5. Heartbeat resources details¶
This chapter provides detailed information on heartbeat resources.
This chapter covers:
5.1. What are heartbeat resources?¶
A server in a cluster configuration monitors whether the other server is being activated. For this monitoring, heartbeat resources are used.
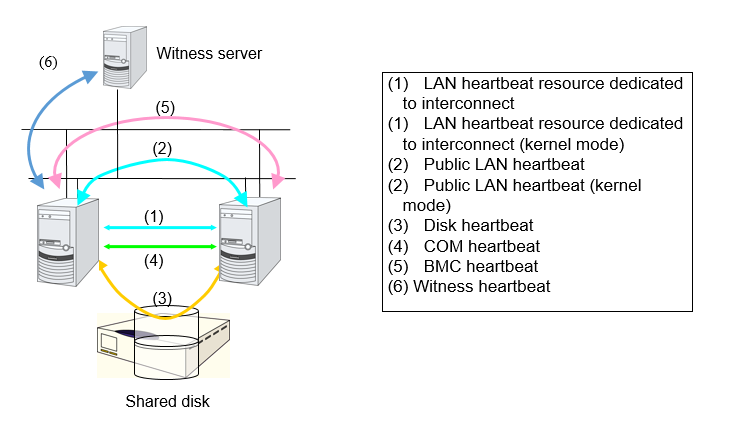
Heartbeat resource name |
Abbreviation |
Functional overview |
|---|---|---|
LAN heartbeat resource (1)(2) |
lanhb |
Uses a LAN to monitor if servers are activated.
Used for communication within the cluster as well.
|
Kernel mode LAN heartbeat resource (1)(2) |
lankhb |
A kernel mode module uses a LAN to monitor if servers are activated. |
Disk heartbeat resource (3) |
diskhb |
Uses a dedicated partition in the shared disk to monitor if servers are activated. |
COM heartbeat resource (4) |
comhb |
Uses a COM cable connecting two servers to monitor if servers are activated. |
BMC heartbeat resource (5) |
bmchb |
Uses BMC to monitor whether servers are activated. |
Witness heartbeat resource (6) |
witnesshb |
A module uses the Witness server to monitor whether or not servers are active |
At least either one LAN heartbeat resource or one kernel mode LAN heartbeat resource must be configured. It is recommended to set two or more LAN heartbeat resources. It is recommended to set both LAN heartbeat resource and kernel mode LAN heartbeat resource together.
Please make sure to set 1 or more LAN heartbeats or Kernel mode LAN heartbeats that can communicate among all the servers.
When you configure the settings of interfaces for disk heartbeat and COM heartbeat resources, follow the specifications described below.
When a shared disk is used:
[Number of servers: up to 2]In principle, COM interface and disk interface[Number of servers: 3 or more]Disk interfaceWhen a shared disk is not used:
[Number of servers: up to 2]COM interface
5.2. Understanding LAN heartbeat resources¶
5.2.1. LAN heartbeat resources¶
You need to set at least one LAN heartbeat resource or kernel mode LAN heartbeat resource. It is recommended to have two or more LAN heartbeat resources; the one dedicated to interconnect and the one shared with interconnect and public.
Communication data for alert synchronization is transmitted on an interface that is registered with the interconnect. You should consider network traffic when you configure the settings.
5.3. Understanding kernel mode LAN heartbeat resources¶
5.3.1. Environment where the kernel mode LAN heartbeat resources works¶
Note
This function is dependent on the distribution and kernel version. Refer to " Supported distributions and kernel versions" in "Software" in "Installation requirements for EXPRESSCLUSTER" in the "Getting Started Guide" before you configure the settings.
5.3.2. The settings of the kernel mode LAN heartbeat resources¶
With the kernel mode driver module, kernel mode LAN heartbeat resource offer similar functions that LAN heartbeats provide. The kernel mode LAN heartbeat resources have the following features.
Kernel mode LAN heartbeat resource is less likely to be impacted by load of OS because it uses the kernel mode driver. This reduces the misinterpreting disconnect of interconnection.
When used with the keepalive settings to watch user-mode monitor resource, the kernel mode LAN heartbeat resource allows reset to be recorded in other servers when the user mode stalling is detected.
