [--detail] [-h <hostname>]clpstat --hb [<hbname>] [--detail] [-h host_name]clpstat --np [<npname>] [--detail] [-h <hostname>]clpstat --svg [<svgname>] [-h <hostname>]clpstat --grp [<grpname>] [--detail] [-h <hostname>]clpstat --rsc [<recname>] [--detail] [-h <hostname>]clpstat --mon [<monname>] [--detail] [-h <hostname>]clpstat --xcl [<xclname>] [--detail] [-h <hostname>]clpstat --local
-
Description This command line displays a cluster status and configuration data.
-
-s¶
-
Nooption¶ Displays a cluster status.
-
--long¶ Displays a name of the cluster name and resource name until the end.
-
-g¶ Displays a cluster group map.
-
-m¶ Displays status of each monitor resource on each server.
-
-n¶ Displays each heartbeat resource status on each server.
-
-p¶ Displays the status of each network partition resolution on each server.
-
-i¶ Displays the configuration information of the whole cluster.
-
--cl¶ Displays the cluster configuration data. Displays the Mirror Agent information as well for the Replicator/Replicator DR.
-
--sv[server_name]¶ Displays the server configuration information. By specifying the name of a server, you can display information of the specified server.
-
--hb[hb_name]¶ Displays heartbeat resource configuration information. By specifying the name of a heartbeat resource, you can display only the information on the specified heartbeat.
-
--np[np_name]¶ Displays the configuration information on the network partition resolution resource. By specifying the name of a network partition resolution resource, you can display only the information on the specified network partition resolution resource.
-
--grp[group_name]¶ Displays group configuration information. By specifying the name of a group, you can display only the information on the specified group.
-
--svg[svgname]¶ Displays server group configuration information. By specifying the name of a server group, you can display only the information on the specified server group.
-
--rsc[resource_name]¶ Displays group resource configuration information. By specifying the name of a group resource, you can display only the information on the specified group resource.
-
--mon[monitor_name]¶ Displays monitor resource configuration information. By specifying the name of a monitor resource, you can display only the information on the specified monitor resource.
-
--xcl[<xclname>]¶ Displays configuration information of exclusion rules. By specifying exclusion rule name, only the specified exclusion name information can be displayed.
-
--detail¶ Displays more detailed information on the setting.
-
-hhost_name¶ Acquires information from the server specified with host_name. Acquires information from the command running server (local server) when the -h option is omitted.
-
--local¶ - Displays the cluster status.This option displays the same information when -s option is specified or when no option is specified. However, this option displays only information of the server on which this command is executed, without communicating with other servers.
-
-
Return Value 0
Success
251
This command was run duplicately.
Other than the above
Failure
-
Remarks According to the combination of options, configuration information shows information in various forms.
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
The EXPRESSCLUSTER service must be activated on the server where you run this command.
When you specify the name of a server for the -h option, the server should be in the cluster.
When you run the clpstat command with the -s option or without any option, names such as a cluster or a resource will not be displayed halfway.
-
Example of Execution Examples of information displayed after running these commands are provided in the next section.
-
Error Messages Message
Cause/Solution
Log in as administrator.
Log in as a user with Administrator privileges.
Invalid configuration file. Create valid cluster configuration data.
Create valid cluster configuration data by using the Cluster WebUI.
Invalid option.
Specify a valid option.
Could not connect to the server. Check if the cluster service is active
Check if the EXPRESSCLUSTER service is operating.
Invalid server status.
Check if the EXPRESSCLUSTER service is operating.
Server is not active. Check if the cluster service is active.
Check if the EXPRESSCLUSTER service is operating.
Invalid server name. Specify a valid server name in the cluster.
Specify the valid server name in the cluster.
Invalid heartbeat resource name. Specify a valid heartbeat resource name in the cluster.
Specify the valid heart beat resource name in the cluster.
Invalid network partition resource name. Specify a valid network partition resource name in the cluster.
Specify the valid network partition resolution resource name in the cluster.
Invalid group name. Specify a valid group name in the cluster.
Specify the valid name of a group in the cluster.
Invalid group resource name. Specify a valid group resource name in the cluster.
Specify the valid name of a group resource in the cluster.
Invalid monitor resource name. Specify a valid monitor resource name in the cluster.
Specify the valid name of a monitor resource in the cluster.
Connection was lost. Check if there is a server where the cluster service is stopped in the cluster.
Check if there is any server on which the EXPRESSCLUSTER service has stopped in the cluster.
Invalid parameter.
An invalid value may be specified to command argument.
Internal communication timeout has occurred in the cluster server. If it occurs frequently, set a longer timeout.
A time-out occurred in the EXPRESSCLUSTER internal communication.If time-out keeps occurring, set the internal communication time-out longer.Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
The cluster is not created.
Create and apply the cluster configuration data.
Could not connect to the server. Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check to see if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
Cluster is stopped. Check if the cluster daemon is active.
Check if the cluster daemon is activated.
Cluster is suspended. To display the cluster status, use --local option.
Cluster is suspended.To display the cluster status, use --local option.
-
Common entry examples
Displaying the status of the cluster (-s option)
The following is an example of display when you run the clpstat command with the -s option or without any option:
-
Example of a command entry # clpstat -s
-
Example of the display after running the command ===================== CLUSTER STATUS ======================== Cluster : cluster <server> *server1........... : Online server1 lankhb1 : Normal LAN Heartbeat lankhb2 : Normal LAN Heartbeat witnesshb1 : Normal Witness Heartbeat pingnp1 : Normal ping resolution httpnp1 : Normal http resolution server2 ........... : Online server2 lankhb1 : Normal LAN Heartbeat lankhb2 : Normal LAN Heartbeat witnesshb1 : Normal Witness Heartbeat pingnp1 : Normal ping resolution httpnp1 : Normal http resolution <group> ManagementGroup : Online Management Group current : server1 ManagementIP : Online 10.0.0.10 failover1.......... : Online failover group1 current : server1 fip1 : Online 10.0.0.11 md1 : Online I: script1 : Online script resource1 failover2 ......... : Online failover group2 current : server2 fip2 : Online 10.0.0.12 md2 : Online J: script1 : Online script resource2 <monitor> fipw1 : Normal fip1 fipw2 : Normal fip2 ipw1 : Normal ip monitor1 mdnw1 : Normal md1 mdnw2 : Normal md2 mdw1 : Normal md1 mdw2 : Normal md2 ===============================================================
Information on each status is provided in " Status Descriptions ".
Displaying a group map (-g option)
To display a group map, run the clpstat command with the -g option.
-
Example of a command entry # clpstat -g
-
Example of the display after running the command: ================= GROUPMAP INFORMATION ======================= Cluster : cluster *server0 : server1 server1 : server2 --------------------------------------------------------------- server0 [o] : failover1[o] failover2[o] server1 [o] : failover3[o] ===============================================================
Groups that are not running are not displayed.
Information on each status is provided in " Status Descriptions ".
Displaying the status of monitor resources (-m option)
To display the status of monitor resources, run the clpstat command with the -m option.
-
Example of a command entry # clpstat -m
-
Example of the display after running the command: =================== MONITOR RESOURCE STATUS ================== Cluster : cluster *server0 : server1 server1 : server2 Monitor0 [fipw1 : Normal] --------------------------------------------------------------- server0 [o] : Online server1 [o] : Offline Monitor1 [fipw2 : Normal] --------------------------------------------------------------- server0 [o] : Offline server1 [o] : Online Monitor2 [ipw1 : Normal] --------------------------------------------------------------- server0 [o] : Online server1 [o] : Online Monitor3 [mdnw1 : Normal] --------------------------------------------------------------- server0 [o] : Online server1 [o] : Online Monitor4 [mdnw2 : Normal] --------------------------------------------------------------- server0 [o] : Online server1 [o] : Online Monitor5 [mdw1 : Normal] --------------------------------------------------------------- server0 [o] : Online server1 [o] : Online Monitor6 [mdw2 : Normal] --------------------------------------------------------------- server0 [o] : Online server1 [o] : Online ===============================================================
Information on each status is provided in " Status Descriptions ".
Displaying the status of heartbeat resources (-n option)
To display the status of heartbeat resources, run clpstat command with the -n option.
-
Example of a command entry # clpstat -n
-
Example of the display after running the command: ================== HEARTBEAT RESOURCE STATUS =================== Cluster : cluster *server0 : server1 server1 : server2 HB0 : lankhb1 HB1 : lankhb2 HB2 : witnesshb1 [on server0 : Online] HB 0 1 2 ----------------------------------------------------------------- server0 : o o o server1 : o x o on server1 : Online] HB 0 1 2 ----------------------------------------------------------------- server0 : o x o server1 : o o o =================================================================
Detailed information on each status is provided in " Status Descriptions ".
The status of the example shown above:
The example above presents the status of all heartbeat resources seen from server0 and server1 when the kernel-mode LAN heartbeat resource that has the second-highest priority is disconnected.
Because kernel-mode LAN heartbeat resource lankhb1 is not able to communicate from both servers, communication to server1 on server0 or communication to server0 on server1 is unavailable.
The rest of heartbeat resources on both servers are in the status allowing communications.
Displaying the status of network partition resolution resources (-p option)
Specify the -p option to the clpstat command and execute the command to display the status of the network partition resolution resources.
-
Example of a command entry # clpstat -p
-
Example of the display after running the command: =============== NETWORK PARTITION RESOURCE STATUS =============== Cluster : cluster *server0 : server1 server1 : server2 NP0 : disknp1 NP1 : pingnp1 NP2 : httpnp1 [on server0 : Online] NP 0 1 2 ----------------------------------------------------------------- server0 : o o o server1 : o o o [on server1 : Online] NP 0 1 2 ----------------------------------------------------------------- server0 : o o o server1 : o o o =================================================================
Detailed information on each status is provided in " Status Descriptions ".
Displaying the cluster configuration data (clpstat command, --cl option)
To display the configuration data of a cluster, run the clpstat command with the -i, --cl, --sv, --hb, --np, --svg, --grp, --rsc, or --mon option. You can see more detailed information by specifying the --detail option. See a separate section, "2. Parameter details" in this guide for details of each item of the list.
To display the cluster configuration data, run the clpstat command with the --cl option.
-
Example of a command entry # clpstat --cl
-
Example of the display after running the command: ===================== CLUSTER INFORMATION ================== [Cluster Name: cluster] Comment : failover cluster =============================================================
Displaying only the configuration data of certain servers (--sv option)
When you want to display only the cluster configuration data on a specified server, specify the name of the server after the --sv option in the clpstat command. To see the details, specify the -- detail option. When the server name is not specified, cluster configuration data of all the servers is displayed.
-
Example of a command entry # clpstat --sv server1
-
Example of the display after running the command: ===================== CLUSTER INFORMATION ===================== [Server0 : server1] Comment : server1 Virtual Infrastructure : vSphere Product : EXPRESSCLUSTER X 4.2 for Windows Internal Version : 12.20 Install Path : C:\Program Files\EXPRESSCLUSTER ================================================================
Displaying only the resource information of certain heartbeats (--hb option)
When you want to display only the cluster configuration data on a specified heartbeat resource, specify the name of the heartbeat resource after the --hb option in the clpstat command. If you want to see the details, specify the --detail option. When the heartbeat resource is not specified, the cluster configuration data of all the heartbeat resources is displayed.
-
Example of a command entry For a kernel-mode LAN heartbeat resource
# clpstat --hb lankhb1
-
Example of the display after running the command: ==================== CLUSTER INFORMATION =================== [HB0 : lanhb1] Type : lankhb Comment : LAN Heartbeat =============================================================
-
Example of a command entry For a BMC heartbeat resource:
# clpstat --hb bmchb1
-
Example of the display after running the command: ==================== CLUSTER INFORMATION ======================= [HB0 : lankhb1] Type : lankhb Comment : LAN Heartbeat =================================================================
-
Tips By using the --sv option and the --hb option together, you can see the information as follows.
-
Example of a command entry # clpstat --sv --hb
-
Example of the display after running the command: ===================== CLUSTER INFORMATION ====================== [Server0 : server1] Comment : server1 Virtual Infrastructure : Product : EXPRESSCLUSTER X 4.2 for Windows Internal Version : 12.20 Install Path : C:\Program Files\EXPRESSCLUSTER [HB0 : lankhb1] Type : lankhb Comment : LAN Heartbeat [HB1 : lanhb2] Type : lankhb Comment : LAN Heartbeat [Server1 : server2] Comment : server2 Virtual Infrastructure : Product : EXPRESSCLUSTER X 4.2 for Windows Internal Version : 12.20 Install Path : C:\Program Files\EXPRESSCLUSTER [HB0 : lankhb1] Type : lankhb Comment : LAN Heartbeat [HB1 : lankhb2] Type : lankhb Comment : LAN Heartbeat ================================================================
Displaying only the resource information of certain network partition resolutions (--np option)
When you want to display only the cluster configuration data on a specified network partition resolution resource, specify the name of the network partition resolution resource after the --np option in the clpstat command. If you want to see the details, specify the --detail option. If the network partition name is not specified, the cluster configuration data on all the network partition resources is displayed.
-
Example of a command entry For a DISK network partition resolution resource:
# clpstat --np disknp1
-
Example of the display after running the command: ==================== CLUSTER INFORMATION ======================= [NP0 : disknp1] Type : disknp Comment : disk resolution =================================================================
-
Example of a command entry For a COM network partition resolution resource:
# clpstat --np comnp1
-
Example of the display after running the command: ==================== CLUSTER INFORMATION ======================= [NP0 : comnp1] Type : comnp Comment : com resolution =================================================================
-
Example of a command entry For a PING network partition resolution resource:
# clpstat --np pingnp1
-
Example of the display after running the command: ==================== CLUSTER INFORMATION ======================= [NP0 : pingnp1] Type : pingnp Comment : ping resolution =================================================================
-
Example of a command entry For an HTTP network partition resolution resource:
# clpstat --np httpnp1
-
Example of the display after running the command: ==================== CLUSTER INFORMATION ======================= [NP0 : httpnp1] Type : httpnp Comment : http resolution =================================================================
-
Example of a command entry For a majority network partition resolution resource:
# clpstat --np majonp1
-
Example of the display after running the command: ==================== CLUSTER INFORMATION ======================= [NP0 : majonp1] Type : majonp Comment : majority resolution ================================================================
Displaying only the configuration data of certain server groups (--svg option)
When you want to display only the cluster configuration data on a specified server group, specify the name of the server group after the --svg option in the clpstat command. When a server group name is not specified, the cluster configuration data on all the server groups is displayed.
-
Example of a command entry # clpstat -- svg servergroup1
-
Example of the display after running the command: ===================== CLUSTER INFORMATION ===================== [Server group 0 : servergroup1] Server0 : server1 Server1 : server2 Server2 : server3 ===============================================================
Displaying only the configuration data of certain groups (--grp option)
When you want to display only the cluster configuration data on a specified group, specify the name of the group after the --grp option in the clpstat command. If you want to see the details, specify the --detail option. When the group name is not specified, the cluster configuration data on all the groups is displayed.
-
Example of a command entry # clpstat --grp
-
Example of the display after running the command: ===================== CLUSTER INFORMATION ================== [Group0 : ManagementGroup] Type : cluster Comment : [Group1 : failover1] Type : failover Comment : failover group1 [Group2 : failover2] Type : failover Comment : failover group2 [Group3 : virtualmachine1] Type : virtualmachine Comment : ============================================================
Displaying only the configuration data of a certain group resource (--rsc option)
When you want to display only the cluster configuration data on a specified group resource, specify the group resource after the --rsc option in the clpstat command. If you want to see the details, specify the --detail option. When the group resource name is not specified, the cluster configuration data on all the group resources is displayed.
-
Example of a command entry For floating IP resource:
# clpstat --rsc fip1
-
Example of the display after running the command: ===================== CLUSTER INFORMATION ================== [Resource0 : fip1] Type : fip Comment : 10.0.0.11 IP Address : 10.0.0.11 =============================================================
-
Tips By using the --grp option and the --rsc option together, you can display the information as follows.
-
Example of a command entry # clpstat --grp --rsc
-
Example of the display after running the command: ===================== CLUSTER INFORMATION ================== [Group0 : ManagementGroup] Type : cluster Comment : [Resource0 : ManagementIP] Type : fip Comment : IP Address : 10.0.0.10 [Group1 : failover1] Type : failover Comment : failover group1 [Resource0 : fip1] Type : fip Comment : 10.0.0.11 IP Address : 10.0.0.11 [Resource1 : md1] Type : md Comment : I: Mirror Disk No. : 1 Drive Letter : I: Mirror Disk Connect : mdc1 [Group2 : failover2] Type : failover Comment : failover group2 [Resource0 : fip2] Type : fip Comment : 10.0.0.12 IP Address : 10.0.0.12 [Resource1 : md2] Type : md Comment : J: Mirror Disk No. : 2 Drive Letter : J: Mirror Disk Connect : mdc1 =============================================================
Displaying only the data of a certain monitor resource (--mon option)
When you want to display only the cluster configuration data on a specified monitor resource, specify the name of the monitor resource after the --mon option in the clpstat command. If you want to see the details, specify --detail option. When a monitor resource name is not specified, the configuration data of all the monitor resources is displayed.
-
Example of a command entry For floating IP monitor resource:
# clpstat --mon fipw1
-
Example of the display after running the command: ===================== CLUSTER INFORMATION ================== [Monitor0 : fipw1] Type : fipw Comment : fip1 =============================================================
Displaying only the configuration data of specific exclusion rules (--xcl option)
When you want to display only the cluster configuration data on a specified exclusion rules, specify the exclusive rule name after the --xcl option in the clpstat command.
-
Example of a command entry # clpstat --xcl excl1
-
Example of the display after running the command: ===================== CLUSTER INFORMATION ===================== [Exclusive Rule0 : excl1] Exclusive Attribute : Normal group0 : failover1 group1 : failover2 =================================================================
Displaying all cluster configuration data (-i option)
By specifying the -i option, you can display the configuration information that is shown when --cl, --sv, --hb, --np, --svg, --grp, --rsc, and --mon options are all specified.