5.3.3. kernel mode LAN heartbeat resources¶
It is recommended to specify two or more kernel mode LAN heartbeat resources; the one dedicated to interconnect and the one shared with interconnect and public.
5.4. Understanding disk heartbeat resources¶
5.4.1. Setting the disk heartbeat resources¶
To use a heartbeat resource, you need to have the following settings.
Allocate a dedicated partition on the shared disk. (You do not need to create any file system.)
Configure settings that allow all servers to access the dedicated partition on the shared disk by the same device name.
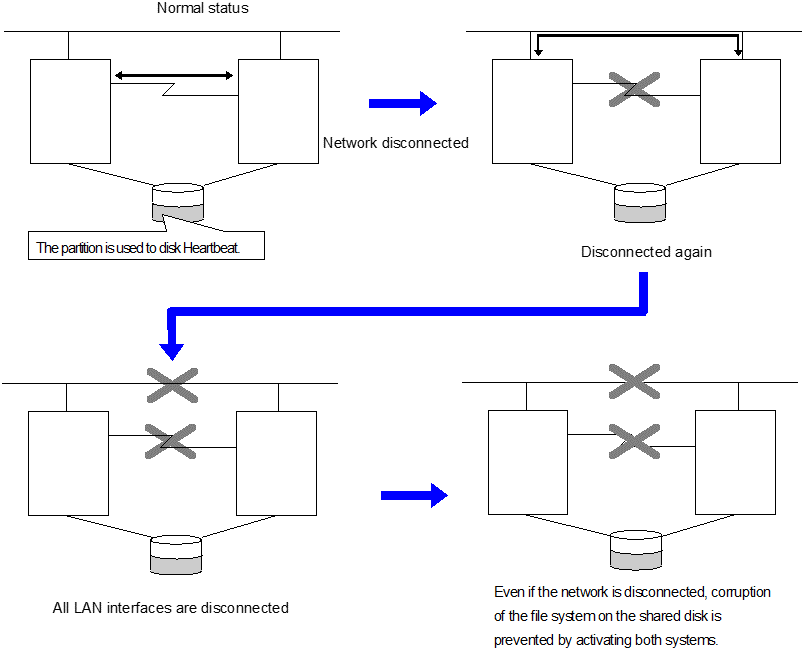
When a disk heartbeat resource is being used, it can be checked if other servers are active even if the network is disconnected.
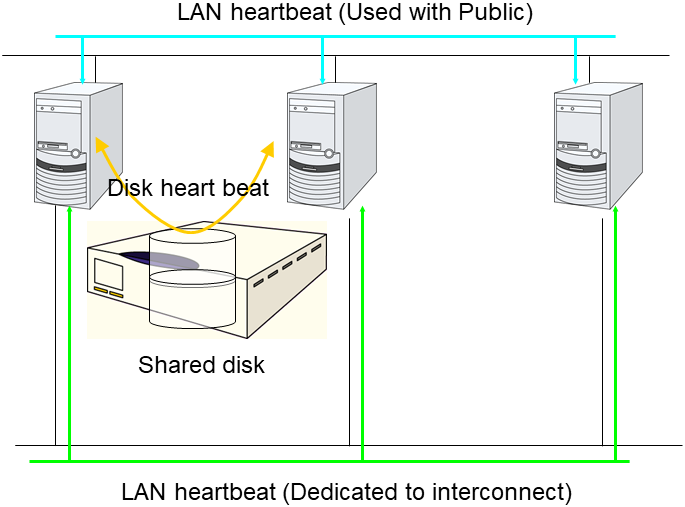
If the cluster consists of three or more servers, you can have a configuration using a disk heartbeat resource as below. You can configure the settings that allow usage of the disk heartbeat resource only among the servers in the cluster using the shared disk.
For details, see "Interconnect tab" in "Cluster properties" in "2. Parameter details" in this guide.
5.4.2. Disk heartbeat resources¶
It is recommended to use both a LAN heartbeat resource and a disk heartbeat resource when you use a shared disk.