If you run the command with the -i option and the --detail option together, all the detailed cluster configuration data is displayed.
Because this option displays large amount of information at a time, use a command, such as the more command, and pipe, or redirect the output in a file for the output.
-
Example of a command entry: # clpstat -i
-
Tips Specifying the -i option displays all the information on a console. If you want to display some of the information, it is useful to combine the --cl, --sv, --hb, --np, --svg, --grp, --rsc, and/or --mon option. For example, you can use these options as follows:
-
Example of a command entry: If you want to display the detailed information of the server whose name is "server0", the group whose name is "failover1", and the group resources of the specified group, enter:
# clpstat --sv server0 --grp failover1 --rsc --detail
Displaying the status of the cluster (--local option)
By specifying the --local option, you can display only information of the server on which you execute the clpstat command, without communicating with other servers.
-
Example of a command entry: # clpstat --local
-
Example of display after running the command: ===================== CLUSTER STATUS ====================== Cluster : cluster cluster : Start cluster <server> *server1...........: Online server1 lankhb1 : Normal LAN Heartbeat lankhb2 : Normal LAN Heartbeat pingnp1 : Normal ping resolution server2............: Online server2 lankhb1 : - LAN Heartbeat lankhb2 : - LAN Heartbeat pingnp1 : - ping resolution <group> ManagementGroup : Online Management Group current : server1 ManagementIP : Online 10.0.0.10 failover1..........: Online failover group1 current : server1 fip1 : Online 10.0.0.11 md1 : Online I: script1 : Online script resource1 failover2..........: - failover group2 current : server2 fip2 : - 10.0.0.12 md2 : - J: script2 : - script resource2 <monitor> fipw1 : Online fip1 fipw2 : Online fip2 ipw1 : Online ip monitor1 mdnw1 : Online md1 mdnw2 : Online md2 mdw1 : Online md1 mdw2 : Online md2 =============================================================
Information on each status is provided in "Status Descriptions".
8.3.1. Status Descriptions¶
-
Cluster Function
Status
Description
Status display (--local)
Start
Starting
Suspend
Being suspended
Stop
Offline pending
Unknown
Status unknown
-
Server Function
Status
Description
Status displayHeartbeat resource status displayOnline
Starting
Offline
Offline pending
Caution
Heartbeat resource failure
Isolated
Suspension (isolated)
Online Pending
Now being started
Offline Pending
Now being stopped
Pending
Suspension (Network partition unsolved)
Unknown
Status unknown
-
Status unknown
Group map displayMonitor resource status displayo
Starting
s
Suspension (isolated)
p
Now being started/stoppedNetwork partition unsolvedx
Offline Pending
-
Status unknown
-
Heartbeat Resource Function
Status
Description
Status display
Normal
Normal
Caution
Failure (Some)
Error
Failure (All)
Not used
Not used
Unknown
Status unknown
-
Status unknown
Heartbeat resource status display
o
Able to communicate
x
Unable to communicate
-
Not used or status unknown
-
Network Partition Resolution Resource Function
Status
Description
Status display
Normal
Normal
Caution
Failure (Some)
Error
Failure (All)
Unused
Not used
Unknown
Status unknown
-
Status unknown
Network partition resolutionresource status displayo
Able to communicate
x
Unable to communicate
-
Not used or status unknown
-
Group Function
Status
Description
Status display
Online
Started
Offline
Stopped
Online Pending
Now being started
Offline Pending
Now being stopped
Error
Error
Unknown
Status unknown
-
Status unknown
Group map display
o
Started
e
Error
p
Now being started/stopped
-
Group Resource Function
Status
Description
Status display
Online
Started
Offline
Stopped
Online Pending
Now being started
Offline Pending
Now being stopped
Online Failure
Starting failed
Offline Failure
Stopping failed
Unknown
Status unknown
-
Status unknown
-
Monitor Resource Function
Status
Description
Status display
Normal
Normal
Caution
Error (Some)
Error
Error (All)
Unused
Not Used
Unknown
Status unknown
Normal (Dummy failure)
Normal (Dummy Failure)
Caution (Dummy failure)
Error (Some) (Dummy Failure)
Error (Dummy failure)
Error (All) (Dummy Failure)
Status display (--local)Monitor resource status displayOnline
Started
Offline
Stopped
Caution
Warning
Suspend
Stopped temporarily
Online Pending
Now being started
Offline Pending
Now being stopped
Online Failure
Starting failed
Offline Failure
Stopping failed
Unused
Not used
Unknown
Status unknown
Online (Dummy failure)
Started (Dummy Failure)
Offline (Dummy failure)
Stopped (Dummy Failure)
Caution (Dummy failure)
Warning (Dummy Failure)
Suspend (Dummy failure)
Stopped temporarily (Dummy Failure)
Online Pending (Dummy failure)
Now being started (Dummy Failure)
Offline Pending (Dummy failure)
Now being stopped (Dummy Failure)
Online Failure (Dummy failure)
Starting failed (Dummy Failure)
Offline Failure (Dummy failure)
Stopping failed (Dummy Failure)
-
Status unknown
8.4. Operating the cluster (clpcl command)¶
The clpcl command operates a cluster
-
Command line: - clpcl -s [-a] [-h hostname]clpcl -t [-a] [-h hostname] [-w time-out] [--apito time-out]clpcl -r [-a] [-h hostname] [-w time-out] [--apito time-out]clpcl --return [-h hostname] [--apito time-out]clpcl --suspend [--force] [-w time-out] [--apito time-out]clpcl --resume
-
Description This command starts, stops, return, suspends, or resumes the EXPRESSCLUSTER service.
-
Option -
-s¶ Starts the EXPRESSCLUSTER service.
-
-t¶ Stops the EXPRESSCLUSTER service.
-
-r¶ Restarts the EXPRESSCLUSTER service.
-
--return¶ Restores a server that is in the suspension (isolated) status to the normal status.
-
--suspend¶ Suspends the entire cluster
-
--resume¶ Resumes the entire cluster
-
-a¶ Executed the command on all servers
-
-h<host_name>¶ Makes a request to run the command to the server specified in host_name. Makes a processing request to the server on which this command runs (local server) if the -h option is omitted.
-
-w<time-out>¶ - When -t, -r, or --suspend option is used, specify the wait time in seconds that the clpcl command waits for the EXPRESSCLUSTER service to be completely stopped or suspended.When a time-out is not specified, it waits for unlimited time.When "0 (zero)" is specified, it does not wait.When the -w option is not specified, it waits for twice the heartbeat time-out (in seconds).
-
--force¶ When used with the --suspend option, forcefully suspends the cluster regardless of the status of all the servers in the cluster.
-
--apito<time-out>¶ - Specify the time in seconds to wait for the EXPRESSCLUSTER service to be stopped, restarted, or suspended (internal communication timeout). A value between 1 to 9999 can be specified.When the --apito option is not specified, the command waits according to the value set for the internal communication timeout in the cluster property.
-
-
Return Value 0
Success
Other than 0
Failure
-
Remarks When this command is executed with the -s or --resume option specified, it returns control when processing starts on the target server. When this command is executed with the -t or --suspend option specified, it returns control after waiting for the processing to complete. When this command is executed with the -r option specified, it returns control when the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon restarts on the target server after stopping once. Run the clpstat command to display the started or resumed status of the EXPRESSCLUSTER daemon.
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
This command cannot be executed while a group is being started or stopped.
For the name of a server for the -h option, specify the name of a server in the cluster that allows name resolution.
When you suspend the cluster, the EXPRESSCLUSTER service should be activated in all servers in the cluster. When the --force option is used, the cluster is forcefully suspended even if there is any stopped server in the cluster.
When you start up or resume the cluster, access the servers in the cluster in the order below, and use one of the paths that allowed successful access.
via the IP address on the interconnect LAN
via the IP address on the public LAN
via the IP address whose name was resolved by the server name in the cluster configuration data
When you resume the cluster, use the clpstat command to see there is no activated server in the cluster.
-
Example of a command entry Example 1: Activating the EXPRESSCLUSTER service in the local server
# clpcl -s Command succeeded
Example 2: Activating the EXPRESSCLUSTER service in server1 from server0
# clpcl -s -h server1 Start server1 : Command succeeded.
If a server name is specified, the display after running the command should look similar to above.
Start server_name : Execution result
Example 3: Activating the EXPRESSCLUSTER service in all servers
# clpcl -s -a Start server0 : Command succeeded. Start server1 : Performed startup processing to the active cluster service.
When all the servers are activated, the display after running the command should look similar to above.
Start server_name : Execution result
Example 4: Stopping the EXPRESSCLUSTER service in all servers
# clpcl -t -a Stop server0 : Command succeeded. Stop server1 : Command succeeded.
When all the servers are stopped, the display after running the command should look similar to above. Stop server_name : Execution result.
When the stopping process fails, the display may be different from the example above depending on the process.
Wait for the stopping of all servers of the EXPRESSCLUSTER service.
-
Error Messages Message
Cause/Solution
Log in as administrator.
Log in as a user with Administrator privileges.
Invalid configuration file. Create valid cluster configuration data.
Create valid cluster configuration data using the Cluster WebUI.
Invalid option.
Specify a valid option
Performed stop processing to the stopped cluster service.
The stopping process has been executed to the stopped EXPRESSCLUSTER service.
Performed startup processing to the active cluster service.
The startup process has been executed to the activated EXPRESSCLUSTER service.
Command timeout.
The command timed out.
Failed to return the server. Check the status of failed server.
Failed to return the server. Check the status of the failed server.
Could not connect to the server. Check if the cluster service is active.
Check if the EXPRESSCLUSTER service is activated.
Failed to obtain the list of nodes. Specify a valid server name in the cluster.
Specify the valid name of a server in the cluster.
Failed to obtain the service name.
Failed to obtain the service name.
Failed to operate the service.
Failed to operate the service.
Resumed the cluster service that is not suspended.
Resumed the EXPRESSCLUSTER service that is not suspended.
invalid server status.
Check if the EXPRESSCLUSTER service is activated.
Server is busy. Check if this command is already run.
This command may be run already. Check it.
Server is not active. Check if the cluster service is active.
Check if the EXPRESSCLUSTER service is activated.
There is one or more servers of which cluster service is active. If you want to perform resume, check if there is any server whose cluster service is active in the cluster.
When you execute the command to resume, check if there is no server in the cluster on which the EXPRESSCLUSTER service is activated.
All servers must be activated. When suspending the server, the cluster service need to be active on all servers in the cluster.
When you execute the command to suspend, the EXPRESSCLUSTER service must be activated in all servers in the cluster.
Resume the server because there is one or more suspended servers in the cluster.
Execute the command to resume because some server(s) in the cluster is suspended.
Invalid server name. Specify a valid server name in the cluster.
Specify the valid name of a server in the cluster.
Connection was lost. Check if there is a server where the cluster service is stopped in the cluster.
Check if there is any server on which the EXPRESSCLUSTER service has stopped in the cluster.
invalid parameter.
The value specified as a command parameter may be invalid.
Internal communication timeout has occurred in the cluster server. If it occurs frequently, set the longer timeout.
A timeout occurred in the EXPRESSCLUSTER internal communication.If time-out keeps occurring, set the internal communication time-out longer.Processing failed on some servers. Check the status of failed servers.
If stopping process is executed to all servers, there is one or more servers on which the stopping process has failed.Check the status of the server(s) on which the stopping process has failed.Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
Failed to shutdown the server.
Shutting down or rebooting the server failed.
Failed to get privilege.
Obtaining the privilege to shut down or reboot the server failed.
8.5. Shutting down a specified server (clpdown command)¶
The clpdown command shuts down a specified server.
-
Command line clpdown [-r] [-h hostname]
-
Description This command stops the EXPRESSCLUSTER service and shuts down a server.
-
Option -
None¶ Shuts down a server.
-
-r¶ Reboots the server.
-
-h<host_name>¶ Makes a processing request to the server specified in host_name. Makes a processing request to the server on which this command runs (local server) if the -h option is omitted.
-
-
Return Value 0
Success
Other than 0
Failure
-
Remarks This command returns control when the group stop processing is completed.
This command shuts down the server even when the EXPRESSCLUSTER service is stopped.
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
This command cannot be executed while a group is being started or stopped.
For the name of a server for the -h option, specify the name of a server in the cluster.
-
Example of a command entry Example 1: Stopping and shutting down the EXPRESSCLUSTER service in the local server
# clpdownExample 2: Shutting down and rebooting server1 from server0
# clpdown -r -h server1
-
Error Message
8.6. Shutting down the entire cluster (clpstdn command)¶
The clpstdn command shuts down the entire cluster
-
Command line clpstdn [-r] [-h hostname]
-
Description This command stops the EXPRESSCLUSTER service in the entire cluster and shuts down all servers.
-
Option -
None¶ Executes cluster shutdown.
-
-r¶ Executes cluster shutdown reboot.
-
-h<host_name>¶ Makes a processing request to the server specified in host_name. Makes a processing request to the server on which this command runs (local server) if the -h option is omitted.
-
-
Return Value 0
Success
Other than 0
Failure
-
Remarks This command returns control when the group stop processing is completed.
-
Notes - Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.This command cannot be executed while a group is being started or stopped.For the name of a server for the -h option, specify the name of a server in the cluster.A server that cannot be accessed from the server that runs the command (for example, a server with all LAN heartbeat resources are off-line.) will not shut down.
-
Error Message
8.7. Operating groups (clpgrp command)¶
The clpgrp command operates groups
-
Command line - clpgrp -s [grpname] [-h hostname] [-f] [--apito time-out]clpgrp -t [grpname] [-h hostname] [-f] [--apito time-out]clpgrp -m [grpname] [-h hostname] [-a hostname] [--apito time-out]clpgrp -l [grpname] [-h hostname] [-a hostname] [--apito time-out]clpgrp -n <grpname>
-
Description This command starts, deactivates or moves groups. This command also migrates groups.
-
Option -
-s[grpname]¶ Starts groups. When you specify the name of a group, only the specified group starts up. If no group name is specified, all groups start up.
-
-t[grpname]¶ Stops groups. When you specify the name of a group, only the specified group stops. If no group name is specified, all groups stop.
-
-m[grpname]¶ Moves groups. When you specify the name of a group, only the specified group is moved. If no group name is specified, all the groups are moved.
-
-l[grpname]¶ - Migrates the specified group. The group type must be "virtualmachine".If no group name is specified, all the active migration groups on the server are migrated.
-
-h<hostname>¶ Makes a processing request to the server specified in hostname. Makes a processing request to the server on which this command runs (local server) if the -h option is omitted.
-
-a<hostname>¶ Defines the server which is specified by hostname as a destination to which a group will be moved. When the -a option is omitted, the group will be moved according to the failover policy.
-
-f¶ - If you use this option with the -s option against a group activated on a remote server, it will forcefully be started on the server that requested the process.If this command is used with the -t option, the group will be stopped forcefully.
-
-n<grpname>¶ Displays the name of the server on which the group has been started.
-
--apito<time-out>¶ - Specify the time in seconds to wait for groups to be started, stopped, moved, or migrated (internal communication timeout). A value between 1 to 9999 can be specified.When the --apito option is not specified, the command waits according to the value set for the internal communication timeout in the cluster property.
-
-
Return Value 0
Success
Other than 0
Failure
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
The EXPRESSCLUSTER service must be activated on the server that runs this command
Specify a server in the cluster when you specify the name of server name for the -h and -a options.
If the group is moved by using the -m option, it is determined to be normal at the time of performing the group start process on the destination server. Please be aware that even if this command is executed successfully, the activation of the resource may fail on the server to which the group is moved. In order to check whether or not the group has started by using the return value, execute the following:
# clpgrp -s [group_name] [-h hostname] -fIn order to move a group belonging to exclusion rules whose exclusion attribute is set to "Normal" by using the [-m] option, explicitly specify a server to which the group is moved by the [-a] option.
With the -a option omitted, moving a group fails if a group belonging to exclusion rules whose exclusion attribute is set to "Normal" is activated in all the movable servers.
-
Example of Execution The following is an example of status transition when operating the groups.
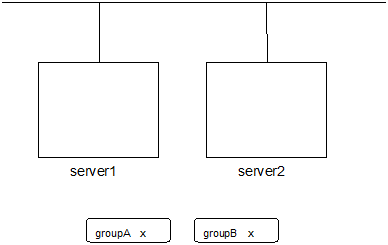
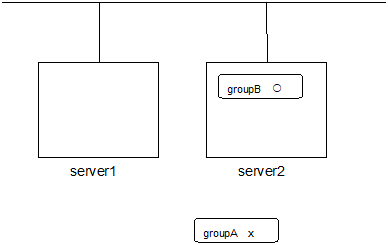
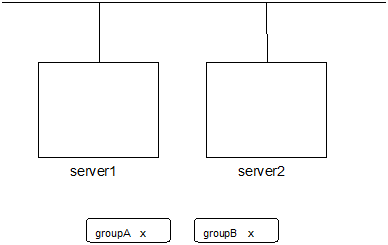
Example: The cluster has two servers and two groups.
Failover policy of group
groupA server1 -> server2groupB server2 -> serveBoth groups are stopped.
Run the following command on server1.
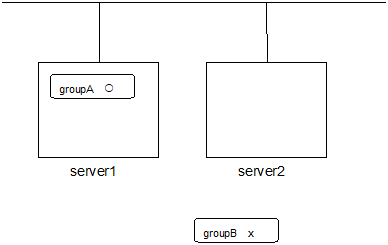
# clpgrp -s groupAGroupA starts in server1.
Run the following command in server2.
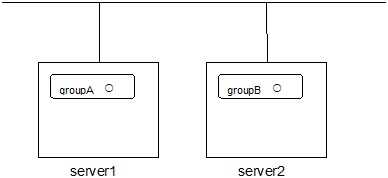
# clpgrp -sAll groups that are currently stopped but can be started start in server2.
Run the following command in server1
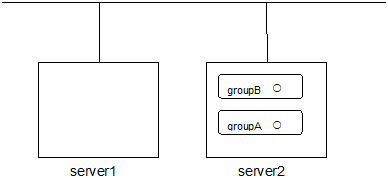
# clpgrp -m groupAGroupA moves to server2.
Run the following command in server1
# clpgrp -t groupA -h server2GroupA stops.
Run the following command in server1.
# clpgrp -t Command Succeeded.
When the command is executed, there is no group running on server1. So, "Command Succeeded." appears.
Add -f to the command you have run in Step 6 and execute it on server1.
# clpgrp -t -fGroups which were started in server2 can be forcefully deactivated from server1.
-
Error message Message
Cause/Solution
Log in as administrator.
Log in as a user with Administrator privileges.
Invalid configuration data. Create valid cluster configuration data.
Create valid cluster configuration data using the Cluster WebUI.
Invalid option.
Specify a valid option
Could not connect to the server. Check if the cluster service is active.
Check if the EXPRESSCLUSTER service is operating.
Invalid server status. Check if the cluster service is active.
Check if the EXPRESSCLUSTER service is operating.
Server is not active. Check if the cluster service is active.
Check if the EXPRESSCLUSTER service is operating.
Invalid server name. Specify a valid server name in the cluster.
Specify the valid server name in the cluster.
Connection was lost. Check if there is a server where the cluster service is stopped in the cluster.
Check if there is any server on which the EXPRESSCLUSTER service has stopped in the cluster.
Invalid parameter.
The value specified as a command parameter may be invalid.
Internal communication timeout has occurred in the cluster server. If it occurs frequently, set a longer timeout.
A time-out occurred in the EXPRESSCLUSTER internal communication.If time-out keeps occurring, set the internal communication time-out longer.Invalid server. Specify a server that can run and stop the group, or a server that can be a target when you move the group.
Server that starts and stops the group or to which the group is moved is invalid.Specify a valid server.Could not start the group. Try it again after the other server is started, or after the Wait Synchronization time is timed out.
Start up the group after waiting for the remote server to start up, or after waiting for the timeout of the start-up wait time.
No operable group exists in the server.
Check if there is any group that is operable in the server which requested the process.
The group has already been started on the local server.
Check the status of the group by using the Cluster WebUI or the clpstat command.
The group has already been started on the other server. To start/stop the group on the local server, use -f option.
Check the status of the group by using the Cluster WebUI or the clpstat command.If you want to start up or stop a group which was started in a remote server from the local server, move the group or run the command with the -f option.The group has already been stopped.
Check the status of the group by using the Cluster WebUI or the clpstat command.
Failed to start one or more resources. Check the status of group.
Check the status of group by using the Cluster WebUI or the clpstat command.
Failed to stop one or more resources. Check the status of group.
Check the status of group by using the Cluster WebUI or the clpstat command.
The group is busy. Try again later.
The group is now being started or stopped. Wait for a while and try again.
An error occurred on one or more groups. Check the status of group.
Check the status of the group by using the Cluster WebUI or the clpstat command.
Invalid group name. Specify a valid group name in the cluster.
Specify the valid name of a group in the cluster.
Server is isolated.
The server has been suspended. The server is rebooted after it went down.
Some invalid status. Check the status of cluster.
The status is invalid. Check the status of the cluster.
Log in as administrator.
Check if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
Failed to migrate the group.
If the -l option is used, check whether the type of the specified group is "virtualmachine".
The specified group cannot be migrated.
Check the status of the group.
The specified group is not vm group.
Check if the type of the group is set to the virtual machine.
Migration resource does not exist.
Check if the virtual machine resource exists in the group.
Migration resource is not online.
Check if the virtual machine resource has already started.
Server is not in a condition to start group. Critical monitor error is detected.
Check the status of each server.
There is no appropriate destination for the group. Critical monitor error is detected.
Check the status of each server.
8.8. Collecting logs (clplogcc command)¶
The clplogcc command collects logs.
-
Command line clplogcc [ [-n targetnode1 -n targetnode2 ......] ] [-t collect_type] [-o path] [--local] [--evt event_type ...]
-
Description This command collects information including logs and the OS information by accessing the data transfer server.
-
Option -
None¶ Collects logs in the cluster.
-
-tcollect_type¶ Specifies a log collection pattern. When this option is omitted, a log collection pattern will be type1. Information on log collection types is provided "Specifying a event log type to collect (--evt option)".
-
-opath¶ Specifies the output destination of collector files. When this option is skipped, logs are output under tmp of the installation path.
-
-ntargetnode¶ Collects logs on the local server without going through the data transfer server. The -n option cannot be specified at the same time.
-
--local¶ Collects logs on the local server without going through the data transfer server. The -n option cannot be specified at the same time.
-
--evtevent_type¶ - Specifies the type of the event log to be collected.When this option is skipped, application logs, system logs and security logs will be collected.If none is specified, the event log is not collected.This option is enabled only when --local option is specified.For details, see "Specifying a event log type to collect (--evt option)".
-
-
Return Value 0
Success
Other than 0
Failure
-
Remarks Since log files are compressed by zip, decompress them using an appropriate application.
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
For the name of server for the -n option, specify the name of server that allows name resolution. If name resolution is not possible, specify the interconnect or public LAN address.When you run this command, access the servers in the cluster in the order below, and use one of the paths that allowed successful access.
via the IP address on the interconnect LAN
via the IP address on the public LAN
via the IP address whose name was resolved by the server name in the cluster configuration data
-
Example of command execution Example 1: Collecting logs from all servers in the cluster
# clplogcc Please wait, now collecting.. server status result ------------------------------- server0 Completion Normal server1 Completion Normal
The execution results of the server that collected logs are displayed.
Server name Progress Result
-
Execution Result For this command, the following processes are displayed.
Steps in Process
Meaning
Preparing
Initializing
Connecting
Connecting to the server
Compressing
Compressing log files
Transmitting
Sending log files
Disconnecting
Disconnecting from the server
Completion
Finished collecting logs
The following results (server status) are displayed:
Result (server status)
Meaning
Normal
Completed successfully
Canceled
Canceled by the user
Invalid Parameters
Parameters are invalid
Compression Error
There was an error while compressing files
Timeout
Time-out occurred.
Busy
The server is busy.
No Free Space
No free space on the disk.
File I/O Error
There was a file I/O error.
Unknown Error
Failure caused by other errors
-
Error Message Message
Cause/Solution
Log in as administrator.
Log in as a user with Administrator privileges.
Invalid option.
Specify a valid option.
Collect type must be specified 'type1' or 'type2' or 'type3' or 'type4' or 'type5' or 'type6'. Incorrect collection type is specified.
Invalid collection type is specified.
Specifiable number of servers are the max number of servers that can constitute a cluster.
The number of servers you can specify is within the maximum number of servers for cluster configuration.
Failed to obtain properties.
Failed to obtain the properties.
Failed to obtain the list of nodes. Specify a valid server name in the cluster.
Specify the valid name of a server in the cluster.
Invalid server name. Specify a valid server name in the cluster.
Specify the invalid server name in the cluster.
Failed to collect log.
Failed to collect logs.
Server is busy. Check if this command is already run.
This command may be run already. Check it.
Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
8.8.1. Collecting logs by specifying a type (-t option)¶
To collect only the specified types of logs, run the clplogcc command with the -t option.
Specify a type from 1 through 6 for the log collection.
type1 |
type2 |
type3 |
type4 |
type5 |
type6 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
y |
y |
y |
n |
n |
n |
|
y |
y |
y |
y |
n |
n |
|
y |
y |
y |
y |
n |
n |
|
y |
y |
n |
n |
n |
n |
|
y |
y |
n |
n |
n |
n |
|
y |
y |
y |
n |
n |
n |
|
y |
y |
y |
n |
n |
n |
|
y |
y |
y |
n |
n |
n |
|
n |
y |
n |
n |
n |
n |
|
n |
n |
n |
n |
y |
n |
|
n |
n |
n |
n |
n |
y |
|
y |
y |
y |
n |
n |
y |
(y=yes, n=no)
Run this command from the command line as follows.
Example: When collecting logs using type2
# clplogcc -t type2
When no option is specified, a log type will be type 1.
Information to be collected by default
Logs of each module in the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server
Attribute information on each module (dir) in the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server
In bin
In cloud
In alert/bin, webmgr/bin
In %SystemRoot%\system32\drivers
EXPRESSCLUSTER version information
OS information
update log
License information
Configuration file
Policy file
Cloud environment configuration directory
Shared memory dump
Local node status of ExpressCluster (clpstat --local execution result)
Host name and domain name information (hostname execution result)
Network information (netstat execution result)
IP routing table information (route print execution result)
Process existing status (tasklist execution result)
ipconfig (ipconfig execution result)
Shared configuration of files (net share execution result)
Session information (net session execution result)
Windows firewall settings (netsh execution result)
SNP (Scalable Networking Pack) setting (netsh execution result)
Task scheduler settings (schtasks execution result)
event log
application log (AppEvent.Evt, Application.evtx, Application.txt)
system log (SysEvent.Evtt, System.evtx, System.txt)
security log (SecEvent.Evt, Security.evtx, Security.txt)
Windows error report
***.wer
User dump
***.*dmp
Diagnostics Report
the result of running msinfo32.exe
Registry
Registry information of the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server
HKLM\SOFTWARE\NEC\EXPRESSCLUSTER\Alert
HKLM\SOFTWARE\NEC\EXPRESSCLUSTER\MirrorList
HKLM \SOFTWARE\NEC\EXPRESSCLUSTER\RC
HKLM \SOFTWARE\NEC\EXPRESSCLUSTER\VCOM
registry information of diskfltr
Registry information of OS
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Disk
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\DOS Devices
HKLM\SYSTEM\MountedDevices
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Enum\SCSI
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Enum\STORAGE
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\symc8xx
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem
Script
Start/stop script for a group that was created with the Cluster WebUI.
If you specify a user-defined script, it is not included in the log collection information. It must be collected separately.
ESMPRO/AC and ESMPRO/UPSC logs
Files collected by running the acupslog.exe command.
HA logs
System resource information
JVM monitor log
System monitor log
Mirror statistics information
Mirror statistics information
In perf\disk
Cluster statistics information
Cluster statistics information
In perf\cluster
System Resource statistics information
System statistics information
In perf\system
8.8.2. Output paths of log files (-o option)¶
Log file is named and be saved as "server_name-log.zip"
Since log files are compressed by zip, decompress them by using an appropriate application.
If not specifying -o option
Logs are output in tmp of installation path.
When the -o option is specified:
If you run the command as follows, logs are located in the specified c:\tmp.
# clplogcc -o C:\tmp
8.8.3. Specifying log collector server (-n option)¶
By using the -n option, you can collect logs only from the specified server.
Example: Collecting logs from Server1 and Server3 in the cluster.
# clplogcc -n Server1 -n Server3
Specify a server in the same cluster.
The number of servers you can specify is within the maximum number of servers in the cluster configuration.
8.8.4. Specifying a event log type to collect (--evt option)¶
You can specify the type of the event log included in the information obtained at the log collection.
Specify one or more text strings that represent event log types as shown in the following table after --evt option.
Event log type |
Character string to specify |
|---|---|
Application log |
app |
System log |
sys |
Security log |
sec |
Not collected |
none |
Example) Collecting the system log and the security log
# clplogcc --local --evt sys sec
This option is enabled only when the --local option is specified.
8.8.5. Collecting information when a failure occurs¶
When the following failure occurs, the information for analyzing the failure is collected.
When the cluster service that forms the cluster fails due to termination by an internal status error.
When a group resource activation error or deactivation error occurs.
When monitoring error occurs in a monitor resource.
Information to be collected is as follows:
Cluster information
Some module logs in EXPRESSCLUSTER servers
Information created by running a command
Host name and domain name information (hostname execution result)
Network information (netstat execution result)
Process existing status (tasklist execution result)
ipconfig (ipconfig execution result)
Shared configuration of files (net share execution result)
Session information (net session execution result)
These are collected by default in the log collection. You do not need to collect them separately.
8.9. Creating a cluster and backing up configuration data (clpcfctrl command)¶
8.9.1. Creating a cluster (clpcfctrl --push)¶
The clpcfctrl --push command delivers cluster configuration data to servers.
-
Command line - clpcfctrl --push [-w] [-x <path>] [-c <hostname>|<IP>] [-h <hostname>|<IP>][-p <portnumber>] [--force]
-
Description This command delivers the configuration data created by the Cluster WebUI to servers.
-
Option -
--push¶ - Specify this option when delivering the data.You cannot omit this option.
-
-x¶ Specify this option to deliver the configuration data that is in the specified directory.
-
-w¶ - Displays that the graphic character code of the cluster configuration data file to be delivered is SJIS.In general, it is not necessary to specify this optionYou cannot specify -l and -w together. Specify either -l or -w.
-
-c¶ Specifies a server to access for acquiring a list of servers. Specify a host name or IP address.
-
-h¶ - Specifies a server to which configuration data is delivered. Specify host name or IP address.When this option is omitted, the default value will be used.In general, it is not necessary to specify this option.
-
-p¶ - Specifies a port number of data transfer port.When this option is omitted, the default value will be used.In general, it is not necessary to specify this option.
-
--force¶ Even if there is a server that has not started, the configuration data is delivered forcefully.
-
--nocheck¶ The configuration data is delivered without the checking operation that is required when applying a settings change to the cluster. To apply the delivered configuration data to the cluster, therefore, execute the required operation manually.
-
-
Return Value 0
Success
Other than 0
Failure
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrative authority.
When you run this command, access the servers in the order below, and use one of the paths that allowed successful access.
via the IP address on the interconnect LAN
via the IP address on the public LAN
via the IP address whose name was resolved by the server name in the cluster configuration data
When delivering the cluster configuration data, the current cluster configuration data and the configuration data to be delivered are compared.
If there is any change in the configuration data, the following message output. Follow the instructions of the message to complete the delivery.
Message
Solution
Please stop the EXPRESSCLUSTER.
Stop the server.
Please suspend the EXPRESSCLUSTER
Suspend the server.
Please stop the following groups.
Stop the group of which setting has been changed.
Reboot of a cluster is necessary to reflect setting.
Shut down and reboot the cluster to apply the change of settings.
To apply the changes you made, restart the EXPRESSCLUSTER Web Alert service.
Restart the Web Alert service to apply the change of settings.
To apply the changes you made, restart the EXPRESSCLUSTER Manager service.
Restart the EXPRESSCLUSTER Manager service to apply the change of settings.
Start of a cluster is necessary to reflect setting.
This is the message displayed at the initial cluster configuration. Start the cluster.
The --nocheck option is used only for special purposes including a maintenance procedure. Do not use the --nocheck option for normal operations.
-
Example of command execution Example 1: Generating a cluster from the floppy disk with the data saved by Cluster WebUI
# clpcfctrl --push -x C:\tmp\config file delivery to server 10.0.0.11 success. file delivery to server 10.0.0.12 success. Command succeeded.(code:0)
Example 2: Delivering configuration data that was saved on the file system using Cluster WebUI
# clpcfctrl --push -x C:\tmp\config -h 10.0.0.11 Command succeeded.(code:0)
-
Error Message Message
Cause/Solution
Command succeeded.
The command ran successfully.
Log in as administrator.
Log in as a user with Administrator privileges.
This command is already run.
This command has already been run.
invalid option.
This option is invalid. Check the option.
Invalid mode. Check if --push or --pull option is specified.
Check if --push is specified.
The target directory does not exist.
The specified directory is not found. Check if the specified directory is valid.
Invalid host name. Server specified by -h option is not included in the configuration
The server specified with -h is not included in configuration data. Check if the specified server name or IP address is correct.
Invalid type of file.
Check that the character code used for the configuration data is correct.
Failed to initialize the xml library. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.orFailed to load the configuration file. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.orFailed to change the configuration file. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.Check if the memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Failed to load the all.pol file. Reinstall the RPM cluster.
Reinstall the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server.
Failed to load the cfctrl.pol file. Reinstall the RPM cluster.
Reinstall the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server.
Failed to get the install path. Reinstall the RPM cluster.
Reinstall the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server.
Failed to get the list of group.
Failed to acquire the list of group.
Failed to get the list of resource.
Failed to acquire the list of resource.
Failed to initialize the trncl library. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check if the memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Failed to connect to trnsv. Check if the other server is active.
Accessing the server has failed. Check if the other server has been started up.
Failed to get the list of node. Check if the server specified by -c is a member of the cluster.
Check if the server specified by -c is a cluster member.
File delivery failed. Failed to deliver the configuration data. Check if the other server is active and run the command again.
Delivering configuration data has failed. Check if other server(s) has been started.Run the command again after the server has started up.Multi file delivery failed. Failed to deliver the configuration data. Check if the other server is active and run the command again.
Delivering configuration data has failed. Check if other server(s) has been started.Run the command again after the server has started up.Failed to deliver the configuration data. Check if the other server is active and run the command again.
Delivering configuration data has failed. Check if other server(s) has been started.Run the command again after the server has started up.Failed to upload the configuration file. Check if the other server is active and run the command again.
Delivering configuration data has failed. Check if other server(s) has been started
Failed to get the collect size.
Getting the size of the collector file has failed. Check if other server(s) has been started.
Failed to collect the file.
Collecting of the file has failed. Check if other server(s) has been started.
Canceled to deliver the configuration file since it failed to connect to one or more server. If you want to deliver the configuration file to servers that can be connected, run the command again with "-force" option.
Canceled the delivery of the configuration data. There are some servers that failed to connect. If you want to deliver the configuration data only to the server that can be connected, run the command again by using the --force option.
The directory "work" is not found. Reinstall the RPM.
Reinstall the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server.