It is recommended to use one or two disk heartbeat resources in the cluster even if you are using two or more LUNs. You should consider how heavy the disk is loaded when you configure the settings because a disk heartbeat resource reads and/or writes to the disk every heartbeat interval.
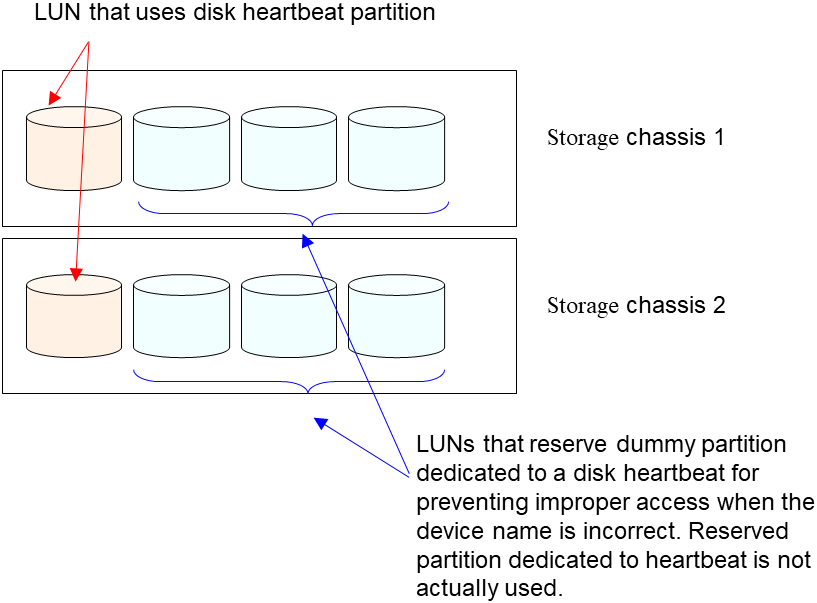
- In each LUN, allocate a partition dedicated to a disk heartbeat. LUNs that do not use a disk heartbeat should also have a dummy partition because the file system can be damaged if device names are moved due to disk failure or other causes.Partitions dedicated to disk heartbeat should have the same number across all the LUNs.
Do not register to storage pool.
5.5. Understanding COM heartbeat resources¶
5.5.1. Note on COM heartbeat resources¶
It is recommended to use a COM heartbeat resource if your environments allows. This is because using a COM heartbeat resource prevents activating both systems when the network is disconnected.
5.6. Understanding BMC heartbeat resources¶
5.6.1. Notes on BMC heartbeat resources¶
BMC heartbeat resources provide functions similar to those of the LAN heartbeat resource. BMC heartbeat resources feature the following:
Activation monitoring is performed with the hardware, and therefore is essentially unaffected by the load on the OS and is less likely to incorrectly recognize the disconnection of interconnects.
The BMC hardware and firmware must support the BMC heartbeat. For the usable BMC versions, see "Servers supporting Express5800/A1080a" or Express5800/A1040a series -related functions" in "Hardware" in the "Getting Started Guide".
5.7. Understanding Witness heartbeat resources¶
5.7.1. Settings of the Witness heartbeat resources¶
To use the Witness heartbeat resources, the following settings are required.
The communication needs to be available between all the servers using Witness heartbeat resources and the server where the Witness server service operates (Witness server). For the Witness server, refer to "Witness server service" in "7. Information on other settings".
The Witness heartbeat resources allow to regularly check the server alive information which the Witness server retains. The server alive information is consolidated, which prevents discrepancies with alive information between servers from easily occurring. In addition, by using the HTTP network partition resolution resource as well, "communication disconnection between a local server and Witness server" and "communication disconnection between other servers and Witness server" are distinguished while the Witness heartbeat resources are operated.
5.7.2. Notes on the Witness heartbeat resources¶
If spaces are included in cluster names, Witness heartbeat resources do not work correctly. Do not use spaces for cluster names.
If the Witness server is shared by multiple clusters with overlapped cluster names, the Witness heartbeat resources do not operate normally. Avoid specifying overlapped cluster names.
In the communication with the Witness server, NIC and a source address are selected according to the OS settings.