Failed to make a working directory.orThe directory does not exist.orThis is not a directory.orThe source file does not exist.orThe source file is a directory.orThe source directory does not exist.orThe source file is not a directory.orFailed to change the character code set (EUC to SJIS).orFailed to change the character code set (SJIS to EUC).Check if the memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Failed to allocate memory.orFailed to change the directory.orFailed to make a directory.orFailed to remove the directory.orFailed to remove the file.orFailed to open the file.orFailed to read the file.orFailed to copy the file.orFailed to create the mutex.Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.Check if the memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Failed to check server property. Check if the server name or ip addresses are correct.
Check if the server name and the IP address of the configuration information are correctly set.
Please stop the following resources.
Stop the resource of which the configuration has been changed.
Failed to get server status.
Failed to acquire the server status. Check that the server is operating normally.
target does not exist.
The specified directory does not exist. Check that the directory is specified correctly.
connect to server succeeded.
Connected to the server successfully.
connect to server failed.
Failed to connect to the server. Check that the server has started.
connect to server failed. (please retry later)
Failed to connect to the server. Check that the server has started. Wait a short while and then retry.
clp.conf delivered.
Configuration data has already been delivered.
To apply the changes you made, reboot the cluster.
To apply the changes you made, restart the cluster.
To apply the changes you made, start the cluster service.
To apply the changes you made, start the cluster.
Failed to deliver the configuration file. Check if the other server is active and run the command again.
Delivering configuration data has failed. Check if other server(s) has been started. Run the command again after the server has started up.
8.9.2. Backing up the cluster configuration data¶
The clpcfctrl --pull command backups cluster configuration data.
-
Command line - clpcfctrl --pull [-w] [-x <path>] [-h <hostname>|<IP>][-p <portnumber>]
-
Description This command backs up cluster configuration data to be used for the Cluster WebUI.
-
Option -
--pull¶ - Specify this option when performing backup.You cannot omit this option.
-
-x¶ Specify this option when backing up configuration data in the specified directory.
-
-w¶ Save the configuration data with graphic character code, SJIS.
-
-h¶ - Specifies the source server for backup.Specify a host name or IP address.When this option is omitted, the configuration data on the server running the command is used.
-
-p¶ - Specifies a port number of data transfer port.When this option is omitted, the default value is used. In general, it is not necessary to specify this option.
-
-
Return Value 0
Success
Other than 0
Failure
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
When you run this command, access the servers in the cluster in the order below, and use one of the paths that allowed successful access.
via the IP address on the interconnect LAN
via the IP address on the public LAN
via the IP address whose name was resolved by the server name in the cluster configuration data
-
Example of command execution Example 1: Backing up configuration data into the specified directory
# clpcfctrl --pull -x C:/tmp/config Command succeeded.(code:0)
Example 2: Backing up configuration data of the specified server into the specified directory
# clpcfctrl --pull -x C:/tmp/config -h 10.0.0.11 Command succeeded.(code:0)
-
Error Message Message
Cause/Solution
Log in as administrator.
Log on as a user with Administrator privileges.
This command is already run.
This command has already been run.
invalid option.
The option is invalid. Check the option.
Invalid mode. Check if --push or --pull option is specified.
Check if --pull is specified.
Failed to initialize the xml library. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.orFailed to load the configuration file. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.orFailed to change the configuration file. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.Check if the memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Failed to load the all.pol file. Reinstall the cluster.
Reinstall the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server.
Failed to load the cfctrl.pol file. Reinstall the cluster.
Reinstall the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server.
Failed to get the install path. Reinstall the cluster.
Reinstall the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server.
Failed to initialize the trncl library. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient
Check if the memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Failed to connect to trnsv. Check if the other server is active.
Accessing the server has failed. Check if other server(s) has been started.
The directory "work" is not found. Reinstall the cluster.
Reinstall the EXPRESSCLUSTER Server.
Failed to make a working directory.orThe directory does not exist.orThis is not a directory.orThe source file does not exist.orThe source file is a directory.orThe source directory does not exist.orThe source file is not a directory.orFailed to change the character code set (EUC to SJIS).orFailed to change the character code set (SJIS to EUC).Check if the memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Failed to allocate memory.orFailed to change the directory.orFailed to make a directory.orFailed to remove the directory.orFailed to remove the file.orFailed to open the file.orFailed to read the file.orFailed to write the file.orFailed to copy the file.orFailed to create the mutex.orFailed to copy the file.orFailed to create the mutex.orInternal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.Check if the memory or OS resources are sufficient.
8.10. Adjusting time-out temporarily (clptoratio command)¶
The clptoratio command extends or displays the current time-out ratio.
-
Command line - clptoratio -r <ratio> -t <time>clptoratio -iclptoratio -s
-
Description This command displays the current time-out ratio or temporarily extends the various time-out values of the following on all servers in the cluster.
Monitor resource
Heartbeat resource
Disk Agent
Alert synchronous service
WebManager service
Note that the following value is not supported.
Kernel mode LAN heartbeat resources
-
Option -
-rratio¶ - Specifies the time-out ratio. Use 1 or larger integer. The maxim time-out ratio is 10,000.If you specify "1," you can return the modified time-out ratio to the original as you can do so when you are using the -i option.
-
-ttime¶ - Specifies the extension period.You can specify minutes for m, hours for h, and days for d. The maximum period of time is 30 days.Example: 2m, 3h, 4d
-
-i¶ Sets back the modified time-out ratio.
-
-s¶ Refers to the current time-out ratio.
-
-
Return Value 0
Success
Other than 0
Failure
-
Remarks When the cluster is shutdown, the time-out ratio you have set will become ineffective. However, if any server in the cluster is not shut down, the time-out ratio and the extension period that you have set will be maintained.
With the -s option, you can only refer to the current time-out ratio. You cannot see other information such as remaining time of extended period.
You can see the original time-out value by using the status display command.
Heartbeat time-out
# clpstat --cl --detailMonitor resource time-out
# clpstat --mon monitor_resource_name --detail
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
Make sure that the EXPRESSCLUSTER service is activated in all servers in the cluster.
When you set the time-out ratio, make sure to specify the extension period. However, if you set "1" for the time-out ratio, you cannot specify the extension period.
You cannot specify a combination such as "2m3h," for the extension period.
When the server restarts within the ratio extension period, the time-out ratio is not returned to the original even after the extension period. In this case, run the clptoratio -i command to return it to the original.
-
Example of a command entry Example 1: Doubling the time-out ratio for three days
# clptoratio -r 2 -t 3dExample 2: Setting back the time-out ratio to original
# clptoratio -iExample 3: Referring to the current time-out ratio
# clptoratio -s present toratio : 2
The current time-out ratio is set to 2.
-
Error Message Message
Cause/Solution
Log in as administrator.
Log on as a user with Administrator privileges.
Invalid configuration file. Create valid cluster configuration data.
Create valid cluster configuration data by using the Cluster WebUI.
invalid option.
Specify a valid option.
Specify a number in a valid range.
Specify a number within a valid range.
Specify a correct number.
Specify a valid number.
Scale factor must be specified by integer value of 1 or more.
Specify 1 or larger integer for ratio.
Specify scale factor in a range less than the maximum scale factor.
Specify a ratio that is not larger than the maximum ratio.
Set the correct extension period.ex) 2m, 3h, 4dSet a valid extension period.
Set the extension period in a range less than the maximum extension period.
Set the extension period which does not exceed the maximum extension period.
Could not connect to the server. Check if the cluster service is active.
Check that the EXPRESSCLUSTER service is operating.
Server is not active. Check if the cluster service is active.
Check that the EXPRESSCLUSTER service is operating.
Connection was lost. Check if there is a server where the cluster service is stopped in the cluster.
Check if there is any server in the cluster that the EXPRESSCLUSTER service stopped.
Invalid parameter.
The value specified as the command parameter may be invalid.
Internal communication timeout has occurred in the cluster server. If it occurs frequently, set a longer timeout.A time-out occurred in the EXPRESSCLUSTER internal communication.If time-out keeps occurring, set the internal communication time-out longer.Processing failed on some servers. Check the status of failed servers.
There is a server in which the processing has failed.Check the statuses of servers in the cluster. Run the command with all servers in the cluster activated.Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check if the memory or OS resources are sufficient.
8.11. Modifying the log level and size (clplogcf command)¶
The clplogcf command modifies and displays log level and log output file size.
-
Command line clplogcf -t <type> -l <level> -s <size>
-
Description This command modifies the log level and log output file size, or displays the values currently configured.
-
Option -
-t¶ - Specifies a module type whose settings will be changed.If both -l and -s are omitted, the information set to the specified module will be displayed. See the list of "Types that can be specified to the -t option" for types which can be specified.
-
-l¶ - Specifies a log level.You can specify one of the following for a log level.1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32You can see more detailed information as the log level increases.See the list of "Default log levels and log file sizes" for default values of each module type.
-
-s¶ - Specifies the size of a file for log output.The unit is byte.
-
None¶ Displays the entire configuration information currently set.
-
-
Return Value 0
Success
Other than 0
Failure
-
Remarks Each type of output logs from EXPRESSCLUSTER uses two log files. Therefore, it is necessary to have the disk space that is twice larger than what is specified by -s.
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
To run this command, the EXPRESSCLUSTER Event service must be started.
Configuration change is effective only to servers on which this command was run.Rebooting the server restores the settings to their pre-change values.
-
Example of command execution Example 1: Modifying the pm log level
# clplogcf -t pm -l 8Example 2:Seeing the pm log level and log file size
# clplogcf -t pm TYPE, LEVEL, SIZE pm, 8, 1000000
Example 3: Displaying the values currently configured
# clplogcf TYPE, LEVEL, SIZE trnsv, 4, 1000000 xml, 4, 1000000 logcf, 4, 1000000
-
Error Message Message
Cause/Solution
Log in as administrator.
Log on as a user with Administrator privileges.
invalid option.
The option is invalid. Check the option.
Failed to change configuration. Check if the event service is running.
clpevent may not have been started.
invalid level
The specified level is invalid.
invalid size
The specified size is invalid.
Failed to initialize the xml library.Check if memory of OS resources are sufficient.
Check if the memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Failed to print current configuration.Check if the event service is running.
clpevent may not be started yet.
-
Types that can be specified for the -t option Type
Module
Description
alert
clpaltinsert.exe
Alert
apicl
clpapicl.dll
API client library
apicl_rc
clpapicl.dll
API client library
apisv
clpapisv.dll
API server
appli
clpappli.dll
Application resource
appliw
clpappliw.dll
Application monitor resource
armdrive
armdrive.exe
Drive letter setting command
awsazw
clpawsazw.dll
AWS AZ monitor resource
awseip
clpawseip.dll
AWS elastic ip resource
awsdns
clpawsdns.dll
AWS DNS resource
awsdnsw
clpawsdnsw.dll
AWS DNS monitor resource
awseipw
clpawseipw.dll
AWS elastic ip monitor resource
awsvip
clpawsvip.dll
AWS virtual ip resource
awsvipw
clpawsvipw.dll
AWS virtual ip monitor resource
azuredns
clpazuredns.dll
Azure DNS resource
azurednsw
clpazurednsw.dll
Azure DNS monitor resource
azurepp
clpazurepp.dll
Azure probe port resource
azureppw
clpazureppw.dll
Azure probe port monitor resource
azurelbw
clpazurelbw.dll
Azure load balance monitor resource
bmc
clpbmc.dll
BMC HB library
bmccnf
clpbmccnf.exe
BMC information update command
bmchb
clpbmchb.dll
BMC heartbeat resource
bwctrl
clpbwctrl.exe
Cluster activation synchronization wait processing control command
cfchk
clpcfchk.exe
Cluster configuration information check command
cfctrl
clpcfctrl.exe
Cluster generation, cluster information and backup command
cl
clpcl.exe
Cluster startup and stop command
clpdnld
clpdnld.exe
Downloader
clpgetsvcstat
clptrnsv.exe
Transaction server
clpshmstat
clpshmstat.dll
Node status management library
clsv
clpclsv.dll
Client server
commcl
clpcommcl.dll
Common communication client library
commcl_trace
clpcommcl.dll
Common communication client library
commcl_ws
clpcommcl.dll
Common communication client library
commcl_wsev
clpcommcl.dll
Common communication client library
comnp
clpcomnp.dll
COM network partition resolution resource
cpufreq
clpcpufreq.exe
CPU frequency control command
ddns
clpddns.dll
Dynamic DNS resources
ddnsw
clpddnsw.dll
Dynamic DNS monitor resources
diskagcl
clpdiskagcl.dll
Disk agent communication client
diskagent
clpdiskagent.exe
Disk agent
diskfltr
clpdiskfltr.dll
Disk filtering library
disknp
clpdisknp.dll
DISK network partition resolution resource
diskperf
clpdiskperf.dll
Disk performance log library
diskperf_conf
clpdiskperf.dll
Disk performance log library
diskperf_trace
clpdiskperf.dll
Disk performance log library
diskutil
clpdiskutil.dll
Mirror disk/disk shared library
diskw
clpdiskw.dll
Disk RW monitor resource
down
clpdown.exe
Server shutdown command
event
clpevent.dll
Event log
exping
clpexpng.dll
PING execution management
fip
clpfip.dll
Floating IP resource
fipw
clpfipw.dll
Floating IP monitor resource
gclbw
clpgclbw.dll
Google Cloud load balance monitor resource
gcvip
clpgcvip.dll
Google Cloud virtual IP resource
gcvipw
clpgcvipw.dll
Google Cloud virtual IP monitor resource
genw
genw.dll
Custom monitor resource
grp
clpgrp.exe
Group startup, stop, move, and migration command
hblog
clplanhb.dll
Kernel-mode LAN heartbeat resource
hd
clphd.dll
Hybrid disk resource
hdadmn
clphdadmn.dll
Hybrid disk management library
hdadmn_act
clphdadmn.dll
Hybrid disk management library
hdadmn_copy
clphdadmn.dll
Hybrid disk management library
hdadmn_cr
clphdadmn.dll
Hybrid disk management library
hdadmn_ex
clphdadmn.dll
Hybrid disk management library
hdadmn_flag
clphdadmn.dll
Hybrid disk management library
hdadmn_info
clphdadmn.dll
Hybrid disk management library
hdadmn_trace
clphdadmn.dll
Hybrid disk management library
hdadmn_z
clphdadmn.dll
Hybrid disk management library
hdapi
clphdapi.dll
Hybrid disk internal API
hddac
clphddac.dll
Hybrid disk control library
hdfunc
clphdfunc.dll
Hybrid disk function library
hdfunc_conf
clphdfunc.dll
Hybrid disk function library
hdfunc_trace
clphdfunc.dll
Hybrid disk function library
hdnm
clphdnm.dll
Hybrid disk node management
hdnm_t
clphdnm.dll
Hybrid disk node management
hdsnapshot
clphdsnapshot.exe
Hybrid disk snapshot backup command
hdtw
clphdtw.dll
Hybrid disk TUR monitor resource
hdw
clphdw.dll
Hybrid disk monitor resource
healthchk
clphealthchk.exe
Process health check command
ibsv
clpibsv.exe
Information Base service
ipw
clpipw.dll
IP monitor resource
lankhb
clplanhb.dll
Kernel-mode LAN heartbeat resource
lcns
clplcns.dll
License library
ledctrl
clpledctrl.exe
Chassis identify control command
logc
clplogcc.exe
Log collection library
logcc
clplogcc.exe
Collect logs command
logcf
clplogcf.exe
Log level and size modification command
logcmd
clplogcmd.exe
Alert producing command
mail
clpmail.exe
Mail Notification
majonp
clpmajnp.dll
Majority network partition resolution resource
md
clpmd.dll
Mirror disk resource
mdadmn
clpmdadmn.dll
Mirror disk management library
mdadmn_ex
clpmdadmn.dll
Mirror disk management library
mdclose
mdclose.exe
Mirror disk resource close command
monctrl
clpmonctrl.exe
Monitor resource control command
mdfunc
clpmdfunc.dll
Mirror disk function library
mdfunc_conf
clpmdfunc.dll
Mirror disk function library
mdfunc_trace
clpmdfunc.dll
Mirror disk function library
mdnw
clpmdnw.dll
Mirror connect monitor resource
mdopen
mdopen.exe
Mirror disk resource open command
mdw
clpmdw.dll
Mirror disk monitor resource
mgmtagt
clpmgtmib.dll
Library for SNMP Service
miiw
clpmiiw.dll
NIC Link Up/Down monitor resource
monctrl
clpmonctrl.exe
Monitor resource control command
mrw
clpmrw.dll
Message receive monitor resource
mtw
clpmtw.dll
Multi target monitor resource
nm
clpnm.exe
Node map management
oclbw
clpoclbw.dll
Oracle Cloud load balance monitor resource
ocvip
clpocvip.dll
Oracle Cloud virtual IP resource
ocvipw
clpocvipw.dll
Oracle Cloud virtual IP monitor resource
oldapi
clpoldapi.exe
Compatible API
oldapi_cnf
clpoldapi.exe
Compatible API
oldapi_evt
clpoldapi.exe
Compatible API
oldapi_if
clpoldapi.exe
Compatible API
oldapi_sts
clpoldapi.exe
Compatible API
perfc
clpperfc.exe
Cluster statistics information display command
pingnp
clppingnp.dll
PING network partition resolution resource
pm
clppm
Process management
pmsvc
clppmsvc.exe
Process management
psw
clppsw.dll
Process name monitor resource
ptun
clpptun.dll
Parameter tuning
ptunlib
clpptun.dll
Parameter tuning
rc
clprc.exe
Group and group resource management
rc_ex
clprc.exe
Group and group resource management
rd
clprd.exe
Process for smart failover
rdl
clprdl.dll
Library for smart failover
regctrl
clpregctrl.exe
Reboot count control command
regsync
clpregsync.dll
Registry synchronization resource
regsyncw
clpregsync.dll
Registry synchronization monitor resource
resdllc
clpresdllc.dll
Resource control library
rm
clprm.dll
Monitor management
script
clpscript.dll
Script resource
scrpc
clpscrpc.exe
Script
scrpl
clpscrpl.ece
Script
sd
clpsd.dll
Disk resource
sdadmn
clpsdadmn.dll
Disk management library
sddknp
clpsddknp.dll
DISK network partition resolution resource
sdfunc
clpsdfunc.dll
Disk function library
sdw
clpsdw.dll
Disk TUR monitor resource
sem
clpsem.dll
Semaphore library
service
clpservice.dll
Service resource
servicew
clpservicew.dll
Service monitor resource
shmcm
clpshmcm.dll
Shared memory library
shmevt
clpshmevt.dll
Event library
shmnm
clpshmnm.dll
Shared memory library
shmrm
clpshmrm.dll
Shared memory library
snmpmgr
clpsnmpmgr.dll
SNMP trap reception library
spool
clpspool.dll
Print spooler resource
spoolw
clpspoolw.dll
Print spooler monitor resource
starup
clpstartup.exe
Startup
stat
clpstat.exe
Status display command
stdn
clpstdn.exe
Cluster shutdown command
toratio
clptoratio.exe
Time-out ratio modification command
trncl
clptrncl.dll
Transaction library
trap
claptrap.exe
SNMP trap command
trnreq
clptrnreq.exe
Inter-cluster processing request command
rexec
clprexec.exe
External monitoring link processing request command
trnsv
clptrnsv.exe
Transaction server
userw
clpuserw.dll
User space monitor resource
vcom
clpvcom.dll
Virtual computer name resource
vcomw
clpvcomw.dll
Virtual computer name monitor resource
vip
clpvip.dll
Virtual IP resource
vipw
clpvipw.dll
Virtual IP monitor resource
webalert
clpaltd.exe
Alert synchronization
webmgr
clpwebmc.exe
WebManager services
xml
xlpxml.dll
XML library
vm
clpvm.dll
VM resource
vmw
clpvmw.dll
VM monitor resource
vmctrl
clpvmctrl.dll
VMCtrl library
-
Default log levels and log file sizes Type
Level
Size (byte)
alert
4
1000000
apicl
4
5000000
apicl_rc
4
5000000
apisv
4
5000000
appli
4
1000000
appliw
4
1000000
armdrive
4
1000000
bmc
4
1000000
awsazw
4
1000000
awsdns
4
1000000
awsdnsw
4
1000000
awseip
4
1000000
awseipw
4
1000000
awsvip
4
1000000
awsvipw
4
1000000
azurelbw
4
1000000
azuredns
4
1000000
azurednsw
4
1000000
azurepp
4
1000000
azureppw
4
1000000
bldrutil
4
1000000
bmccnf
4
1000000
bmchb
4
1000000
bwctrl
4
1000000
cfchk
4
1000000
cfctrl
4
1000000
cifs
4
1000000
cifsw
4
1000000
cl
4
1000000
clpdnld
4
1000000
clpgetmonstat
4
1000000
clpgetrscstat
4
1000000
clpgetsvcstat
4
1000000
clpshmstat
4
1000000
clptrnver
4
1000000
clsv
4
1000000
commcl
4
80000000
commcl_trace
4
80000000
commcl_ws
4
80000000
commcl_wsev
4
80000000
comnp
4
1000000
cpufreq
4
1000000
ddns
4
1000000
ddnsw
4
1000000
diskagcl
4
1000000
diskagent
4
10000000
diskfltr
4
1000000
disknp
4
1000000
diskperf
8
2000000
diskperf_conf
8
2000000
diskperf_trace
8
2000000
diskutil
4
1000000
diskw
4
1000000
down
4
1000000
event
4
1000000
exping
4
1000000
fip
4
1000000
fipw
4
1000000
gclbw
4
1000000
gcvip
4
1000000
gcvipw
4
1000000
genw
4
1000000
grp
4
1000000
hblog
4
1000000
hd
4
1000000
hdadmn
8
1000000
hdadmn_act
8
1000000
hdadmn_copy
8
1000000
hdadmn_cr
8
1000000
hdadmn_ex
8
1000000
hdadmn_flag
8
1000000
hdadmn_info
8
1000000
hdadmn_trace
8
1000000
hdadmn_z
8
1000000
hdapi
8
1000000
hddac
4
4000000
hdfunc
8
8000000
hdfunc_conf
8
8000000
hdfunc_trace
8
8000000
hdnm
8
4000000
hdnm_t
8
4000000
hdsnapshot
8
2000000
hdtw
4
1000000
hdw
4
2000000
healthchk
4
1000000
ibsv
4
5000000
ipw
4
1000000
lankhb
4
1000000
lcns
4
1000000
ledctrl
4
1000000
logc
4
1000000
logcc
4
1000000
logcf
4
1000000
logcmd
4
1000000
mail
4
1000000
majonp
4
1000000
md
4
1000000
mdadmn
4
1000000
mdadmn_ex
4
1000000
mdclose
4
1000000
mdctrl
4
1000000
mdfunc
4
2000000
mdfunc_conf
8
2000000
mdfunc_trace
8
2000000
mdnw
4
1000000
mdopen
4
1000000
mdw
4
1000000
mgmtagt
4
1000000
miiw
4
1000000
mmproxy
4
1000000
monctrl
4
1000000
mrw
4
1000000
mtw
4
1000000
nas
4
1000000
nasw
4
1000000
natisv
4
1000000
nm
4
2000000
NP_STAT
4
1000000
oclbw
4
1000000
ocvip
4
1000000
ocvipw
4
1000000
oldapi
4
1000000
oldapi_cnf
4
1000000
oldapi_evt
4
1000000
oldapi_if
4
1000000
oldapi_sts
4
1000000
perfc
4
1000000
pingnp
4
1000000
pm
4
1000000
pmsvc
4
2000000
psw
4
1000000
ptun
4
1000000
ptunlib
4
1000000
rc
4
5000000
rc_ex
4
5000000
rd
4
1000000
rdl
4
1000000
regctrl
4
1000000
regsync
4
1000000
regsyncw
4
1000000
resdllc
4
2000000
rexec
4
1000000
rm
4
5000000
script
4
1000000
scrpc
4
1000000
scrpl
4
1000000
sd
4
1000000
sdadmn
4
1000000
sddknp
4
1000000
sdfunc
4
1000000
sdw
4
1000000
sem
4
1000000
service
4
1000000
servicew
4
1000000
shmcm
4
1000000
shmevt
4
1000000
shmnm
4
1000000
shmrm
4
1000000
snmpmgr
4
1000000
spool
4
1000000
spoolw
4
1000000
startup
4
1000000
stat
4
1000000
stdn
4
1000000
toratio
4
1000000
trap
4
1000000
trncl
4
2000000
trnsv
4
2000000
trnreq
4
1000000
userw
4
1000000
util
4
1000000
rexec
4
1000000
vcom
4
1000000
vcomw
4
1000000
vip
4
1000000
vipw
4
1000000
webalert
4
1000000
webmgr
4
1000000
xml
4
1000000
vm
4
1000000
vmw
4
1000000
vmctrl
4
1000000
Total
577000000 * 2
-
Monitoring Agent Types that can be specified for the -t option Type
Module
Description
db2w
clp_db2w.dll
DB2 Monitor (Database Agent)
ftpw
clp_ftpw.dll
FTP Monitor (Internet Server Agent)
httpw
clp_httpw.dll
HTTP Monitor (Internet Server Agent)
imap4w
clp_imap4w.dll
IMAP4 Monitor (Internet Server Agent)
jra
clpjrasvc.exe
JVM monitor resource (Java Resource Agent)
jraw
clpjraw.dll
JVM monitor resource (Java Resource Agent)
odbcw
clp_odbcw.dll
ODBC Monitor (Database Agent)
oraclew
clp_oraclew.dll
Oracle Monitor (Database Agent)
otxw
clp_otxw.dll
WebOTX Monitor (Application Server Agent)
pop3w
clp_pop3w.dll
POP3 Monitor (Internet Server Agent)
psqlw
clp_psqlw.dll
PostgreSQL Monitor (Database Agent)
smtpw
clp_smtpw.dll
SMTP Monitor (Internet Server Agent)
sqlserverw
clp_sqlserverw.dll
SQL Server Monitor (Database Agent)
sra
clpsraserviceproc.exe
System monitor resource/Process monitor resource (System Resource Agent)
sraw
clpsraw.dll
System monitor resource (System Resource Agent)
psrw
clppsrw.dll
Process monitor resource (System Resource Agent)
tuxw
clp_tuxw.dll
Tuxedo Monitor (Application Server Agent)
wasw
clp_wasw.dll
Websphere Monitor (Application Server Agent)
wlsw
clp_wlsw.dll
Weblogic Monitor (Application Server Agent)
-
Monitoring Agent Default Values of Log Level/Log File Size Type
Level
Size (byte)
db2w
4
4000000
ftpw
4
1000000
httpw
4
1000000
imap4w
4
1000000
jra
4
1000000
jraw
4
1000000
odbcw
4
4000000
oraclew
4
4000000
otxw
4
1000000
pop3w
4
1000000
psqlw
4
4000000
smtpw
4
1000000
sqlserverw
4
4000000
sra
8
1000000
sraw
4
1000000
psrw
4
1000000
tuxw
4
1000000
wasw
4
1000000
wlsw
4
1000000
Total
34000000 * 2
8.12. Managing licenses (clplcnsc command)¶
The clplcnsc command manages licenses.
-
Command line clplcnsc -i [licensefile...] clplcnsc -l [-a] clplcnsc -d serialno [-q] clplcnsc -d -t [-q] clplcnsc -d -a [-q] clplcnsc --distribute clplcnsc --reregister licensefile...
-
Description This command registers, refers to and remove the licenses of the product version and trial version of this product.
-
Option -
-i[licensefile...]¶ When a license file is specified, license information is acquired from the file for registration. You can specify multiple licenses. If nothing is specified, you need to enter license information interactively.
-
-l[-a]¶ References the registered license.
The name of displayed items are as follows.
Item
Explanation
Serial No
Serial number (product version only)
User name
User name (trial version only)
Key
License key
Licensed Number of CPU
The number of license(per CPU)
Licensed Number of Computers
The number of license (per node)
Start date
End date
Status
Status of the license
- 1(1,2,3,4)
Displayed in the case of the fixed term license
- 2(1,2,3,4)
Displayed in the case of the license of trial version
When -a option not specifed, the license status of "invalid", "unknown" and "expired" are not displayed.
When specifying -a option, all the licenses are displayed regardless of the license status.
-
-d<param>¶ param
- serialno
Deletes the license with the specified serial number.
- -t
Deletes all the registered licenses of the trial version.
- -a
Deletes all the registered licenses.
-
-q¶ Deletes licenses without displaying a warning message. This is used with -d option.
-
--distribute¶ License files are delivered to all servers in the cluster. Generally, it is not necessary to run the command with this option.
-
-
Return Value 0
Normal termination
1
Normal termination (with licenses not synchronized)
* This means that license synchronization failed in the cluster at the time of license registration.
For the actions to be taken, refer to "Troubleshooting for licensing" in "troubleshooting" in the "Installation and Configuration Guide".
2
Initialization error
4
Invalid option
7
Other internal error
-
Example of a command entry for registration
Registering the license interactively
# clplcnsc -i
Product Version/Product Version (Fixed Term)
Select a product division.
Selection of License Version 1. Product Version 2. Trial Version e. Exit Select License Version. [1, 2, or e (default:1)] ...
Enter a serial number.
Enter serial number [ Ex. XXXXXXXX000000] .
Enter a license key.
Enter license key [ Ex. XXXXXXXX-XXXXXXXX-XXXXXXXX-XXXXXXXX] ...
Trial Version
Select a product division.
Selection of License Version 1. Product Version 2. Trial Version e. Exit Select License Version. [1, 2, or e (default:1)] ...
Enter a user name.
Enter user name [ 1 to 63byte ] .
Enter a license key.
Enter license key [Ex. XXXXX-XXXXXXXX-XXXXXXXX-XXXXXXXX].
Specify a license file
# clplcnsc -i /tmp/cpulcns.key
for referring to the license
# clplcnsc -l
Product version
< EXPRESSCLUSTER X <PRODUCT> > Seq... 1 Key..... A1234567-B1234567-C1234567-D1234567 Licensed Number of CPU... 2 Status... valid Seq... 2 Serial No..... AAAAAAAA000002 Key..... E1234567-F1234567-G1234567-H1234567 Licensed Number of Computers... 1 Status... valid
Product version (fixed term)
< EXPRESSCLUSTER X <PRODUCT> > Seq... 1 Serial No..... AAAAAAAA000001 Key..... A1234567-B1234567-C1234567-D1234567 Start date..... 2018/01/01 End date...... 2018/01/31 Status........... valid Seq... 2 Serial No..... AAAAAAAA000002 Key..... E1234567-F1234567-G1234567-H1234567 Status........... inactive
Trial version
< EXPRESSCLUSTER X <TRIAL> > Seq... 1 Key..... A1234567-B1234567-C1234567-D1234567 User name... NEC Start date..... 2018/01/01 End date...... 2018/02/28 Status........... valid
for deleting the license
# clplcnsc -d AAAAAAAA000001 -qfor deleting the license
# clplcnsc -d -t -qfor deleting the license
# clplcnsc -d -a
Deletion confirmation
Are you sure to remove the license? [y/n] ...
-
Notes Run this command as the Administrator user.
When you register a license, verify that the data transfer server is started up and a cluster has been generated for license synchronization.
When synchronizing the licenses, access the cluster servers in the order below, and use one of the paths that allowed successful access:
via the IP address on the interconnect LAN
via the IP address on the public LAN
via the IP address whose name was resolved by the server name in the cluster configuration data.
When you delete a license, only the license information on the server where this command was run is deleted. The license information on other servers is not deleted. To delete the license information in the entire cluster, run this command in all servers.
Furthermore, when you use -d option and -a option together, all the trial version licenses and product version licenses will be deleted. To delete only the trial license, also specify the -t option. If the licenses including the product license have been deleted, register the product license again.
When you refer to a license which includes multiple licenses, all included licenses information are displayed.
If one or more servers in the cluster are not working, it may take time to execute this command.
-
Error Messages Message
Cause/Solution
Processed license num
The number of processed licenses (success: %d, error: %d)
(success: %d, error: %d).
If error is not 0, check if the license information is correct.
Command succeeded.
The command ran successfully.
Command failed.
The command did not run successfully.
Command succeeded. But the license was not applied to all the servers in the cluster because there are one or more servers that are not started up.
There is one or more server that is not running in the cluster. Perform the cluster generation steps in all servers in the cluster. Refer to "Installing EXPRESSCLUSTER" in "the Installation and Configuration Guide" for information on cluster generation.
Log in as administrator.
Log on as the Administrator user.
Invalid cluster configuration data. Check the cluster configuration information.
The cluster configuration data is invalid. Check the cluster configuration data by using the Cluster WebUI.
Initialization error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check to see if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
The command is already run.
The command is already running.
The license is not registered.
The license has not been registered yet.
Could not open the license file. Check if the license file exists on the specified path.orCould not read the license file. Check if the license file exists on the specified path.Input/Output cannot be done to the license file. Check to see if the license file exists in the specified path.
The field format of the license file is invalid. The license file may be corrupted. Check the destination from where the file is sent.
The field format of the license file is invalid. The license file may be corrupted. Check it with the file sender.
The cluster configuration data may be invalid or not registered.
The cluster configuration data may be invalid or not registered. Check the configuration data.
Failed to terminate the library. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check to see if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
Failed to register the license. Check if the entered license information is correct.orFailed to open the license. Check if the entered license information is correct.Check to see if the entered license information is correct.
Failed to remove the license.
License deletion failed. Parameter error may have occurred or resources (memory or OS) may not be sufficient.
This license is already registered.
This license has already been registered.Check the registered license.This license is already activated.
This license has already been activated.Check the registered license.This license is unavailable for this product.
This license is unavailable for this product.Check the license.The maximum number of licenses was reached.
The maximum number of registrable licenses was reached.Delete the expired licenses.Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check to see if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
8.14. Outputting messages (clplogcmd command)¶
The clplogcmd command registers the specified message with Alert logs.
-
Command line clplogcmd -m message [--alert] [--mail] [-i ID] [-l level]
Note
Generally, it is not necessary to run this command for constructing or operating the cluster. You need to write the command in the script resource script.
-
Description Write this command in the script resource script and output messages you want to send to the destination.
Messages are produced in the following format:
[ID] message
-
Options -
-mmessage¶ - Specifies a message. This option cannot be omitted. The maximum size of message is 498 bytes.You may use alphabets, numbers, and symbols. See below 6 for notes on them.
-
--alert¶ Specify the output destination from alert, mail.(Multiple destinations can be specified.)
-
--mail¶ - This parameter can be omitted. The alert will be the output destinations when the parameter is omitted.For more information on output destinations, see "Directory structure of EXPRESSCLUSTER" in "The system maintenance information".
-
-iID¶ - Specify event ID.This parameter can be omitted. The default value 1 is set for the event ID when the parameter is omitted.
-
-llevel¶ - Select a level of alert output from ERR, WARN, or INFO. The icon on the alert view of the Cluster WebUI is determined according to the level you select here.This parameter can be omitted. The default value INFO is set to level when the parameter is omitted.For more information, see the online manual.
- 6
Notes on using symbols in the message
The symbols below must be enclosed in double quotes (" "):
& | < >
(For example, if you specify "&" in the message, & is produced.)
The symbols below must have a backslash \ in the beginning:
\
(For example, if you specify \\ in the message, \ is produced.)
When there is a space in the message, it must be placed in enclosed in double quotes (" ").
The symbol % cannot be used in the message.
-
-
Return Value 0
Success
Other than 0
Failure
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
The specification of the -i option is different from that of the Linux version. The event ID that is displayed in alert is fixed and unchangeable in the Windows version.
-
Example of command execution Example 1: When specifying message, message ID, and level:
When the following is written in the script resource script, the message is displayed in the Alert logs.
clplogcmd -m test1 -i 100 -l ERR
Example 2: When specifying message, output destination, event ID, and level (output destination is mail):
When the following is written in the script resource script, the message is sent to the mail address set in the Cluster Properties. For more information on the mail address settings, see "Alert Service tab" in "Cluster properties" in "2. Parameter details" in this guide.
clplogcmd -m test2 --mail -i 100 -l ERR
The following information is sent to the mail destination:
Message:test2 Type: logcmd ID: 100 Host: server1 Date: 2019/04/10 10:00:00
8.15. Controlling monitor resources (clpmonctrl command)¶
The clpmonctrl command controls the monitor resources.
-
Command line - clpmonctrl -s [-h <hostname>] [-m resource name ...] [-w wait time]clpmonctrl -r [-h <hostname>] [-m resource name ...] [-w wait time]clpmonctrl -c [-m resource name ...]clpmonctrl -v [-m resource name ...]clpmonctrl -e [-h <hostname>] -m resource nameclpmonctrl -n [-h <hostname>] [-m resource name]
Note
The -c and -v options must be run on all servers that control monitoring because the command controls the monitor resources on a single server.If you want to suspend/resume the monitor resources on all the servers in the clusters, it is recommended to use Cluster WebUI.When [Cluster] is selected for [Failover Couting Method], -c and --clear options are applied only to several servers, the number of recovery operation count may be inconsistent among the servers and the recovery operations may fail.
-
Description This command suspends and/or resumes the monitor resources, displays and/or initializes the recovery operation count, and enabel and/or disable dummy failure.
-
Option -
-s,--suspend¶ Suspends monitoring
-
-r,--resume¶ Resumes monitoring
-
-c,--clear¶ Initializes the recovery operation count.
-
-v,--view¶ Displays the recovery operation count.
-
-e¶ Enables dummy failure. Be sure to specify a monitor resource name with the -m option.
-
-n¶ Disables dummy failure. When a monitor resource name is specified with the -m option, the function is disabled only for the resource. When the -m option is omitted, the function is disabled for all monitor resources.
-
-m,--monitor¶ - Specifies one or more monitor resources to be controlled.This option can be omitted. All monitor resources are controlled when the option is omitted.
-
-w,--wait¶ - Waits for control monitoring on a monitor resource basis (in seconds).This option can be omitted. The default value of 5 is set when the option is omitted.
-
-h¶ Makes a processing request to the server specified in hostname. Makes a processing request to the server on which this command runs (local server) if the -h option is omitted. The -c and -v options cannot specify the server.
-
-
Return Value 0
Normal termination
1
Privilege for execution is invalid
2
The option is invalid
3
Initialization error
4
The cluster configuration data is invalid
5
Monitor resource is not registered.
6
The specified monitor resource is invalid
10
The cluster is not activated
11
The EXPRESSCLUSTER service is suspended
12
Waiting for cluster synchronization
90
Monitoring control wait time-out
128
Duplicated activation
200
Server Connection Error
201
Invalid Status
202
Invalid Server Name
255
Other internal error
-
Example of command execution Example 1: When suspending all monitor resources:
# clpmonctrl -s Command succeeded.
Example 2: When resuming all monitor resources:
# clpmonctrl -r Command succeeded.
-
Remarks If you suspend a monitor resource that is already suspended or resume that is already resumed, this command terminates successfully without changing the status of the monitor resource. If you suspend a monitor resource that is already suspended or resume the one that is already resumed, this command terminates with error, without changing the status of the monitor resource.
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
Check the status of monitor resource by using the status display command or Cluster WebUI.
Before you run this command, use the clpstat command or Cluster WebUI to verify that the status of monitor resources is in either "Online" or "Suspend"
In the case of a monitor resource of which monitor timing is "Active", if a target resource stops temporarily in the active status, and then the target resource or the group which the target resource belongs to is activated, the monitor resource which has been stopped temporarily cannot detect an error. This is because the monitor resource does not start monitoring.
The following are examples of the case described above:
Stops an application monitor that is monitoring application resource temporarily.
Reactivate the application resource or the group that the application resource belongs to.
This reactivation procedure applies both manual and automatic when a monitor resource detects an error and reactivates an application by the recovery operation.
If the recovery action for the monitor resource is set as follows, "Final Action Count", which displayed by the -v option, means the number of times "Execute Script before Final Action" is executed.
Execute Script before Final Action: Enable
final action: No Operation
-
Error Messages Message
Causes/Solution
Command succeeded.
The command ran successfully.
You are not authorized to run the command. Log in as Administrator.
You are not authorized to run this command. Log in as a user with Administrator privileges.
Initialization error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
Invalid cluster configuration data. Check the cluster configuration information.
The cluster configuration data is invalid. Check the cluster configuration data by using the Cluster WebUI.
Monitor resource is not registered.
The monitor resource is not registered.
Specified monitor resource is not registered. Check the cluster configuration information.
The specified monitor resource is not registered.Check the cluster configuration data by using the Cluster WebUI.The cluster has been stopped. Check the active status of the cluster service by using the command such as ps command.
The cluster has been stopped.Check the activation status of the EXPRESSCLUSTER service by using the ps command.The cluster has been suspended. The cluster service has been suspended. Check activation status of the cluster service by using a command such as the ps command.
The EXPRESSCLUSTER service has been suspended. Check the activation status of the EXPRESSCLUSTER service by using a command such as ps command.
Waiting for synchronization of the cluster. The cluster is waiting for synchronization. Wait for a while and try again.
Synchronization of the cluster is awaited.Try again after synchronization of the cluster is completed.Monitor %1 was unregistered, ignored. The specified monitor resources %1is not registered, but continues processing. Check the cluster configuration data.
There is an unregistered monitor resource in the specified monitor resources, but it is ignored and the process is continuedCheck the cluster configuration data by using the Cluster WebUI.%1: Monitor resource nameThe command is already executed. Check the execution state by using the "ps" command or some other command.
The command has already been run. Check the status by using the ps command.
Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
Could not connect to the server.Check if the cluster service is active.Check if the cluster service has started.
Some invalid status. Check the status of cluster.
The status is invalid. Check the status of the cluster.
Invalid server name. Specify a valid server name in the cluster.
Specify the valid server name in the cluster.
-
Monitor resource types that can be specified for the -m option (y=yes, n=no) Type
Suspending/Resume
Reset Recovery Count
Dummy Failure Possibility
appliw
y
y
y
diskw
y
y
y
fipw
y
y
y
ipw
y
y
y
mdnw
y
y
n
mdw
y
y
n
miiw
y
y
y
mtw
y
y
y
regsyncw
y
y
y
sdw
y
y
y
servicew
y
y
y
spoolw
n
y
y
vcomw
y
y
y
vipw
n
y
y
cifsw
y
y
y
nasw
y
y
y
hdw
y
y
n
hdtw
y
y
y
genw
y
y
y
vmw
y
y
n
mrw
y
y
n
db2w
y
y
y
ftpw
y
y
y
httpw
y
y
y
imap4w
y
y
y
odbcw
y
y
y
oraclew
y
y
y
pop3w
y
y
y
psqlw
y
y
y
smtpw
y
y
y
sqlserverw
y
y
y
tuxw
y
y
y
userw
y
y
y
wasw
y
y
y
wlsw
y
y
y
otxw
y
y
y
jraw
y
y
y
sraw
y
y
y
psrw
y
y
y
psw
y
y
y
ddnsw
n
y
n
awsazw
y
y
y
awsdnsw
y
y
y
awseipw
y
y
y
awsvipw
y
y
y
azurednsw
y
y
y
azurelbw
y
y
y
azureppw
y
y
y
gclbw
y
y
y
gcvipw
y
y
y
oclbw
y
y
y
ocvipw
y
y
y
8.16. Controlling group resources (clprsc command)¶
The clprsc command controls group resources.
-
Command line - clprsc -s resource_name [-h hostname] [-f] [--apito timeout]clprsc -t resource_name [-h hostname] [-f] [--apito timeout]clprsc -n resource_nameclprsc -v resource_name
-
Description This command starts and stops group resources.
-
Option -
-s¶ Starts group resources.
-
-t¶ Stops group resources.
-
-h¶ - Requests processing to the server specified by the hostname.When this option is skipped, request for processing is made to the following servers.- When the group is offline, the command execution server (local server) .- When the group is online, the server where group is activated.
-
-f¶ - When the group resource is online, all group resources that the specified group resource depends starts up.When the group resource is offline, all group resources that the specified group resource depends stop.
-
-n¶ Displays the name of the server on which the group resource has been started.
-
--apitotimeout¶ - Specify the time in seconds to wait for group resources to be started or stopped (internal communication timeout). A value between 1 to 9999 can be specified.When the --apito option is not specified, the command waits according to the value set for the internal communication timeout in the cluster property.
-
-v¶ Displays the failover counter of the group resource.
-
-
Return Value 0
success
Other than 0
failure
-
Example Group resource configuration
# clpstat ========== CLUSTER STATUS ========== Cluster : cluster <server> *server1...............: Online lankhb1 : Normal lankhb2 : Normal pingnp1 : Normal server2................: Online lankhb1 : Normal lankhb2 : Normal pingnp1 : Normal <group> ManagementGroup.......: Online current : server1 ManagementIP : Online failover1.............: Online current : server1 fip1 : Online md1 : Online script1 : Online failover2.............: Online current : server2 fip2 : Online md2 : Online script1 : Online <monitor> fipw1 : Normal fipw2 : Normal ipw1 : Normal mdnw1 : Normal mdnw2 : Normal mdw1 : Normal mdw2 : Normal =========================================
Example 1: When stopping the resource (fip1) of the group (failover 1)
# clprsc -t fip1 Command succeeded.
#clpstat ========== CLUSTER STATUS ========== <abbreviation> <group> ManagementGroup........: Online current : server1 ManagementIP : Online failover1..............: Online current : server1 fip1 : Offline md1 : Online script1 : Online failover2..............: Online current : server2 fip2 : Online md2 : Online script1 : Online <abbreviation> ====================================
Example 2: When starting the resource (fip1) of the group(failover 1)
# clprsc -s fip1 Command succeeded.
#clpstat ========== CLUSTER STATUS ========== <Abbreviation> <group> ManagementGroup.........: Online current : server1 ManagementIP : Online failover1...............: Online current : server1 fip1 : Online md1 : Online script1 : Online failover2...............: Online current : server2 fip2 : Online md2 : Online script1 : Online <Abbreviation>
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
Check the status of the group resources by the status display or the Cluster WebUI.
When there is an active group resource in the group, the group resources that are offline cannot be started on another server.
-
Error Messages Message
Causes/Solution
Log in as Administrator.
Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
Invalid cluster configuration data. Check the cluster configuration information.
The cluster construction information is not correct. Check the cluster construction information by Cluster WebUI.
Invalid option.
Specify a correct option.
Could not connect server. Check if the cluster service is active.
Check if the EXPRESSCLUSTER is activated.
Invalid server status. Check if the cluster service is active.
Check if the EXPRESSCLUSTER is activated.
Server is not active. Check if the cluster service is active.
Check if the EXPRESSCLUSTER is activated.
Invalid server name. Specify a valid server name in the cluster.
Specify a correct server name in the cluster.
Connection was lost. Check if there is a server where the cluster service is stopped in the cluster.
Check if there is any server with EXPRESSCLUSTER service stopped in the cluster,
Internal communication timeout has occurred in the cluster server. If it occurs frequently, set the longer timeout.
Timeout has occurred in internal communication in the EXPRESSCLUSTER.Set the internal communication timeout longer if this error occurs frequently.The group resource is busy. Try again later.
Because the group resource is in the process of starting or stopping, wait for a while and try again.
An error occurred on group resource. Check the status of group resource.
Check the group resource status by using the Cluster WebUI or the clpstat command.
Could not start the group resource. Try it again after the other server is started, or after the Wait Synchronization time is timed out.
Wait till the other server starts or the wait time times out, then start the group resources.
No operable group resource exists in the server.
Check there is a processable group resource on the specified server.
The group resource has already been started on the local server.
Check the group resource status by using the Cluster WebUI or clpstat command.
The group resource has already been started on the other server. To start the group resource on the local server, stop the group resource.
Check the group resource status by using the Cluster WebUI or clpstat command.Stop the group to start the group resources on the local server.The group resource has already been stopped.
Check the group resource status by using the Cluster WebUI or clpstat command.
Failed to start group resource. Check the status of group resource.
Check the group resource status by using the Cluster WebUI or clpstat command.
Failed to stop resource. Check the status of group resource.
Check the group resource status by using the Cluster WebUI or clpstat command.
Depending resource is not offline. Check the status of resource.
Because the status of the depended group resource is not offline, the group resource cannot be stopped. Stop the depended group resource or specify the -f option.
Depending resource is not online. Check the status of resource.
Because the status of the depended group is not online, the group resource cannot be started. Start the depended group resource or specify the -f option.
Invalid group resource name. Specify a valid group resource name in the cluster.
The group resource is not registered.
Server is isolated.
The server is suspended. (Rebooting after down)
Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Not enough memory space or OS resource. Check if there is enough space.
Server is not in a condition to start resource. Critical monitor error is detected.
Check the status of the server.
8.17. Switching off network warning light (clplamp command)¶
The clplamp command switches off network warning light.
-
Command line clplamp -h host_name
-
Description This command switches off the network warning light corresponding to the specified server.
If the reproduction of audio file is set, audio file reproduction is stopped.
-
Option -
-hhost_name¶ Specify the target server whose network warning light you want to switch off.
This must be configured.
-
-
Return value 0
Completed successfully.
Other than 0
Terminated due to a failure.
-
Example Example 1: When turning off the warning light and audio alert associated with server1
# clplamp -h server1 Command succeeded.(code:0)
-
Notes This command must be executed by a user with the administrator privilege.
8.18. Controlling CPU frequency (clpcpufreq command)¶
The clpcpufreq command controls CPU frequency.
-
Command line - clpcpufreq --high [-h hostname]clpcpufreq --low [-h hostname]clpcpufreq -i [-h hostname]clpcpufreq -s [-h hostname]
-
Description This command enables/disables power-saving mode by CPU frequency control.
-
Option -
--high¶ Sets CPU frequency to the highest.
-
--low¶ Sets CPU frequency to the lowest.
-
-i¶ Switch to automatic control by cluster.
-
-s¶ - Displays the current CPU frequency level.high: Frequency is the highestlow: Frequency is lowered and it is in power-saving mode
-
-h¶ - Requests the server specified in hostname for processing.If this is omitted, it requests the local server for processing.
-
-
Return Value 0
Completed successfully.
Other than 0
Terminated due to a failure.
-
Example # clpcpufreq -s high Command succeeded.(code:0)
# clpcpufreq -- high Command succeeded.(code:0)
# clpcpufreq --low -h server1 Command succeeded.(code:0)
-
Remark If the Use CPU frequency control check box is not selected in the Extension settings in cluster properties, this command results in error.
-
Notes This command must be executed by a user with the administrator privilege.
When you use CPU frequency control, it is required that frequency is changeable in the BIOS settings, and that the CPU supports frequency control by Windows OS power management function.
-
Error Messages Message
Cause/Solution
Log in as Administrator.
Log in as a user with Administrator privileges.
This command is already run.
This command has already been run.
Invalid option.
This option is invalid. Check the option.
Invalid mode.Check if --high or --low or -i or -s option is specified.Check if either of the --high, --low, -I or -s option is specified.
Failed to initialize the xml library.Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.Check to see if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
Failed to change CPU frequency settings.
Check the BIOS settings and the OS settings.Check if the cluster is started.Check if the setting is configured so that CPU frequency control is used.Failed to acquire CPU frequency settings.
Check the BIOS settings and the OS settings.Check if the cluster is started.Check if the setting is configured so that CPU frequency control is used.Failed to create the mutex.
Check if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
8.19. Controlling chassis identify lamp (clpledctrl command)¶
The clpledctrl command controls the chassis identify function.
-
Command line - clpledctrl -d [-h hostname] [-a] [-w timeout]clpledctrl -i [-h hostname] [-a] [-w timeout]
-
Description This command disables/enables chassis identify function.
-
Option -
-d¶ Disables the chassis identify function.
-
-i¶ Enables the chassis identify function.
-
-hhostname¶ Specifies the name of the server which enables/disables the chassis identify function. Specify -a to omit this.
-
-a¶ - All servers in the cluster are the targets.The -a option can be omitted. If so, specify -h hostname.
-
-wtimeout¶ - Specifies the timeout value of the command by the second.If the -w option is not specified, it waits for 30 seconds.
-
-
Return Value 0
Completed successfully.
Other than 0
Terminated due to a failure.
-
Notes This command must be executed by a user with the administrator privilege.
Execute this command in the server operating normally in the same cluster as the one which the target server belongs to.
If you disable the chassis identify function by this command, it is canceled when the cluster is restarted or when the target server recovers the normal status.
-
Examples Example 1: When disabling (i.e. turn off the lamp which is turned on) the chassis identify function in server1 (specify the command timeout as 60 seconds)
# clpledctrl -d -h server1 -w 60Example 2: When disabling chassis identify in all servers in the cluster
# clpledctrl -d -aExample 3: When enabling the chassis identify function in server1 where the function was disabled
# clpledctrl -i -h server1The result of command execution is displayed as follows:
Detail of the processing Server name: Result (Cause if failed)
-
Error messages Message
Cause/solution
Log in as Administrator.
Log in as a user with Administrator privileges.
Invalid option.
The command line option is invalid. Specify the correct option.
Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
Could not connect to all data transfer server. Check if the server has started up.
Could not connect to all the IP addresses specified. Check the IP addresses and the status of the target server.
Could not connect to the data transfer server. Check if the server has started up.
Could not connect to all the IP addresses specified. Check the IP addresses and the status of the target server.
Command timeout
The cause may be heavy load on OS and so on. Check this.
Chassis identify is not setting or active at all server.
Chassis identify is disabled or not used.
All servers are busy. Check if this command is already run.
This command may be run already. Check it.
Failed to obtain the list of nodes.Specify a valid server name in the cluster.Specify a valid server name in the cluster.
8.20. Processing inter-cluster linkage (clptrnreq command)¶
The clptrnreq command requests a server to execute a process.
-
Command line clptrnreq -t request_code -h IP [-r resource_name] [-s script_file] [-w timeout]
-
Description The command issues the request to execute specified process to the server in another cluster.
-
Option -
-trequest_code¶ - Specifies the request code of the process to be executed. The following request codes can be specified:GRP_FAILOVER Group failoverEXEC_SCRIPT Execute script
-
-hIP¶ - Specifies the server to issue the request to execute the process with IP address. You can specify more than one server by separating by commas. The maximum number of IP addresses you can specify is 32.When you specify group failover for request code, specify the IP addresses of all the servers in the cluster.
-
-rresource_name¶ - Specifies the resource name which belongs to the target group for the request for process when GRP_FAILOVER is specified for request code.If GRP_FAILOVER is specified, -r cannot be omitted.
-
-sscript_file¶ - Specifies the file name (within 30 characters) of the script to be executed (e.g. batch file or executable file) when EXEC_SCRIPT is specified for request code. The script needs to be created in the work\trnreq folder in the folder where EXPRESSCLUSTER is installed in each server specified with -h.If EXEC_SCRIPT is specified, -s cannot be omitted.
-
-wtimeout¶ - Specifies the timeout value of the command by the second. The minimum value is 5 seconds.If the -w option is not specified, it waits for 30 seconds.
-
-
Return Value 0
Completed successfully.
Other than 0
Terminated due to a failure.
-
Notes This command must be executed by a user with the administrator privilege.
It is required that EXPRESSCLUSTER for Windows of internal version 10.02 or later, or EXPRESSCLUSTER for Linux of internal version 2.0.2_1 or later is set up in the server which executes this command and the server with the IP address specified by -h.
-
Examples Example 1: When performing a failover on the group having the appli1 resource of another cluster
# clptrnreq -t GRP_FAILOVER -h 10.0.0.1,10.0.0.2 -r appli1 GRP_FAILOVER 10.0.0.1: Success GRP_FAILOVER 10.0.0.2: Group that specified resource (appli1) belongs is offline.
Example 2: When executing the scrpit1.bat script by the server with IP address 10.0.0.1
# clptrnreq -t EXEC_SCRIPT -h 10.0.0.1 -s script1.bat EXEC_SCRIPT 10.0.0.1: Success
-
Error messages Message
Cause/solution
Log in as Administrator.
Log in as a user with Administrator privileges.
Invalid option.
The command line option is invalid. Specify the correct option.
All servers are busy. Check if this command is already run.
This command may be run already. Check it.
Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
Command timeout
The cause may be heavy load on OS and so on. Check this.
Failed to obtain the list of nodes.
Failed to obtain the list of nodes.
Specify a valid server name in the cluster.
Specify a valid IP address.
Could not connect to all data transfer server. Check if the server has started up.
Could not connect to all IP addresses specified. Check the IP addresses and the status of the target server.
Could not connect to the data transfer server. Check if the server has started up.
Could not connect to the IP address specified. Check the IP address and the status of the target server.
GRP_FAILOVER IP: Group that specified resource (resource_name) belongs to is offline.
Failover process is not performed because the group to which the specified resource belongs is not started on the target server.
EXEC_SCRIPT IP: Specified script ( script_file ) does not exist.
The script does not exist on the specified server.Check it.EXEC_SCRIPT IP: Specified script (script_file) is not executable.
The specified script could not be executed.Check that execution is permitted.request_code IP : This server is not permitted to execute clptrnreq.
The server that executed the command does not have permission. Check that the server is registered to the connection restriction IP list of Cluster WebUI.
request_code IP : REQEST_TYPE failed in execute.
The execution processing of the request type failed.(Either of a present request type Failover or Script is specified. )
8.21. Requesting processing to cluster servers (clprexec command)¶
The clprexec command requests a server to execute a process.
-
Command line - clprexec --failover [group_name] -h IP [-r resource_name] [-w timeout] [-p port_number] [-o logfile_path]clprexec --script script_file -h IP [-p port_number] [-w timeout] [-o logfile_path]clprexec --notice [mrw_name] -h IP [-k category [.keyword]] [-p port_number] [-w timeout] [-o logfile_path]clprexec --clear [mrw_name] -h IP [-k category [.keyword]] [-p port_number] [-w timeout] [-o logfile_path]
-
Description This command is an expansion of the existing clptrnreq command and has additional functions such as issuing a processing request (error message) from the external monitor to the EXPRESSCLUSTER server.
-
Option -
--failover¶ - Requests group failover. Specify a group name for group_name.When not specifying the group name, specify the name of a resource that belongs to the group by using the -r option.
-
--scriptscript_name¶ - Requests script execution.For script_name, specify the file name of the script to execute (such as a batch file or executable file).The script must be created in the work/trnreq folder, which is in the folder where EXPRESSCLUSTER is installed, on each server specified using -h.
-
--notice¶ - Sends an error message to the EXPRESSCLUSTER server.Specify a message reception monitor resource name for mrw_name.When not specifying the monitor resource name, specify the monitor type and monitor target of the message reception monitor resource by using the -k option.
-
--clear¶ - Requests changing the status of the message reception monitor resource from "Abnormal" to "Normal."Specify a message reception monitor resource name for mrw_name.When not specifying the monitor resource name, specify the monitor type and monitor target of the message reception monitor resource by using the -k option.
-
-hIP Address¶ - Specify the IP addresses of EXPRESSCLUSTER servers that receive the processing request.Up to 32 IP addresses can be specified by separating them with commas.If this option is omitted, the processing request is issued to the local server.
-
-rresource_name¶ Specify the name of a resource that belongs to the target group for the processing request when the --failover option is specified.
-
-kcategory[.keyword]¶ - For category, specify the category specified for the message receive monitor when the --notice or --clear option is specified.To specify the keyword of the message receive monitor resource, specify them by separating them with period after category.
-
-pport_number¶ - Specify the port number.For port_number, specify the data transfer port number specified for the server that receives the processing request.The default value, 29002, is used if this option is omitted.
-
-ologfile_path¶ - For logfile_path, specify the file path along which the detailed log of this command is output.The file contains the log of one command execution.If this option is not specified on a server where EXPRESSCLUSTER is not installed, the log is always output to the standard output.
-
-wtimeout¶ - Specify the command timeout time. The default, 180 seconds, is used if this option is not specified.A value from 5 to 999 can be specified.
-
-
Return Value 0
Completed successfully.
Other than 0
Terminated due to a failure.
-
Notes When issuing error messages by using the clprexec command, the message reception monitor resources for which executing an action when an error occurs is specified in EXPRESSCLUSTER server must be registered and started.
The server that has the IP address specified for the -h option must satisfy the following conditions:= EXPRESSCLUSTER X 3.0 or later must be installed.= EXPRESSCLUSTER must be running.(When an option other than --script is used)= mrw must be set up and running.(When the --notice or --clear option is used)When Limiting the access by using client IP addresses is enabled, add the IP address of the device to execute the clprexec command.For details of the Limiting the access by using client IP addresses function, see "WebManager tab" of "Cluster properties" in "2. Parameter details" in this guide.
-
Examples Example 1: This example shows how to issue a request to fail over the group failover1 to EXPRESSCLUSTER server 1 (10.0.0.1):
# clprexec --failover failover1 -h 10.0.0.1 -p 29002Example 2: This example shows how to issue a request to fail over the group to which the group resource (exec1) belongs to EXPRESSCLUSTER server 1 (10.0.0.1):
# clprexec --failover -r exec1 -h 10.0.0.1Example 3: This example shows how to issue a request to execute the script (script1.bat) on EXPRESSCLUSTER server 1 (10.0.0.1):
# clprexec --script script1.bat -h 10.0.0.1Example 4: This example shows how to issue an error message to EXPRESSCLUSTER server 1 (10.0.0.1):
* mrw1 set, category: earthquake, keyword: scale3
This example shows how to specify a message reception monitor resource name:
# clprexec --notice mrw1 -h 10.0.0.1 -w 30 -o /tmp/clprexec/ clprexec.logThis example shows how to specify the category and keyword specified for the message reception monitor resource:
# clprexec --notice -h 10.0.0.1 -k earthquake.scale3 -w 30 -o /tmp/clprexec/clprexec.log
Example 5: This example shows how to issue a request to change the monitor status of mrw1 to EXPRESSCLUSTER server 1 (10.0.0.1):
* mrw1 set, category: earthquake, keyword: scale3
This example shows how to specify a message reception monitor resource name:
# clprexec --clear mrw1 -h 10.0.0.1This example shows how to specify the category and keyword specified for the message reception monitor resource:
# clprexec --clear -h 10.0.0.1 -k earthquake.scale3
-
Error messages Message
Cause/solution
Success
-
Invalid option.
Check the command argument.
Could not connect to the data transfer servers. Check if the servers have started up.
Check whether the specified IP address is correct and whether the server that has the IP address is running.
Could not connect to all data transfer server.
Check whether the specified IP address is correct and whether the server that has the IP address is running.
Command timeout.
Check whether the processing is complete on the server that has the specified IP address.
All servers are busy. Check if this command is already run.
This command might already be running.
Group(%s) is offline.
Check the processing result on the server that received the request.
Group that specified resource(%s) belongs to is offline.
Check the group status.
Specified script(%s) does not exist.
Check if the specified script exist.
Specified resource(%s) is not exist.
Check the resource name or monitor resource name.
Specified resource(Category:%s, Keyword:%s) is not exist.
Check the resource name or monitor resource name.
Specified group(%s) does not exist.
Check the group name.
This server is not permitted to execute clprexec.
Check whether the IP address of the server that executes the command is registered in the list of client IP addresses that are not allowed to connect to the Cluster WebUI.
%s failed in execute.
Check the status of the EXPRESSCLUSTER server that received the request.
8.22. Changing BMC information (clpbmccnf command)¶
The clpbmccnf command changes the information on BMC user name and password.
-
Command line clpbmccnf [-u username] [-p password]
-
Description This command changes the user name/password for the LAN access of the baseboard management controller (BMC) which EXPRESSCLUSTER uses for chassis identify or forced stop.
-
Option -
-uusername¶ Specifies the user name for BMC LAN access used by EXPRESSCLUSTER. A user name with Administrator privilege needs to be specified. The -u option can be omitted. Upon omission, when the -p option is specified, the value currently set for user name is used. If there is no option specified, it is configured interactively.
-
-ppassword¶ Specifies the password for BMC LAN access used by EXPRESSCLUSTER. The -p option can be omitted. Upon omission, when the -u option is specified, the value currently set for password is used. If there is no option specified, it is configured interactively.
-
-
Return Value 0
Completed successfully.
Other than 0
Terminated due to a failure.
-
Notes This command must be executed by a user with the administrator privilege.
Execute this command when the cluster is in normal status.
BMC information update by this command is enabled when the cluster is started/resumed next time.
This command does not change the BMC settings. Use a tool attached with the server or other tools in conformity with IPMI standard to check or change the BMC account settings.
-
Examples When you changed the IPMI account password of the BMC in server1 to mypassword, execute the following on server1:
# clpbmccnf -p mypasswordAlternatively, enter the data interactively as follows:
# clpbmccnf New user name: <- If there is no change, press Return to skip New password: ********** Retype new password: ********** Cluster configuration updated successfully.
-
Error messages Message
Cause/solution
Log in as Administrator.
Log in as a user with Administrator privileges.
Invalid option.
The command line option is invalid. Specify the correct option.
Failed to download the cluster configuration data. Check if the cluster status is normal.
Downloading the cluster configuration data has been failed. Check if the cluster status is normal.
Failed to upload the cluster configuration data. Check if the cluster status is normal.
Uploading the cluster configuration data has been failed. Check if the cluster status is normal.
Invalid configuration file. Create valid cluster configuration data.
The cluster configuration data is invalid. Check the cluster configuration data by using the Cluster WebUI.
tmp_dir already exists. Please delete it and try again.
The folder to store temporary file already exists. Delete the folder and execute the command again.
Can not remove directory: tmp_dir.
Deleting the folder to store temporary file failed. Delete the folder separately.
Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
8.23. Controlling cluster activation synchronization wait processing (clpbwctrl command)¶
The clpbwctrl command controls the cluster activation synchronization wait processing.
-
Command line - clpbwctrl -cclpbwctrl -h
-
Description This command skips the cluster activation synchronization wait time that occurs if the server is started when the cluster services for all the servers in the cluster are stopped.
-
Option -
-c,--cancel¶ Cancels the cluster activation synchronization wait processing.
-
-h,--help¶ Displays the usage.
-
-
Return Value 0
Completed successfully.
Other than 0
Terminated due to a failure.
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
-
Examples This example shows how to cancel the cluster activation synchronization wait processing:
#clpbwctrl -c Command succeeded.
-
Error messages Message
Cause/solution
Log in as Administrator
Log in as a user with administrator privileges.
Invalid option.
The command option is invalid. Specify correct option.
Cluster service has already been started.
The cluster has already been started. It is not in startup synchronization waiting status.
The cluster is not waiting for synchronization.
The cluster is not in startup synchronization waiting processing. The cluster service stop or other causes are possible.
Command Timeout.
Command execution timeout.
Internal error.
Internal error occurred.
8.24. Controlling reboot count (clpregctrl command)¶
The clpregctrl command controls reboot count limitation.
-
Command line - clpregctrl --getclpregctrl -gclpregctrl --clear -t type -r registryclpregctrl -c -t type -r registry
Note
This command must be run on all servers that control the reboot count limitation because the command controls the reboot count limitation on a single server.
-
Description This command displays and/or initializes reboot count on a single server
-
Option -
-g,--get¶ Displays reboot count information
-
-c,--clear¶ Initializes reboot count
-
-ttype¶ Specifies the type to initialize the reboot count. The type that can be specified is rc or rm.
-
-rregistry¶ Specifies the registry name. The registry name that can be specified is haltcount.
-
-
Return Value 0
Completed successfully.
1
Privilege for execution is invalid
2
Duplicated activation
3
Option is invalid
4
The cluster configuration data is invalid
10 to 17
Internal error
20 to 22
Obtaining reboot count information has failed.
90
Allocating memory has failed.
-
Examples Display of reboot count information
# clpregctrl -g ****************************** ------------------------- type : rc registry : haltcount comment : halt count kind : int value : 0 default : 0 ------------------------- type : rm registry : haltcount comment : halt count kind : int value : 3 default : 0 ****************************** success.(code:0) #
The reboot count is initialized in the following examples.
Run this command on the server which actually control the reboot count, because the reboot count is recorded on each server.
Example1: When initializing the count of reboots caused by group resource error:
# clpregctrl -c -t rc -r haltcount success.(code:0) #
Example2: When initializing the count of reboots caused by monitor resource error:
# clpregctrl -c -t rm -r haltcount success.(code:0) #
-
Notes See "What is a group?" "Reboot count limit" in "3. Group resource details" in this guide for information on reboot count limit.
-
Examples Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
-
Error messages Message
Cause/solution
Command succeeded.
The command ran successfully.
Log in as Administrator.
You are not authorized to run this command. Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
The command is already executed.
The command is already running.
Invalid option.
Specify a valid option.
Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Not enough memory space or OS resource.
8.25. Estimating the amount of resource usage (clpprer command)¶
Estimates the future value from changes in the resource usage amount written to the input file and outputs the result to a file. It can also be used to check the result of threshold judgment for estimated data.
-
Command line clpprer -i inputfile -o outputfile [-p number] [-t number [-l]]
-
Description Estimates the future value from the tendency of the given resource use amount data.
-
Option -
-iinputfile¶ The clpprer command specifies the resource data for which a future value is to be obtained.
-
-ooutputfile¶ Specifies the name of the file to which the estimate result is output.
-
-pnumber¶ Specifies the number of estimate data items. If omitted, 30 items of estimate data are obtained.
-
-tnumber¶ Specifies the threshold to be compared with the estimate data.
-
-l¶ Valid only when the threshold is set with the -t option. Judges the status to be an error when the data value is less than the threshold.
-
-
Return Value 0
Normal end without threshold judgment
1
Error occurrence
2
As a result of threshold judgment, the input data is determined to have exceeded the threshold.
3
As a result of threshold judgment, the estimate data is determined to have exceeded the threshold.
4
As a result of threshold judgment, the data is determined to have not exceeded the threshold.
5
If the number of data items to be analyzed is less than the recommended number of data items to be analyzed (120), the input data is determined to have exceeded the threshold as a result of threshold judgment.
6
If the number of data items to be analyzed is less than the recommended number of data items to be analyzed (120), the estimate data is determined to have exceeded the threshold as a result of threshold judgment.
7
If the number of data items to be analyzed is less than the recommended number of data items to be analyzed (120), the data is determined to have not exceeded the threshold as a result of threshold judgment.
-
Notes This command can be used only when the license for the system monitor resource (System Resource Agent) is registered. (If the license is registered, you do not need to configure system monitor resources for the cluster configuration.)
The maximum number of input data items of the resource data file specified with the -i option is 500. A certain number of input data items are required to estimate the amount of resource usage. However, if the number of input data items is large, it takes a considerable amount of time to perform the analysis. So, it is recommended that the number of input data items be restricted to about 120. Moreover, the maximum number of output data items that can be specified in option -p is 500.
If the time data for the input file is not arranged in ascending order, the estimate will not be appropriate. In the input file, therefore, set the time data arranged in ascending order.
-
Input file The input file format is explained below. You need to have an input file, written in the following format, for the resource usage amount for which you want to estimate a result.
The input file format is CSV. One piece of data is coded in the form of date and time, numeric value.
Moreover, the data and time format is YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.
File example
-
Examples The estimation of the future value is explained using a simple example.
When an error is detected in the input data:
If the latest value of the input data exceeds the threshold, an error is assumed and a return value of 2 is returned. If the number of input data items is less than the recommended value (=120), a return value of 5 is returned.
When an error is detected in the estimate data:
If the estimate data exceeds the threshold, an error is assumed and a return value of 3 is returned. If the number of input data items is less than the recommended value (=120), a return value of 6 is returned.
When no threshold error is detected:
If neither the input data nor the estimate data exceeds the threshold, a return value of 4 is returned. If the number of input data items is less than the recommended value (=120), a return value of 7 is returned.
When the -l option is used:
If the -l option is used, an error is assumed when the data is less than the threshold.
-
Examples If you use a file written in the specified format and run the clpprer command, you can output the estimate result to a file and check it.
Input file test.csv
2012/06/14 10:00:00,10.0 2012/06/14 10:01:00,10.5 2012/06/14 10:02:00,11.0
# clpprer -i test.csv -o result.csvOutput result result.csv
2012/06/14 10:03:00,11.5 2012/06/14 10:04:00,12.0 2012/06/14 10:05:00,12.5 2012/06/14 10:06:00,13.0 2012/06/14 10:07:00,13.5
If you set a threshold for option, you can check the result of threshold judgment for estimate data at the command prompt.
# clpprer -i test.csv -o result.csv -t 12.5Execution result
Detect over threshold. datetime = 2012/06/1410:06:00, data = 13.00, threshold = 12.5
-
Error messages Message
Causes/Solution
Normal state.
As a result of threshold judgment, no data exceeding the threshold is detected.
Detect over threshold. datetime = %s, data = %s, threshold = %s
As a result of threshold judgment, data exceeding the threshold is detected.
Detect under threshold. datetime = %s, data = %s, threshold = %s
As a result of threshold judgment with the -l option, data less than the threshold is detected.
License is nothing.
The license for the valid System Resource Agent is not registered. Check to see the license.
Inputfile is none.
The specified input data file does not exist.
Inputfile length error.
The path for the specified input data file is too long. Specify no more than 1023 bytes.
Output directory does not exist.
The directory specified with the output file does not exist. Check whether the specified directory exists.
Outputfile length error.
The path for the specified output file is too long. Specify no more than 1023 bytes.
Invalid number of -p.
The value specified in the -p option is invalid.
Invalid number of -t.
The value specified in the -t option is invalid.
Not analyze under threshold(not set -t) .
The -t option is not specified. When using the -I option, also specify the -t option.
File open error [%s]. errno = %s
The file failed to open. The amount of memory or OS resources may be insufficient. Check for any insufficiency.
Inputfile is invalid. cols = %s
The number of input data items is not correct. Set the number of input data items to 2 or more.
Inputfile is invalid. rows = %s
The input data format is incorrect. One line needs to be divided into two rows.
Invalid date format. [expected YYYY/MM/DD HH:MM:SS]
The date of the input data is not of the correct format. Check to see the data.
Invalid date format. Not sorted in ascending order.
Input data is not arranged in ascending order of date and time. Check the data.
File read error.
An invalid value is set in the input data. Check the data.
Too large number of data [%s]. Max number of data is %s.
The number of input data items exceeds the maximum value (500). Reduce the number of data items.
Input number of data is smaller than recommendable number.
The number of input data items is less than the recommended number of data items to be analyzed (120).* Data is analyzed even if the recommended number of data items to be analyzed is small.Internal error.
An internal error has occurred.
8.26. Checking the process health (clphealthchk command)¶
Checks the process health.
-
Command line clphealthchk [ -t pm | -t rc | -t rm | -t nm | -h]
Note
This command must be run on the server whose process health is to be checked because this command checks the process health of a single server.
-
Description This command checks the process health of a single server.
-
Option -
None¶ Checks the health of all of pm, rc, rm, and nm.
-
-t<process>¶ <process>
- pm
Checks the health of pm.
- rc
Checks the health of rc.
- rm
Checks the health of rm.
- nm
Checks the health of nm.
-
-h¶ Displays the usage.
-
-
Return Value 0
Normal termination
1
Privilege for execution is invalid
2
Duplicated activation
3
Initialization error
4
The option is invalid
10
The process stall monitoring function has not been enabled.
11
The cluster is not activated (waiting for the cluster to start or the cluster has been stopped.)
12
The cluster daemon is suspended
100
There is a process whose health information has not been updated within a certain period.If the -t option is specified, the health information of the specified process is not updated within a certain period.255
Other internal error
-
Examples Example 1: When the processes are healthy
# clphealthchk pm OK rc OK rm OK nm OK
Example 2: When clprc is stalled
# clphealthchk pm OK rc NG rm OK nm OK # clphealthchk -t rc rc NG
Example 3: When the cluster has been stopped
# clphealthchk The cluster has been stopped
-
Remarks If the cluster has been stopped or suspended, the process is also stopped.
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
-
Error Messages Message
Cause/Solution
Log in as Administrator.
Log in as a user with Administrator privileges.
Initialization error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check to see if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
Invalid option.
Specify a valid option.
The function of process stall monitor is disabled.
The process stall monitoring function has not been enabled.
The cluster has been stopped.
The cluster has been stopped.
The cluster has been suspended.
The cluster has been suspended.
This command is already run.
The command has already been started.
Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check to see if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.
8.27. Setting an action for OS shutdown initiated by other than cluster service (clpstdncnf command)¶
The clpstdncnf command sets an action for OS shutdown initiated by other than cluster service.
-
Command line - clpstdncnf -e [time]clpstdncnf -dclpstdncnf -v
Note
This command sets an action for OS shutdown initiated by other than cluster service on a single server. The command must be executed on all of the servers in which you want to set.
-
Description This command sets an action for OS shutdown initiated by other than cluster service on a single server.
-
Option -
-e[time]¶ - Waits for cluster services to be stopped when OS shutdown is initiated by other than cluster service.You can specify a timeout value in minutes (A value between 1 to 1440 can be specified).It is necessary to specify the timeout value at first execution.From the second execution on, if you don't specify the timeout value, the current value is used.
-
-d¶ Does not wait for cluster services to be stopped when OS shutdown is initiated by other than cluster service.
-
-v¶ shows the current setting.
-
-
Return Value 0
Success
Other than 0
Failure
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
In case of a virtual environment, such as cloud environment, when OS shutdown is initiated from the virtual infrastructure, power-off may be executed depending on the virtual infrastructure.
-
Example of command execution Example 1: Waits for cluster service to be stopped (timeout = 30 minutes)
# clpstdncnf -e 30 Command succeeded. # clpstdncnf -v Mode : wait Timeout: 30 min
Example 2: Does not wait for cluster service to be stopped
# clpstdncnf -d Command succeeded. # clpstdncnf -v Mode : no wait Timeout: 30 min
8.28. Controlling the rest point of DB2 (clpdb2still command)¶
Controls the rest point of DB2.
-
Command line - clpdb2still -d databasename -u username -sclpdb2still -d databasename -u username -r
-
Description Controls the securing/release of the rest point of DB2.
-
Option -
-ddatabasename¶ Specifies the name of the target database for the rest point control.
-
-uusername¶ Specifies the name of a user who executes the rest point control.
-
-s¶ Secures the rest point.
-
-r¶ Releases the rest point.
-
-
Return Value 0
Normal completion
2
Invalid command option
4
Authentication error for the user specified in the -u option
5
Failed to secure the rest point.
6
Failed to release the rest point.
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
Set the user name and password specified in the -u option in advance from the Account tab in Properties of the cluster in the config mode of EXPRESSCLUSTER.
A user specified in the -u option needs to have the privilege to run the SET WRITE command of DB2.
-
Examples # clpdb2still -d sample -u db2inst1 -s Database Connection Information Database server = DB2/NT64 11.1.0 SQL authorization ID = DB2ADMIN Local database alias = SAMPLE DB20000I The SET WRITE command completed successfully. DB20000I The SQL command completed successfully. DB20000I The SQL DISCONNECT command completed successfully. Command succeed
# clpdb2still -d sample -u db2inst1 -r Database Connection Information Database server = DB2/NT64 11.1.0 SQL authorization ID = DB2ADMIN Local database alias = SAMPLE DB20000I The SET WRITE command completed successfully. DB20000I The SQL command completed successfully. DB20000I The SQL DISCONNECT command completed successfully. Command succeed.
-
Error Messages Message
Cause/Solution
Invalid option.
Invalid command option.Check the command option.Cannot connect to database.
Failed to connect to the database.Check the name and the status of the database.Username or password is not correct.
User authentication failed.Check your user name and password.Suspend database failed.
Failed to secure the rest point.Check the user privileges and the database settings.Resume database failed.
Failed to release the rest point.Check the user privileges and the database settings.Internal error.
An internal error has occurred.
8.29. Controlling the rest point of Oracle (clporclstill command)¶
Controls the rest point of Oracle.
-
Command line - clporclstill -d connectionstring [-u username] -sclporclstill -d connectionstring -r
-
Description Controls the securing/release of the rest point of Oracle.
-
Option -
-dconnectionstring¶ Specifies the connection string for the target database for rest point control.
-
-uusername¶ Specifies the name of a database user who executes rest point control. This option can be specified only when the -s option is specified. If it is omitted, OS authentication is used.
-
-s¶ Secures the rest point.
-
-r¶ Releases the rest point.
-
-
Return Value 0
Normal completion
2
Invalid command option
3
DB connection error
4
User authentication error
5
Failed to secure the rest point.
6
Failed to release the rest point.
99
Internal error
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
If OS authentication is used without specifying the -u option, a user who runs his command needs to belong to the dba group, in order to gain administrative privileges for Oracle.If you want to change a user with OS authentication, run this command by specifying the /U option with the ARMLOAD command.
Set the user name and password specified in the -u option in advance from the Account tab in Properties of the cluster in the config mode of EXPRESSCLUSTER.
A user specified in the -u option needs to have administrative privileges for Oracle.
If the rest point has been secured by running the command for securing the rest point with the -s option, the control is not returned while the command remains resident. By running the command for releasing the rest point with the -r option at a different process, the resident command for securing the rest point finishes and the control is returned.
Configure Oracle in the ARCHIVELOG mode in advance to run this command.
If an Oracle data file is acquired while this command is used to secure the rest point, the backup mode will be set for the data file. To restore and use the data file, disable the backup mode on Oracle to restore the data file.
-
Examples # clporclstill -d orcl -u oracle -s Command succeeded.
# clporclstill -d orcl -r Command succeeded.
-
Error Messages Message
Cause/Solution
Invalid option.
Invalid command option.Check the command option.Cannot connect to database.
Failed to connect to the database.Check the name and the status of the database.Username or password is not correct.
User authentication failed.Check your user name and password.Suspend database failed.
Failed to secure the rest point.Check the user privileges and the database settings.Resume database failed.
Failed to release the rest point.Check the user privileges and the database settings.Internal error.
An internal error has occurred.
8.30. Controlling the rest point of PostgreSQL (clppsqlstill command)¶
Controls the rest point of PostgreSQL.
-
Command line - clppsqlstill -d databasename -u username -sclppsqlstill -d databasename -r
-
Description Controls the securing/release of the rest point of PostgreSQL.
-
Option -
-ddatabasename¶ Specifies the name of the target database for rest point control.
-
-uusername¶ Specifies the name of the database user who executes rest point control.
-
-s¶ Secures the rest point.
-
-r¶ Releases the rest point.
-
-
Return Value 0
Normal completion
2
Invalid command option
3
DB connection error
4
Authentication error for the user specified in the -u option
5
Failed to secure the rest point.
6
Failed to release the rest point.
99
Internal error
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
If any number other than the default value (5432) is set to the port number connected to PostgreSQL, configure the port number in PQPORT, an environment variable.
A user specified in the -u option needs to have superuser privileges for PostgreSQL.
Enable WAL archive of PostgresSQL in advance to run this command.
If the rest point has been secured by running the command for securing the rest point with the -s option, the control is not returned while the command remains resident. By running the command for releasing the rest point with the -r option at a different process, the resident command for securing the rest point finishes and the control is returned.
-
Examples # clppsqlstill -d postgres -u postgres -s Command succeeded.
# clppsqlstill -d postgres -r Command succeeded.
-
Error Messages Message
Cause/Solution
Invalid option.
Invalid command option.Check the command option.Cannot connect to database.
Failed to connect to the database.Check the name and the status of the database.Username or password is not correct.
User authentication failed.Check your user name and password.Suspend database failed.
Failed to secure the rest point.Check the user privileges and the database settings.Resume database failed.
Failed to release the rest point.Check the user privileges and the database settings.Internal error.
An internal error has occurred.
8.31. Controlling the rest point of SQL Server (clpmssqlstill command)¶
Controls the rest point of SQL Server.
-
Command line - clpmssqlstill -d databasename -u username -v vdiusername -sclpmssqlstill -d databasename -v vdiusername -r
-
Description Controls the securing/release of the rest point of SQL Server.
-
Option -
-ddatabasename¶ Specifies the connection string for the target database for rest point control.
-
-uusername¶ Specifies the name of a database user who executes rest point control. This option can be specified only when the -s option is specified. If it is omitted, OS authentication is used.
-
-s¶ Secures the rest point.
-
-r¶ Releases the rest point.
-
-
Return Value 0
Normal completion
2
Invalid command option
3
DB connection error
4
Authentication error for the user specified in the -u option
5
Failed to secure the rest point.
6
Failed to release the rest point.
99
Internal error
-
Notes Run this command as a user with Administrator privileges.
The user needs to have administrator privileges for SQL Server to run this command if the OS authentication is used without specifying the -u option. If you want to change a user with OS authentication, run this command by specifying the /U option with the ARMLOAD command.
Set the user name and password specified in the -u option in advance from the Account tab in Properties of the cluster in the config mode of EXPRESSCLUSTER.
A user specified in the -u option needs to have the privilege to run the BACKUP DATABASE statement of SQL Server.
If the rest point has been secured by running the command for securing the rest point with the -s option, the control is not returned while the command remains resident. By running the command for releasing the rest point with the -r option at a different process, the resident command for securing the rest point finishes and the control is returned.
-
Examples # clpmssqlstill -d userdb -u sa -v mssql -s Command succeeded.
# clpmssqlstill -d userdb -v mssql -r Command succeeded.
-
Error Messages Message
Cause/Solution
Invalid option.
Invalid command option.Check the command option.Cannot connect to database.
Failed to connect to the database.Check the name and the status of the database.Username or password is not correct.
User authentication failed.Check your user name and password.Suspend database failed.
Failed to secure the rest point.Check the user privileges and the database settings.Resume database failed.
Failed to release the rest point.Check the user privileges and the database settings.Internal error.
An internal error has occurred.
8.32. Displaying the cluster statistics information (clpperfc command)¶
Displays the cluster statistics information.
-
Command line - clpperfc --starttime -g group_nameclpperfc --stoptime -g group_nameclpperfc -g [group_name]clpperfc -m monitor_name
-
Description Displays the median values (millisecond) of the group start time and group stop time.
Displays the monitoring processing time (millisecond) of the monitor resource.
-
Option -
--starttime-g group_name¶ Displays the median value of the group start time.
-
--stoptime-g group_name¶ Displays the median value of the group stop time.
-
-g[group_name]¶ Displays the each median value of the group start time and group stop time.
If groupname is omitted, it displays the each median value of the start time and stop time of all the groups.
-
-mmonitor_name¶ Displays the last monitor processing time of the monitor resource.
-
-
Return value 0
Normal termination
1
Invalid command option
2
User authentication error
3
Configuration information load error
4
Configuration information load error
5
Initialization error
6
Internal error
7
Internal communication initialization error
8
Internal communication connection error
9
Internal communication processing error
10
Target group check error
12
Timeout error
-
Example of Execution When displaying the median value of the group start time:
# clpperfc --starttime -g failover1 200
When displaying each median value of the start time and stop time of the specific group:
# clpperfc -g failover1 start time stop time failover1 200 150
When displaying the monitor processing time of the monitor resource:
# clpperfc -m monitor1 100
-
Remarks The time is output in millisecond by this commands.
If the valid start time or stop time of the group was not obtained, - is displayed.
If the valid monitoring time of the monitor resource was not obtained, 0 is displayed.
-
Notes Execute this command as Administrator.
-
Error Messages Message
Cause/Solution
Log in as Administrator.
Execute this command as Administrator.
Invalid option.
The command option is invalid. Check the command option.
Command timeout.
Command execution timed out .
Internal error.
Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
8.33. Checking the cluster configuration information (clpcfchk command)¶
Checks the cluster configuration information.
-
Command line - clpcfchk -o path [-i conf_path]
-
Description Checks the validness of the setting values based on the cluster configuration information.
-
Option -
-opath¶ Specifies the directory to store the check results.
-
-iconf_path¶ Specifies the directory which stored the configuration information to check.
If this option is omitted, the applied configuration information is checked.
-
-
Return value 0
Normal termination
Other
than 0 Termination with an error
-
Example of Execution When checking the applied configuration information:
# clpcfchk -o /tmp server1 : PASS server2 : PASS
When checking the stored configuration information:
# clpcfchk -o /tmp -i /tmp/config server1 : PASS server2 : FAIL
-
Execution Result For this command, the following check results (total results) are displayed.
Check Results (Total Results)
Description
PASS
No error found.
FAIL
An error found.Check the check results.
-
Remarks Only the total results of each server are displayed.
-
Notes Execute this command as Administrator.
When checking the configuration information exported through Cluster WebUI, decompress it in advance.
-
Error Messages Message
Cause/Solution
Log in as Administrator.
Execute this command as Administrator.
Invalid option.
Specify a valid option.
Could not opened the configuration file. Check if the configuration file exists on the specified path.
The specified path does not exist. Specify a valid path.
Server is busy. Check if this command is already run.
This command has been already activated.
Failed to obtain properties.
Failed to obtain the properties.
Failed to check validation.
Failed to check the cluster configuration.
Internal error. Check if memory or OS resources are sufficient.
Check if the memory or OS resource is sufficient.